Choroid lesions indicate systemic disease
By Francisco Almeida, MD, MS, and Arun D. Singh, MD
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
A 62-year-old woman has had flashing lights and floaters in her left eye with progressive loss of vision over the past month. She has not had recent trauma. She does not smoke.
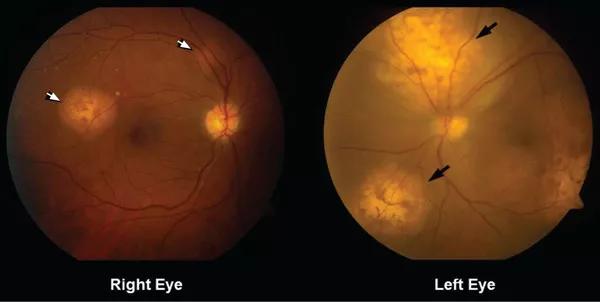
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/dce8b37b-4027-4a08-bfa4-88348b32bf47/17-EYE-3713-CCJM-CQD-Fig1_jpg)
Figure 1. Funduscopy showed multiple lobulated, yellowish choroidal lesions in the posterior pole, with overlying subretinal fluid (arrows). Similar but smaller lesions were seen in the right eye (arrows).
She was referred for an ophthalmologic evaluation. Her visual acuity was 20/20 in the right eye, but she could only count fingers with the left. The anterior segment appeared normal in both eyes. Funduscopic examination of the left eye revealed numerous lobulated, yellowish, choroidal lesions in the posterior pole with overlying subretinal fluid. The lesions involved the fovea, accounting for the poor visual acuity. There were two similar but smaller lesions in the right eye (Figure 1). Ultrasonography confirmed the choroidal location of the lesions (Figure 2). We diagnosed uveal metastatic tumor as funduscopic findings of bilateral yellow choroidal lesions are consistent with metastatic cancer.
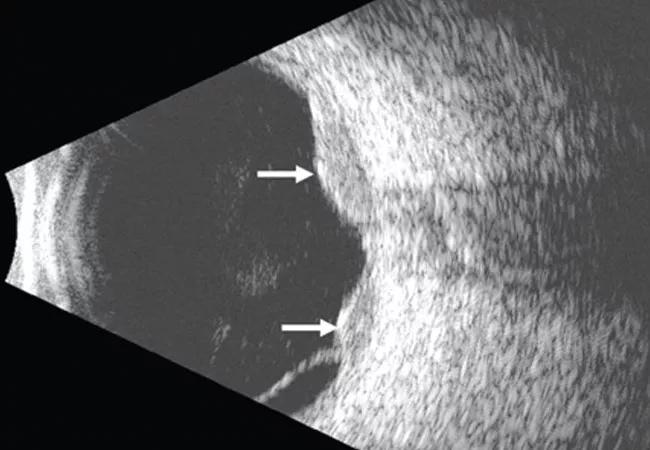
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/6af9f87e-590d-4e9f-a4ed-fd4b41c2e47e/17-EYE-3713-CCJM-CQD-Hero_jpg)
Figure 2. Ultrasonography of the left eye confirmed the choroidal location of the lesions noted on fundoscupy (arrows).
The patient was admitted to the hospital for a thorough evaluation. Computed tomography of the chest showed a 2.1-by-4.5-cm mass in the lower lobe of the left lung, highly suspicious for malignancy and associated with left hilar lymphadenopathy and right acute pulmonary embolism. Bronchoscopy showed an endobronchial tumor completely occluding the left lower lobe and the lingular orifices.
Advertisement
Pathologic specimens from the endobronchial tumor confirmed adenocarcinoma, consistent with a primary lung cancer.
Uveal metastasis is the most common intraocular malignancy and is found on autopsy in up to 12 percent of people who die of cancer; it involves both eyes in 4.4 percent of cases. Multiple metastases are seen in one eye in up to 20 percent of cases.
The tumors are most often in the choroid, probably because of its extensive blood supply. Breast cancer (in women) and lung cancer (in men) are the most common cancers with uveal metastasis. Uveal metastasis from cancers of the prostate, kidney, thyroid, and gastrointestinal tract and from lymphoma and leukemia is less common.
Patients with choroidal metastases can see flashing lights, floating spots and have distortion of their vision. In such patients, a careful history and physical examination can uncover signs and symptoms of the hidden cancer, especially of lung cancer.
Once uveal metastasis is suspected, both eyes and orbits and the central nervous system should be examined, as this disease tends to present bilaterally and to involve the central nervous system. Uveal metastases respond to chemotherapy and radiotherapy, depending on the nature of the primary tumor. In general, treatment is based on the extent of the metastasis, prior treatments and the patient’s overall functional status.
This article originally appeared in Cleveland Clinic Journal of Medicine. Read the full article here.
Advertisement
Advertisement

Radiation therapy helped shrink hand nodules and improve functionality

Standard of care is linked to better outcomes, but disease recurrence and other risk factors often drive alternative approaches

Phase 1 study demonstrates immune response in three quarters of patients with triple-negative breast cancer

Multidisciplinary teams bring pathological and clinical expertise

Genetic variants exist irrespective of family history or other contributing factors

Study shows significantly reduced risk of mortality and disease complications in patients receiving GLP-1 agonists

Structured interventions enhance sleep, safety and caregiver resiliency in high-acuity units

Addressing rare disease and challenging treatment course in an active young patient