Countermeasures reduce length of stay by more than 30%

Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/04fdc599-c236-43dc-aef1-0f3bd0fdfa49/newborn-lip-blister-2031340689)
Sleeping late-preterm infant in NICU
At Cleveland Clinic Children’s, infants are admitted to the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit (NICU) if they are born prematurely or if they have a condition that prevents them from going to the newborn nursery. They are discharged home when deemed safe. During this hospital stay, infants are stabilized, lactation consultants address feeding problems and a multidisciplinary group of caregivers provides education to parents about possible complications and recovery from their illness. But the ultimate goal is to discharge these neonates and get them into their homes with their families as quickly as is feasible in order to increase familial bonding, breastfeeding and reduce the cost to families.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
In an effort to decrease this length of stay, caregivers in the NICU at Cleveland Clinic Fairview Hospital identified several potential opportunities for intervention and developed a process improvement project with a goal of reducing the length of stay by 20% for infants born at or beyond 35 weeks of gestation.
Discharge readiness is determined by a host of metrics, including thermoregulation, control of breathing, respiratory stability, feeding skills and weight gain. To address these areas, the team implemented a number of changes over several months, including:
At baseline, the average length of stay for infants born ≥ 35 weeks was 5.35 days. “We set our target goal at 4.28 days, which was a 20% reduction,” says Ajith Mathew, MD a neonatologist at Cleveland Clinic Children’s. “After implementing these countermeasures, we were able to surpass our goal within a month. From March 31, 2020 through Feb. 28, 2021, our average length of stay was 3.71 days, which is a 30.6% reduction that touched 313 infant lives.”
Advertisement
After discharge, families were scheduled for follow-up visits with Cleveland Clinic Children’s neonatologists virtually. In these follow-up visits, neonatologists answer parent questions about feeding, jaundice, medications, and laboratory and investigational results.
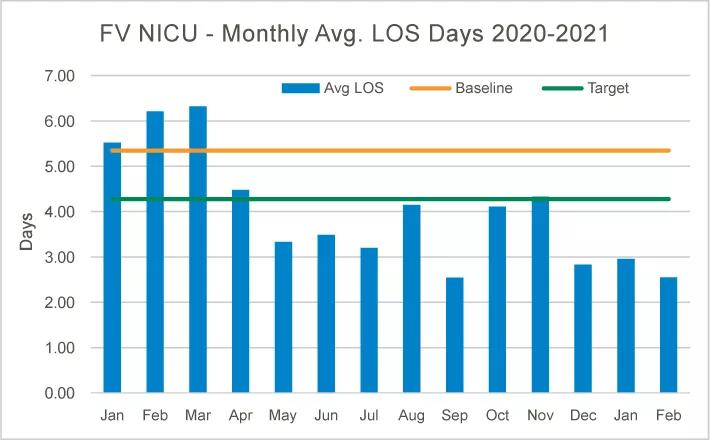
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/6f9426c3-ab35-4391-9193-bbe7bb4ac31f/21-CHP-2091512_Graph_jpg)
“Not only did we reduce our average length of stay but we also saved time for our caregivers. On average, it takes approximately 90 minutes to clean an isolette. But it only takes approximately 5 minutes to clean a warmer. In transitioning to admitting more infants into warmers, we have saved our caregivers approximately 213 hours since March 2020 to Feb. 2021 – hours that can now be spent in direct infant care and preparing families for life with their babies,” Dr. Mathew adds.
The countermeasures had benefits beyond earlier discharge, according to Dr. Mathew. “By admitting to warmers, we have increased our bed space by 2 square feet (an increase of 4%). Additionally, the transition to bassinettes increased our bed space by 4 square feet (an increase of 7%). This gives both our caregivers and parents more room to care for the infant.”
Additionally, reducing the length of stay should reduce costs to families. “The figures have not been fully completed yet, but we have reduced the cost of the NICU stay to our families considerably,” concludes Dr. Mathew.
Advertisement
Advertisement
Infants with > 30° of cervical tightness were also more likely to be younger at evaluation
Findings hold lessons for future pandemics
One pediatric urologist’s quest to improve the status quo
Overcoming barriers to implementing clinical trials
Interim results of RUBY study also indicate improved physical function and quality of life
Innovative hardware and AI algorithms aim to detect cardiovascular decline sooner
The benefits of this emerging surgical technology
Integrated care model reduces length of stay, improves outpatient pain management