13-year retrospective shows evolution of treatment for aggressive disease
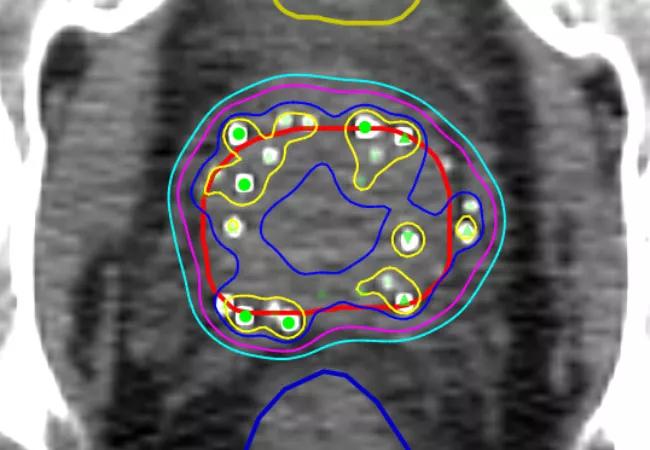
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/d6b1fb10-a464-483b-9f84-1e0830dc02ee/650x450-Prostate-Cancer_jpg)
650×450-Prostate-Cancer
Localized treatment — adding brachytherapy to external beam radiotherapy — appears to improve survival outcomes for men with high-risk prostate cancer, according to a large retrospective study by Cleveland Clinic researchers published in JAMA.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
“The improved survival is probably due to our ability to increase that localized dose far higher with brachytherapy than with external beam alone,” explains radiation oncologist Jay P. Ciezki, MD, Department of Radiology, study co-author. “And a higher dose kills more cancer, which is a good thing.”
Despite a trend toward earlier detection and treatment, prostate cancer remains the second leading cause of cancer death in American men. High-risk prostate cancer affects 7 to 10 percent of men with the disease and is the most difficult form to treat.
In the study, a retrospective review of 1,809 patient records from the Cleveland Clinic and 11 other tertiary care centers around the country plus Norway, researchers compared the clinical outcomes of men with Gleason score 9-10 prostate cancer who had received one of three treatment modalities:
Key outcomes included prostate cancer-specific mortality, distant metastasis-free survival and overall survival. (Because the definition of biochemical recurrence differs among the three outcomes, the researchers’ selection of prostate cancer-specific mortality was designed to avoid potential confusion.)
The study’s data spans 2000 through 2013, providing a birds’ eye view of the evolution of treatment modalities for this aggressive form of this disease:
Advertisement
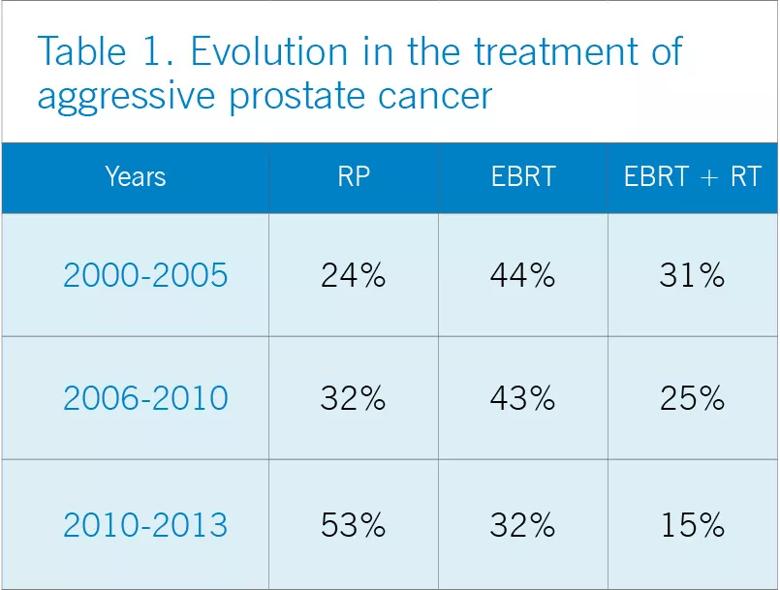
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/b8251410-bc1d-4398-a1dd-595c09113ec7/805x-Inset-Table-1_-Evolution-in-the-treatment-of-aggressive-prostate-cancer_jpg)
Contrasting this shift toward surgery, however, the analyses found that the EBRT+BT group fared better across all three outcomes, with a significantly lower adjusted five-year prostate cancer-specific mortality rate at 3 percent, compared to 12 percent for RP and 13 percent for EBRT. For distant metastasis, adjusted five-year rates were 8 percent for EBRT-BT, compared with 24 percent for both RP and EBRT. As for adjusted 7.5-year all-cause mortality, the rates were 10 percent for EBRT-BT, compared with 17 percent for RP and 18 percent for EBRT.
