Produces favorable oncologic outcomes, wound healing and quality of life
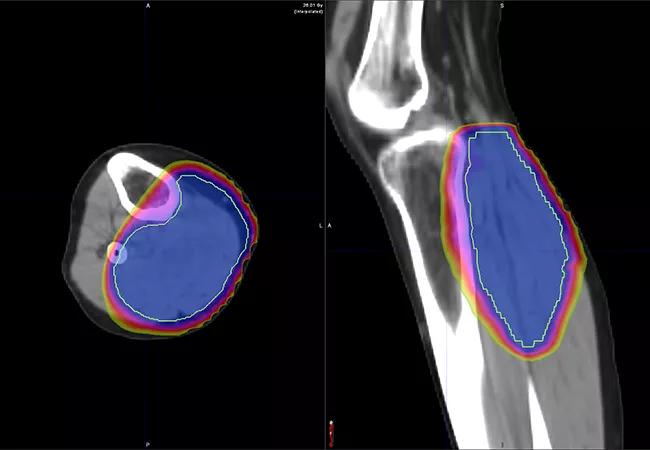
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/217b16f3-43bb-4ac8-85e5-de8e8ca2206d/21-ORI-2350074-CQD-650x450-1_png)
21-ORI-2350074 CQD 650×450
Treatment for soft tissue sarcoma typically involves a long course of radiation followed by surgery. As a result, it can be weeks or even months before the cancer is removed and treatment is complete.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
A new approach is reducing the wait. Instead of five to six weeks of radiation therapy, patients now have the option to undergo five days of hypofractionated external beam radiation. This shorter although higher daily intensity approach has been used in breast, lung and colorectal cancers. Cleveland Clinic is helping lead the charge in the sarcoma space.
“We are shifting the paradigm in treating soft tissue sarcomas,” says Nathan Mesko, MD, Center Director, Orthopaedic Oncology, and Director of Sarcoma Care at Cleveland Clinic. “Our institution and a few others around the country are challenging the tradition that calls for a long course of radiation for this patient population.”
Complete surgical resection in combination with either neoadjuvant or adjuvant radiation therapy is the mainstay of treatment for soft tissue sarcomas. While there is no significant difference in survival outcomes between neoadjuvant and adjuvant radiation therapy, preoperative radiation is shown to have fewer long-term effects, according to Dr. Mesko.
Conventional neoadjuvant radiation therapy regimens consist of 50 Gy in 25 fractions delivered over the course of five weeks.
“We then wait anywhere from four to six weeks to allow for recovery before we perform surgery,” says Dr. Mesko. “From the time a patient is diagnosed to the time the tumor is removed, it can be three months.”
This can be challenging for a patient, especially those who need to travel for treatment, he notes. By shifting away from this approach, patients now have an option that significantly decreases the length of their treatment, which can improve their quality of life.
Advertisement
Short-course radiation therapy has been used for Cleveland Clinic patients with extremity sarcomas for about four years, according to Dr. Mesko. Patients receive five fractions over the course of five days. Surgery occurs 24 to 72 hours after the last dose of radiation.
Early outcomes reported by Dr. Mesko and colleagues suggest favorable local control and wound healing. In one study published in Advances in Radiation Oncology, 16 patients were treated for sarcomas in their lower extremity, upper extremity or trunk. Most were treated with 30 Gy in five fractions over five consecutive days, followed by resection. The median time to resection following the completion of radiation therapy was one day, and median time from initial biopsy results to the completion of primary oncologic therapy was 20 days.
Of these patients, 10 achieved R0 resection and six achieved R1 resection. Local failure was not reported in any of the 13 patients evaluated. Five patients (31%) had complications with wound healing, but only three (19%) required surgical treatment for it.
Researchers continue to treat patients with hypofractionated preoperative radiation therapy, and long-term follow-up is ongoing.
Cleveland Clinic employs two types of short-course radiation for extremity sarcomas.
“We have traditional beam radiation, which involves five days of preoperative treatment followed by resection,” explains radiation oncologist Shauna Campbell, DO. “The other option is brachytherapy. In this approach, we use a small radioactive source to deliver radiation in the tumor bed immediately following surgery.”
Advertisement
Brachytherapy can deliver a higher dose of radiation faster and in a more targeted way compared with standard external beam radiation.
“The advantage of brachytherapy is that the tumor is removed as a first step, and during the same operation, the catheters are laid in the area where the sarcoma was removed,” adds Dr. Mesko. “Radiation is then delivered over five days. A few days after completion of radiation, the wound is closed or reconstructed. In less than two weeks, the entire cancer treatment for localized sarcoma is complete.”
Every patient is discussed in a multidisciplinary fashion to determine which radiation treatment option is most appropriate for their diagnosis.
Looking beyond extremity sarcomas, a trial is now exploring the use of short-course radiation for retroperitoneal sarcomas.
The trial, “CASE 2720: Prospective Study Evaluating Hypofractionated Radiation Therapy for Retroperitoneal Sarcomas,” is currently accruing patients with histologically confirmed disease whose treatment plan includes neoadjuvant radiation followed by surgery.
“This study will further explore the impact of short-course radiation on sarcoma patients,” notes Dr. Campbell. “This is a life-changing diagnosis, and prolonged treatment courses only add to the stress and anxiety patients are already feeling. While our hope is to see an improvement in outcomes overall, improvements in quality of life are a huge win as well. The field as a whole must continue to look for ways to help ease the burden of treatment, which can improve our patients’ lives exponentially.”
Advertisement
Advertisement
Combination therapy improves outcomes, but lobular patients still do worse overall than ductal counterparts
Bringing empathy and evidence-based practice to addiction medicine
Supplemental screening for dense breasts
Combining advanced imaging with targeted therapy in prostate cancer and neuroendocrine tumors
Early results show strong clinical benefit rates
The shifting role of cell therapy and steroids in the relapsed/refractory setting
Radiation therapy helped shrink hand nodules and improve functionality
Standard of care is linked to better outcomes, but disease recurrence and other risk factors often drive alternative approaches