Combination therapy shows promise in pediatric patient population
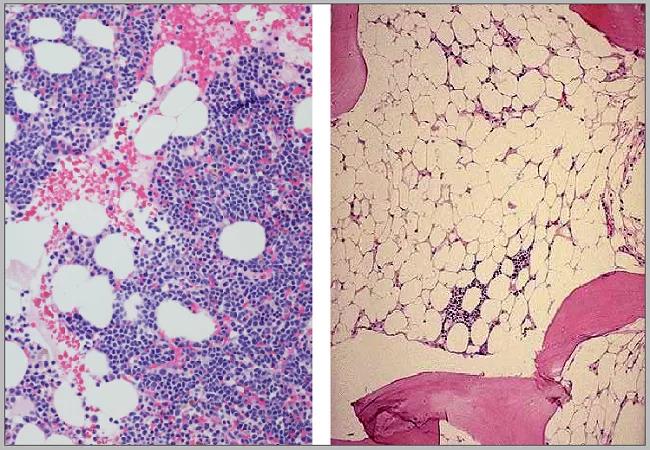
Aplastic anemia is the most common cause of bone marrow failure disorders across all ages. The annual incidence of aplastic anemia (AA) in the pediatric population was estimated to be two to four cases per millions.1
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Severe aplastic anemia in children (SAA) is fatal if not treated appropriately. The long-term survival in SAA strongly correlates with hematologic response to treatments. Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation is currently the only curative option for SAA; however, not everyone has access to matched donors and using alternative (mismatched) donors is associated with increased risk for graft versus host disease.2
Immunosuppressive therapy (IST) with horse antithymocyte globulin and cyclosporine currently remains the standard therapy for children with SAA who lack matched sibling donors. Compared to adults, children with SAA had a higher response to IST; however, approximately 30% never responded to this therapy.3 Additionally, some of these responders eventually relapsed from their disease requiring additional therapies.
In 2018, the Food and Drug Administration approved the use of eltrombopag in combination with standard IST in newly diagnosed patients with SAA who are 2 years or older. A recent systematic review and meta-analysis of the efficacy of eltrombopag in AA revealed hematologic response in 88% of patients treated with eltrombopag and IST.4
In the pediatric population, however, data are lacking to develop a standard of care. To address this, in a single-center retrospective cohort study, a team of investigators, including Harry Lesmana, MD, pediatric hematologist/oncologist at Cleveland Clinic Children’s and first author of the study, analyzed the hematologic response to treatments in patients ≤ 18 years old consecutively diagnosed with SAA. The study identified 16 patients receiving standard IST and nine patients receiving a combination of standard IST and eltrombopag.
Advertisement
In the cohort of patients receiving standard IST, only 71% had a hematologic response at six months post-therapy, compared to 100% in those receiving both IST and eltrombopag. The authors also concluded no differences in the rate of adverse events between the two cohorts, although longer follow-up is needed.
This study showed that the addition of eltrombopag to standard IST was well-tolerated and resulted in satisfactory hematological response in children with SAA. The investigators hope to perform a larger prospective multi-institutional study to validate these findings.5
References
1. Young NS, Kaufman DW. The epidemiology of acquired aplastic anemia. Haematologica. 2008;93:489-492.
2. Williams DA, Bennett C, Bertuch A, et al. Diagnosis and treatment of pediatric acquired aplastic anemia (AAA): an initial survey of the North American Pediatric Aplastic Anemia Consortium (NAPAAC). Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2014;61:869-874.
3. Rogers ZR, Nakano TA, Olson TS, et al. Immunosuppressive therapy for pediatric aplastic anemia: a North American Pediatric Aplastic Anemia Consortium study. Haematologica. 2019;104:1974-1983.
4. Hong Y, Li X, Wan B, Li N, Chen Y. Efficacy and safety of eltrombopag for aplastic anemia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Drug Investig. 2019;39:141-156.
5. Lesmana H, Jacobs T, Boals M, Gray N, Lewis S, Ding J, Kang G, Hale M, Weiss M, Reiss U, Wang W, Wlodarski M. Eltrombopag in children with severe aplastic anemia. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2021 Aug;68(8):e29066. doi: 10.1002/pbc.29066. Epub 2021 Apr 15. PMID: 33855784.
Advertisement
Advertisement
Advertisement

Findings hold lessons for future pandemics

One pediatric urologist’s quest to improve the status quo

Overcoming barriers to implementing clinical trials

Interim results of RUBY study also indicate improved physical function and quality of life

Innovative hardware and AI algorithms aim to detect cardiovascular decline sooner

The benefits of this emerging surgical technology

Integrated care model reduces length of stay, improves outpatient pain management

A closer look at the impact on procedures and patient outcomes