Acknowledging that the majority of the EBRT and EBRT+BT patients included androgen deprivation therapy (89.5 percent and 92.4 percent, respectively), the authors noted that there was a significant difference in the duration of the therapy, with the ERBT+BT group receiving it for only 12 months, compared to the 21.9 months the EBRT cohort received it. However, authors note that neither duration nor dose had significant impact on any of the outcomes.
Surprisingly, neither were there differences in outcomes related to brachytherapy dose rate (low dose rate [LDR] versus high dose rate [HDR]). Toxicity was kept to a minimum as well, explains Andrew Stephenson, MD, Department of Urology, Glickman Urological & Kidney Institute, another co-author. The key difference, he notes, was timing: LDR takes about an hour where HDR is given over several days. Indeed, in a 2017 paper published in the International Journal of Radiation Oncology Biology Physics, the two were part of a team that reported LDR alone was as good as EBRT or RP.
Advertisement
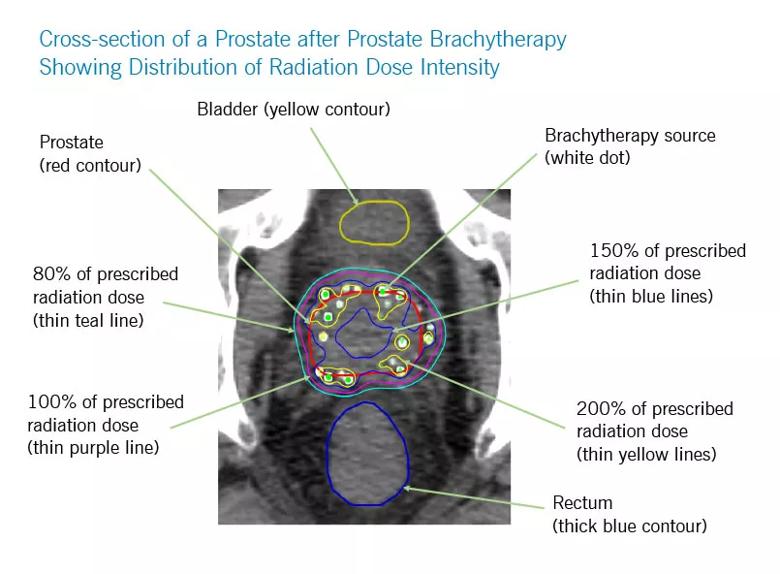
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/26941fe4-de1f-41fb-bba5-179bfa9b8d5f/805x-Inset-Prostate-Radiation-Dose_jpg)
“It is clear that the local modalities work well locally,” Dr. Ciezki says, referring to the brachytherapy cohort outcomes, “most likely by improving the local control at the site.
“But local modalities don’t work in distant metastasis. The real game changer in the future will be the systemic agents that offer promise in distant disease,” says Dr. Ciezki. He notes that current systemic therapies have not been effective in this group of patients, but that newer drugs are showing effectiveness against distant metastases.
According to Dr. Ciezki, this study shows that physicians need to be open-minded and offer their patients options not only for surgery, but for external beam radiotherapy and for brachytherapy. “This study shows that brachytherapy works, so it should be offered to appropriate candidates,” he says, adding that brachytherapy is a demanding procedure by itself and physicians need to keep up their skills to make certain the therapy is as effective as it can be.
Advertisement
Advertisement
Combination therapy improves outcomes, but lobular patients still do worse overall than ductal counterparts
Bringing empathy and evidence-based practice to addiction medicine
Supplemental screening for dense breasts
Combining advanced imaging with targeted therapy in prostate cancer and neuroendocrine tumors
Early results show strong clinical benefit rates
The shifting role of cell therapy and steroids in the relapsed/refractory setting
Radiation therapy helped shrink hand nodules and improve functionality
Standard of care is linked to better outcomes, but disease recurrence and other risk factors often drive alternative approaches