Cleveland Clinic urologist performs first procedure in Europe

Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/0107e39f-1dfa-4bf6-b851-60e870cebb40/URL_4417259_11-20-23_166_MLC-jpg)
Robotic surgery
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
It’s been more than two decades since urologists began favoring a retropubic approach over a perineal approach for radical prostatectomy. Better visibility and the ability to remove pelvic lymph nodes to check for metastasis made retropubic prostatectomy preferable.
Robotically assisted laparoscopic techniques made it even better — a minimally invasive procedure, going in through the abdomen, sometimes through a single port in the navel.
But retropubic surgery hasn’t been perfect. Even when performed minimally invasively, it sometimes leaves patients with life-altering complications, such as urinary incontinence and erectile dysfunction.
Throughout thousands of cases, I and other urologic surgeons have tried to refine the retropubic approach, changing how and where we cut, how we close incisions, and countless other details. We’ve looked for ways to improve surgical options for patients who are obese or have abdominal scar tissue.
In the end, I’ve concluded that the best solution is to revert to a procedure we all-but-abandoned in the 1990s, radical perineal prostatectomy (RPP), but with a 21st century twist — robotics.
In March 2018, I performed the first-ever robotic RPP in Europe, at London’s Royal Marsden Hospital. While I initially published the approach in 2017 and performed 12 cases in Cleveland, robotic RPP now is drawing attention worldwide.
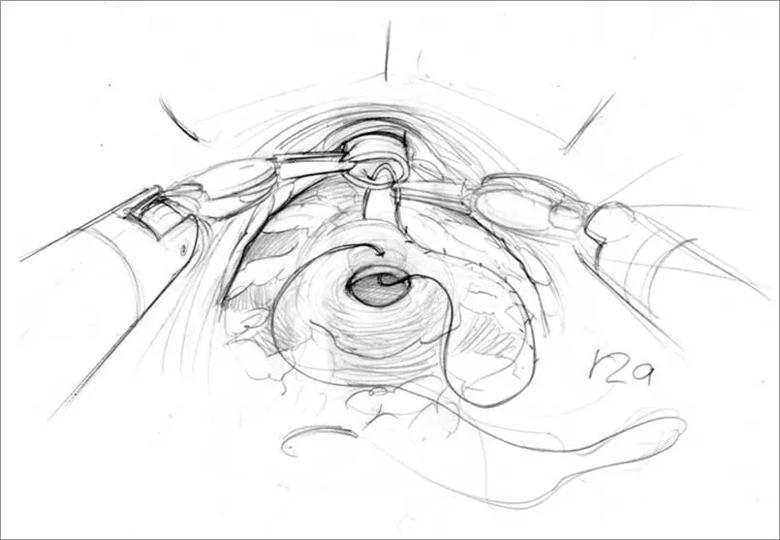
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/c822b7c9-bbe8-4a42-a342-b86a0f73acbc/805x-Inset-Anostomosis_jpg)
Robotic RPP allows for tiny incisions between the patient’s legs, through the perineal area. The prostate is only an inch or two under the skin — a much shorter, less invasive route than coming through the abdomen. Through the perineum, we have direct access to the prostate and no need to move the bowel and bladder out of the way.
Advertisement
Blood loss is minimal during robotic RPP, and patients have less pain and retain better urine control because the bladder isn’t dissected. Hospital stays are shorter.
RPP had originally lost favor because of its limited surgical exposure and poor visibility. Even a small amount of bleeding could make it hard to see, and therefore difficult to ensure clean margins and avoid damaging nerves. Training new surgeons was logistically difficult.
However, robotic arms and cameras have changed that. With robotically controlled laparoscopic equipment, RPP now is easier to see and easier to teach, clearing the way for more prostate cancer patients to experience its benefits.
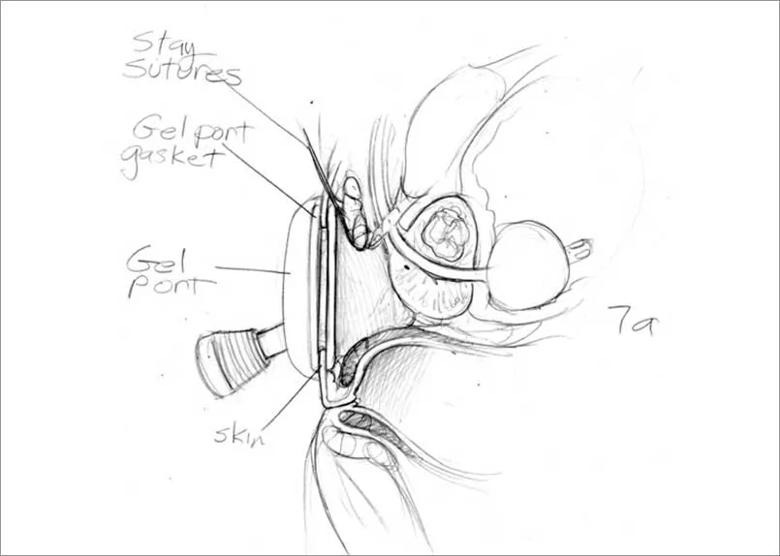
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/4da8b617-67f2-4548-a784-f8b6604a441d/805x-Inset-Port_jpg)
There’s more that we still need to refine about robotic RPP. The bulky arms and instrumentation on current robots are a tight fit in a small perineal area. Experience with robotic single-port surgeries is helpful.
The next generation of more slender, single-port robots, to be introduced this year, will make the procedure easier. It also will enable us to dissect pelvic lymph nodes through the perineum — something we have not been able to do with current technology. We will be able to work on refining nerve-sparing techniques as well.
I expect that even more centers will pursue robotic RPP when the new robots become available.
In London, we were able to use the same robotic instruments used for retropubic prostatectomy. The procedure in a 65-year-old man took approximately five hours, including time for preparation and instruction.
Advertisement
The patient was quite enthusiastic about undergoing a procedure that was the first in the hospital and one of the first in the world. His outcome has been excellent, with negative resection margins. When I visited him a few hours after the procedure, he said his pain was minimal. He was discharged two days after the procedure. His urine control returned almost immediately after the catheter was removed about one week later.
Co-surgeon and urologist Chris Ogden, MS, FRCS, and urology registrar Jonathan Noël, FRCS, who assisted with the procedure at the Royal Marsden, intend to continue offering the procedure there. Dr. Ogden recently presented the procedure at a urology grand rounds in London and also will be presenting it this fall at the World Congress of Endourology in Paris.
We will continue to research nerve-sparing techniques to preserve erectile function, but we already are well on our way to offering men worldwide a surgical treatment that thoroughly removes prostate cancer with less blood loss, reduced pain, fewer complications and shorter hospital stays.
Dr. Kaouk is a professor of urology at Glickman Urological & Kidney Institute, where he is Director of the Center for Laparoscopic and Robotic Surgery, and Vice Chair for Surgical Innovations.
Advertisement
Advertisement
Clinical trials and de-escalation strategies
Combination therapy improves outcomes, but lobular patients still do worse overall than ductal counterparts
Bringing empathy and evidence-based practice to addiction medicine
Supplemental screening for dense breasts
Combining advanced imaging with targeted therapy in prostate cancer and neuroendocrine tumors
Early results show strong clinical benefit rates
The shifting role of cell therapy and steroids in the relapsed/refractory setting
Radiation therapy helped shrink hand nodules and improve functionality