Tag debug info: client: {"assets":{},"datasets":{},"live":{},"projects":{},"users":{},"observable":{"assets":{},"datasets":{},"live":{},"projects":{},"users":{}}} Now: 1770717350246 Cache Key: cqdTagPageBySlug:eric-ricchetti fetchCache[cqdTagPageBySlug:eric-ricchetti].expirationTime: falsey fetchCache[cqdTagPageBySlug:eric-ricchetti]. seconds remaining: falsey All fetchCache expiration times: -- Key: cqdNotFoundPage, seconds remaining: 2327 -- Key: cqdTagPageBySlug:n2o, seconds remaining: -9152 -- Key: cqdPostsByTag:cqd-migrated-tag-22274,1,10, seconds remaining: -9077 -- Key: cqdTagPageBySlug:mild-procedure, seconds remaining: -8687 -- Key: cqdPostsByTag:cqd-migrated-tag-16787,1,10, seconds remaining: -8619 -- Key: cqdTagPageBySlug:bococizumab, seconds remaining: -8261 -- Key: cqdPostsByTag:cqd-migrated-tag-12338,1,10, seconds remaining: -8197 -- Key: cqdTagPageBySlug:nursing-students, seconds remaining: -7378 -- Key: cqdPostsByTag:cqd-migrated-tag-2889,1,10, seconds remaining: -7299 -- Key: cqdTagPageBySlug:anaphylaxis, seconds remaining: -6456 -- Key: cqdPostsByTag:cqd-migrated-tag-1709,1,10, seconds remaining: -6387 -- Key: cqdTagPageBySlug:bentall-procedure, seconds remaining: -5578 -- Key: cqdPostsByTag:cqd-migrated-tag-25144,1,10, seconds remaining: -5520 -- Key: cqdTagPageBySlug:cleft-palate, seconds remaining: -4654 -- Key: cqdPostsByTag:cqd-migrated-tag-19667,1,10, seconds remaining: -4588 -- Key: cqdTagPageBySlug:sentinel-device, seconds remaining: -3750 -- Key: cqdPostsByTag:cqd-migrated-tag-16815,1,10, seconds remaining: -3685 -- Key: cqdTagPageBySlug:telestroke, seconds remaining: -3324 -- Key: cqdPostsByTag:cqd-migrated-tag-2683,1,10, seconds remaining: -3261 -- Key: cqdTagPageBySlug:bone-loss, seconds remaining: -1309 -- Key: cqdPostsByTag:cqd-migrated-tag-22518,1,10, seconds remaining: -1154 -- Key: cqdTagPageBySlug:glomerulonephritis, seconds remaining: 47 -- Key: cqdPostsByTag:cqd-migrated-tag-1365,1,10, seconds remaining: 175 -- Key: cqdTagPageBySlug:allergies, seconds remaining: 2327 -- Key: cqdPostsByTag:cqd-migrated-tag-2227,1,10, seconds remaining: 2382 -- Key: cqdTagPageBySlug:bestpractice-advisory, seconds remaining: 3657 -- Key: cqdPostsByTag:cqd-migrated-tag-24248,1,10, seconds remaining: 3725 -- Key: cqdTagPageBySlug:hypoxia, seconds remaining: 4109 -- Key: cqdPostsByTag:cqd-migrated-tag-24102,1,10, seconds remaining: 4185 -- Key: cqdTagPageBySlug:ferritin, seconds remaining: 4549 -- Key: cqdPostsByTag:cqd-migrated-tag-23184,1,10, seconds remaining: 4635 -- Key: cqdTagPageBySlug:smoking, seconds remaining: 5005 -- Key: cqdPostsByTag:cqd-migrated-tag-23631,1,10, seconds remaining: 5077 -- Key: cqdTagPageBySlug:akron-general, seconds remaining: 5458 -- Key: cqdPostsByTag:cqd-migrated-tag-4348,1,10, seconds remaining: 5525 -- Key: cqdTagPageBySlug:spinal-stimulation, seconds remaining: 6841 -- Key: cqdPostsByTag:cqd-migrated-tag-22276,1,10, seconds remaining: 6936 -- Key: cqdTagPageBySlug:niraj-varma, seconds remaining: 7749 -- Key: cqdPostsByTag:cqd-migrated-tag-2690,1,10, seconds remaining: 7805 -- Key: cqdTagPageBySlug:virtual-reality-vr, seconds remaining: 9063 -- Key: cqdPostsByTag:cqd-migrated-tag-15801,1,10, seconds remaining: 9127 -- Key: cqdTagPageBySlug:robert-dean, seconds remaining: 9531 -- Key: cqdPostsByTag:cqd-migrated-tag-21013,1,10, seconds remaining: 9593 conditions: -- false, -- NA, -- NA, -- NA -- false Cache miss for key cqdTagPageBySlug:eric-ricchetti - retrieving from Sanity CCCache.dataFetchCount: 1124 Cache cleanup seconds remaining: 18846
Advertisement
Advertisement
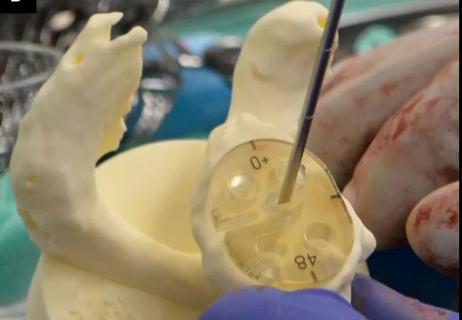
No significant differences related to instrumentation choice in 3-D CT preoperative planning
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Rendered: Tue Feb 10 2026 09:55:50 GMT+0000 (Coordinated Universal Time)
9500 Euclid Avenue, Cleveland, Ohio 44195 |
800.223.2273 | ©
2026 Cleveland Clinic. All Rights Reserved.