Response to locoregional therapy helps predict tumor behavior and transplant success
For a substantial number of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), their tumors are so large that they extend well beyond the Milan criteria (one tumor that’s up to 5 cm or up to three tumors that are up to 3 cm each). Since most of these patients are not candidates for hepatectomy, their only option may be a liver transplant. However, patients with large tumors have a high risk of post-transplant recurrence. With a limited number of organs available, it’s vital for physicians to identify the candidates who will benefit the most from the procedure.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Physician-researchers in association with the Liver Cancer Consortium recently conducted a national study to determine how HCC patients with tumors that presented beyond the Milan criteria would respond to locoregional therapy prior to transplant. With contributions from Federico Aucejo, MD, Director of Cleveland Clinic’s Liver Cancer Program, and Kazunari Sasaki, MD, Clinical Fellow of Liver Transplant and Hepatobiliary Program, the study helped prove that using locoregional therapy to shrink the tumor to the confines of the Milan criteria would improve the patient’s odds of achieving a positive outcome following transplant.
“The study emphasizes an important message to the transplant community: If you can downstage the tumor successfully, patients with advanced disease can achieve very positive survival rates,” explains Dr. Aucejo. The results of the study will be helpful in predicting HCC patient outcomes following transplant and will be presented at the American Transplant Congress in June 2018.
About 20 medical centers throughout the U.S. participated in the study, which involved about 3,000 patients — 789 of which had tumors that extended beyond the Milan criteria. Cleveland Clinic provided data on 50 patients (beyond Milan) for the study.
Focusing on patients whose tumors presented beyond the Milan criteria, the researchers analyzed the tumor response to locoregional therapy. “The goal was to retrospectively evaluate post-transplant survival and tumor recurrence based on tumor response to locoregional therapy and successfully downstage into the Milan criteria,” notes Dr. Aucejo. “These results confirm the importance of locoregional therapy in the selection criteria of patients with high oncologic risk.”
Advertisement
The study yielded the following key results:
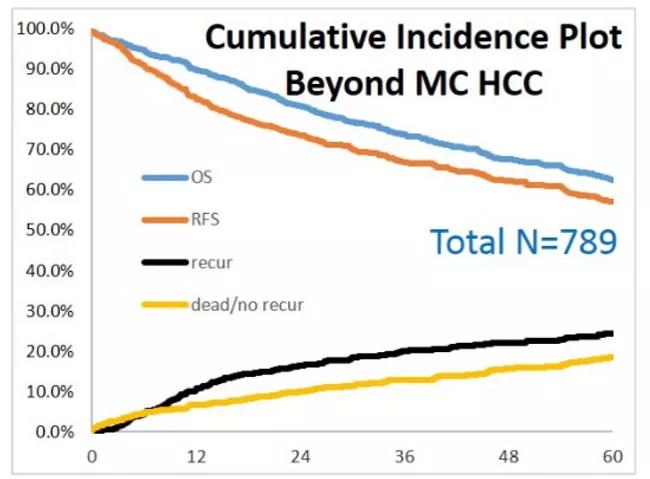
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/63b393e3-f2fc-45c7-81bc-e3c3c7e9b04a/hepatocellular-carcinoma-fig-1_jpg)
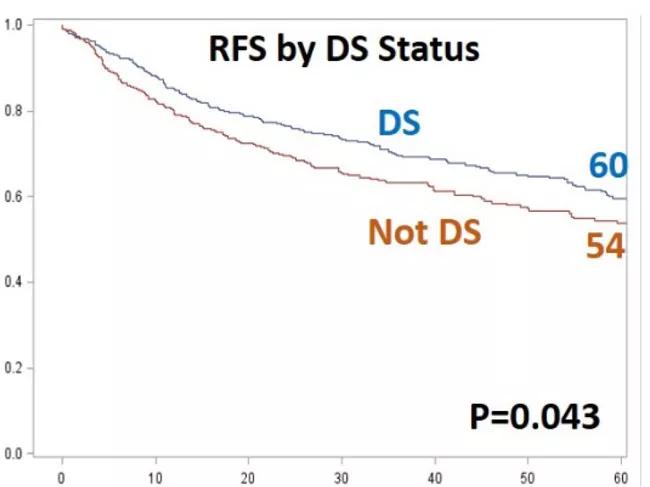
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/93ac3a6b-31de-4d63-baa7-f9cbaa03e17e/hepatocellular-carcinoma-fig-2_jpg)
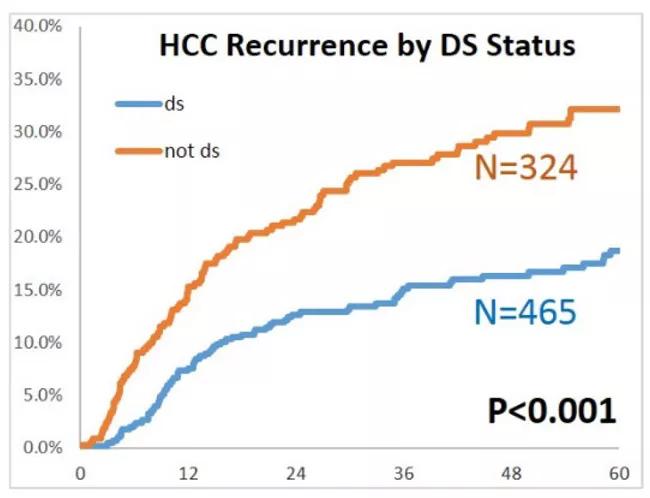
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/470ee395-6f8a-4b7b-a0ce-fc530918d364/hepatocellular-carcinoma-fig-3_jpg)
