Cleveland Clinic surgeons remove first brain tumor with Myriad NOVUS tool
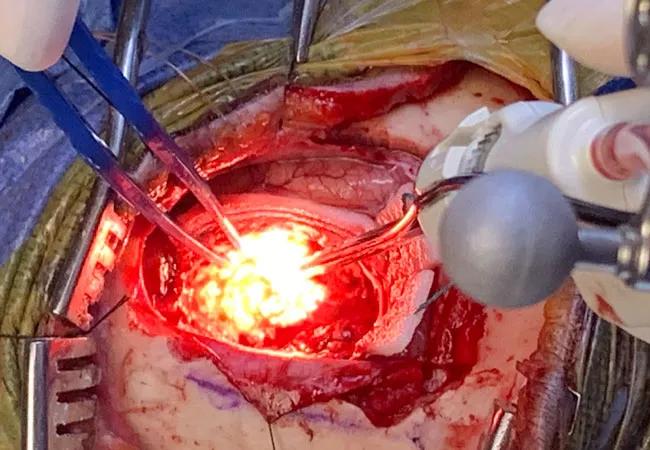
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/0d2ee3fe-0a1e-44cd-b4c8-4e4b0ac5493d/19-NEU-6546_glioma-resection-illuminated-field-650x450_jpg)
glioma resection using Myriad NOVUS
In early December 2019, a Cleveland Clinic surgical team ushered in an era of enhanced visualization during subcortical brain tumor resection with the first U.S. clinical use of the recently approved NICO Myriad NOVUS resection tool.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
The next-generation NICO Myriad, which won FDA clearance in September 2019, provides an enhancement to improve the efficiency of the Myriad resection tool’s suction capability and comes with the new Myriad-LX xenon light source at the tip of the device to illuminate the surgical field for enhanced visualization of tissue.
“The new device offers enhanced, variable suction and cutting along with the addition of the xenon light, which provides much better visualization without need for a microscope or external lighting,” says Alireza Mohammadi, MD, the neurosurgeon with Cleveland Clinic’s Rose Ella Burkhardt Brain Tumor and Neuro-Oncology Center who performed the initial U.S. resection with the tool.
The successful procedure was performed in a glioma patient undergoing awake surgery (see intraoperative photo above), although the device can be used for resection of all brain tumor types.
“We believe the enhanced visualization of the surgical field made possible by the built-in light will translate to safer and more efficacious tumor resection and shorter operative times,” says Dr. Mohammadi. “The improved visualization should be particularly helpful for resection of deep-seated tumors.”
Because Dr. Mohammadi was experienced in the use of the first-generation Myriad tool, he needed no additional training to adopt the new device, which he says will replace the prior version at Cleveland Clinic. He and his colleagues plan to use the new device in an upcoming clinical trial.
Like its predecessor version, the Myriad NOVUS tool is approved for neurosurgical indications including removal of primary and secondary brain tumors, vascular abnormalities and malformations, and intraventricular tumors and cysts. Neurosurgeons in Cleveland Clinic’s Cerebrovascular Center are adopting it for use as well.
Advertisement
Advertisement
Clinical trials and de-escalation strategies
Combination therapy improves outcomes, but lobular patients still do worse overall than ductal counterparts
Bringing empathy and evidence-based practice to addiction medicine
Supplemental screening for dense breasts
Combining advanced imaging with targeted therapy in prostate cancer and neuroendocrine tumors
Early results show strong clinical benefit rates
The shifting role of cell therapy and steroids in the relapsed/refractory setting
Radiation therapy helped shrink hand nodules and improve functionality