A ‘fitness tracker for the bladder’ as replacement for urodynamic testing?
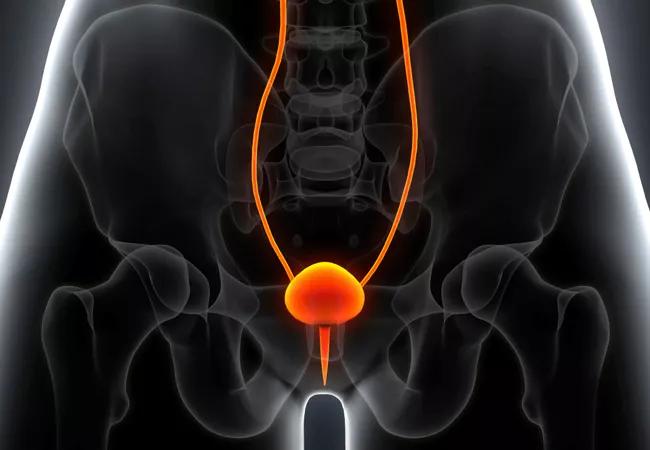
A wireless insertable pressure sensor for diagnosis and treatment of urinary incontinence in women has the potential to eliminate the need for urodynamics and the discomfort and inconvenience it entails.
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
“Urodynamics, the standard method for diagnosing urinary incontinence, involves the insertion of catheters in the urethra and the rectum in an office procedure,” says Margot Damaser, PhD, researcher in the Department of Biomedical Engineering at Cleveland Clinic’s Lerner Research Institute and lead researcher in the pressure sensor project. “The method is very uncomfortable and particularly unreliable in women. So, this project was started with women in mind.” She notes that with a different type of insertion tool, the device should also be applicable in men.
The pressure sensor device, shaped like a coil and designed in a way that it cannot block the urethra or get voided out with urine, is inserted into the bladder lumen where it remains for a few days or up to a week for diagnostic purposes, Dr. Damaser explains. Throughout the diagnostic period, the sensor transmits urine pressure and volume data at regular intervals.
“The idea is similar to a ‘Fitbit for the bladder,’” she says.
Dr. Damaser’s team is developing a smartphone application that will upload data into an encrypted cloud database where the physician will be able to access it.
In addition to diagnostic applications, the device could have potential treatment applications in patients with bladder dysfunction due to neurologic damage. Other possible applications include controlled drug delivery and feedback to neuromodulation or electrical stimulation systems.
The team is currently refining and improving a method for reliable measurement of urine volume. Once optimized, Dr. Damaser believes this feature will be especially useful for the subset of patients who have lost the sensation to urinate.
“This is very important for patients with neurogenic bladder, such as people with spinal cord injuries,” she says. “In these cases, the sensor could remain inserted long-term and notify the patients of the need to catheterize and drain their bladder.”
The results of preclinical testing of a wired prototype of the pressure monitor were recently published in PLOS One. The findings confirmed the correlation between suburothelial pressure readings and intravesical bladder pressure in test animals after placement of the device in the bladder lumen.
Dr. Damaser is optimistic that testing the device in human clinical trials will take place in the next few years.
“The device should not cause any pain or discomfort to the patient. Ideally, the patient would not even be aware of it,” she notes. “Testing conducted in animals did not show any problems.”
Dr. Damaser is partnering with experts from several institutions on this project: Glickman Urological & Kidney Institute (Hui Zhu, MD, SciD; Howard Goldman, MD; and Bradley Gill, MS, MD); Advanced Platform Technology Center, Louis Stokes Cleveland VA Medical Center; and Case School of Engineering, Case Western Reserve University. Dr. Damaser has received funding from the National Institutes of Health, U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs, Ohio Third Frontier program, and Cleveland Clinic.

Discovery Accelerator Partnership with IBM Deploys Advanced Computing Technologies to Supercharge Healthcare Research

Testable models of communities can identify effective strategies to address place-based inequalities of care

Cleveland Clinic is a Founding Partner in Quantum Innovation Hub

Expediting the future of healthcare
Leveraging Microsoft HoloLens and 3D printing to improve surgical outcomes
Lymphocenter investigates therapeutic resistance and more
The pseudokinase binds to proteins to form IPP
NCI grant supported organotypic model