The researchers helped prove the efficacy of locoregional therapy (e.g., chemoembolization, radioembolization or microwave ablation) at predicting patient outcomes based on tumor response to treatment. “The Milan criteria only assess tumor morphology (size and number of tumors) and do not consider tumor biology, the patient’s overall health or changes in oncological risk over time,” says Dr. Sasaki. “The tumor’s reaction to locoregional therapy provides a superior method of predicting tumor behavior and transplant outcomes.”
Currently, there are no accurate biomarkers that can be used to characterize the biology of liver tumors, predicting how they will behave and if they will recur after transplant. “One of the most important tools we have in the absence of accurate biomarkers is the patient’s response to locoregional therapy,” notes Dr. Aucejo. “If the tumor shrinks and remains at its downstaged size, we can assume that it has a better biology and that the post-transplant outcome would likely be positive.”
Advertisement
In response to locoregional therapy, tumors that presented with a drop in alpha-fetoprotein (a blood protein secreted by the tumor) were more promising than tumors with alpha-fetoprotein levels that remained the same. Steady alpha-fetoprotein levels following locoregional therapy may indicate that the tumor would not respond favorably to a transplant.
The study helps bring awareness to the significant number of patients that present with advanced-stage liver cancer. “Thanks to locoregional therapy, these patients still have a chance to achieve good long-term survival after transplant,” says Dr. Aucejo.
The study will also help physicians adopt more aggressive strategies in administering locoregional therapies to shrink tumors more effectively. “By using different kinds of advanced therapies, including radiation, and combining them with other treatment methods, we can synergize their power to optimize patient outcomes,” explains Dr. Sasaki.
Ongoing research will continue to be used to analyze liver tumor response to locoregional therapy. The results of this research will likely be embedded into new models, which may impact the current allocation policy for liver transplants.
Advertisement
Advertisement

Multidisciplinary framework ensures safe weight loss, prevents sarcopenia and enhances adherence

Study reveals key differences between antibiotics, but treatment decisions should still consider patient factors

Key points highlight the critical role of surveillance, as well as opportunities for further advancement in genetic counseling

Potentially cost-effective addition to standard GERD management in post-transplant patients

Findings could help clinicians make more informed decisions about medication recommendations

Insights from Dr. de Buck on his background, colorectal surgery and the future of IBD care

Retrospective analysis looks at data from more than 5000 patients across 40 years

Surgical intervention linked to increased lifespan and reduced complications