Skilled team provides advanced surgical interventions
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Liver resection continues to be a mainstay treatment for patients presenting with primary and secondary liver malignancies. In the case of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), liver resection is a curative alternative. However in HCC patients with cirrhosis and portal hypertension, liver transplantation is the standard of care.
Pretransplant locoregional therapy or liver resection are common approaches to keep patients within transplant eligibility. In line with this, organ allocation in HCC patients undergoing transplantation in the setting of severe organ scarcity continues to be challenging, as accurate predictors of posttransplant tumor recurrence are lacking.
At Cleveland Clinic’s Hepato-Biliary Cancer Center, we offer advanced surgical interventions via sophisticated surgical techniques to patients with complex tumors.
The patient is a 77-year-old male diagnosed with a large, central HCC abutting the portal vein bifurcation. After undergoing evaluation at a large, out-of-state tertiary facility, the patient received locoregional therapy but was denied surgery due to his age and advanced disease.
Seeking a surgical option and therefore a second opinion, the patient consulted the multidisciplinary Liver Tumor Clinic at Cleveland Clinic.
A large R0 central hepatectomy was successfully performed and the patient was discharged from the hospital on post-operative Day 7 without complications.
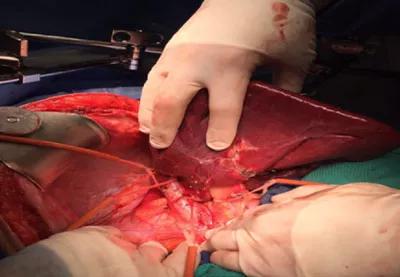
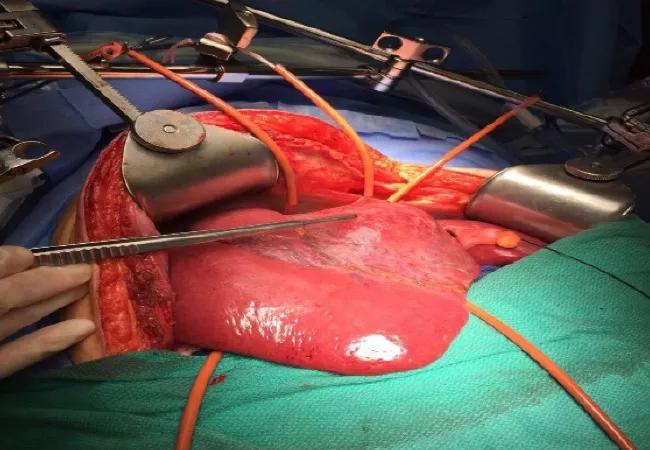
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/f204493f-cda2-472a-94d0-d9d386f72573/17-DDI-3851-Complex-Liver-CQD-Ins1_jpg)
Total vascular control (supra-hepatic and infra-hepatic vena cava, and liver hilum) in preparation for parenchymal transection.
Advertisement
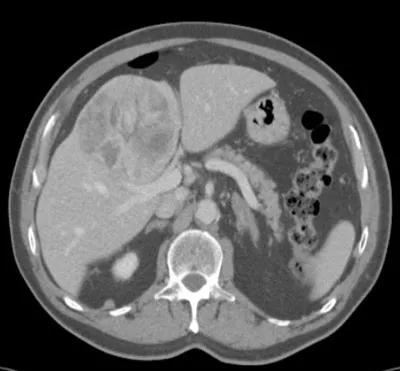
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/2a5d09d5-a31a-4f45-885c-f0127cb8b552/17-DDI-3851-Complex-Liver-CQD-Ins2_jpg)
Cross sectional imaging via computed tomography demonstrating a large central liver mass (hepatocellular carcinoma).
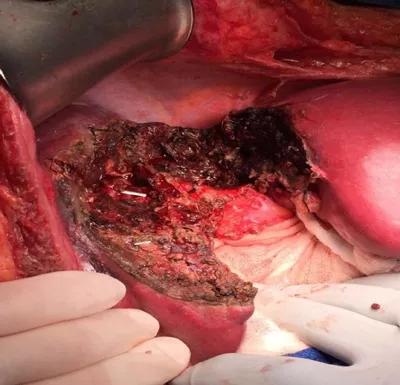
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/64cd09d9-8a16-415b-bd5d-7c03b83f6299/17-DDI-3851-Complex-Liver-CQD-Ins3_jpg)
Surgical resection bed (histopathology analysis confirmed negative tumor margins).
References
Advertisement
Advertisement

The shifting role of cell therapy and steroids in the relapsed/refractory setting

Radiation therapy helped shrink hand nodules and improve functionality

Standard of care is linked to better outcomes, but disease recurrence and other risk factors often drive alternative approaches

Phase 1 study demonstrates immune response in three quarters of patients with triple-negative breast cancer

Multidisciplinary teams bring pathological and clinical expertise

Genetic variants exist irrespective of family history or other contributing factors

Study shows significantly reduced risk of mortality and disease complications in patients receiving GLP-1 agonists

Structured interventions enhance sleep, safety and caregiver resiliency in high-acuity units