
Focus on metabolic bone disease

International expert Alberto Rubio Tapia, MD, leads treatment, research efforts

Medications for patients with diabetes and cardiovascular disease

Factors to consider when prescribing or changing diabetes treatment regimen
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy

Full circle multidisciplinary care for patients with complex comorbidities

Prospective study demonstrates value of technology beyond what can be seen by the eyes
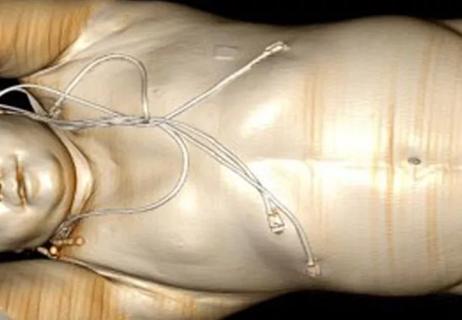
Case report illustrates the importance of maintaining high levels of clinical suspicion
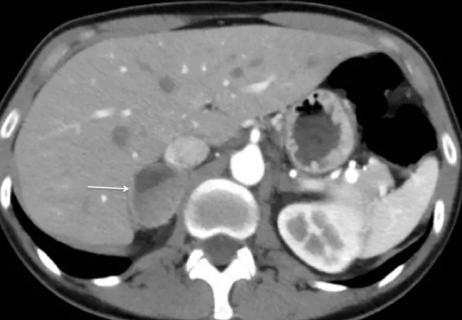
Cortical-sparing surgery may be best option
Shared decision-making tool published in a recent study fills void
Risks and rewards of supplementation must be carefully weighed for older men with secondary hypogonadism
Advertisement
Advertisement