Repairing Complex Valve Defects in Infants: Challenging, but Achievable
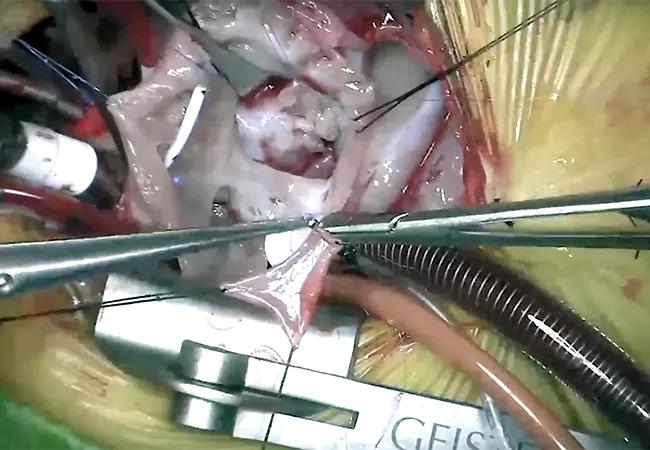
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/a197f60c-fb84-473d-bc63-74b07bfef579/650x450-AVC-repair_jpg)
650×450-AVC-repair
A complex valve repair in an infant with unbalanced partial atrioventricular canal (AVC) defects is extremely challenging, but Cleveland Clinic surgeons have devised a sequential approach that has proven successful despite the long odds.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
The team, led by Hani K. Najm, MD, performed a repair in a 6-week-old premature 2.6kg male infant who had a right dominant partial AVC defect that was further complicated by a severely regurgitant double-orifice left atrioventricular valve (LAVV) and a severely regurgitant Ebstenoid right atrioventricular valve (RAVV), with significant restriction of leaflet components and atrial arrhythmias.
Since there are no prosthetic valves available for infants that small, repair offers the best chance for survival. But, many surgeons will view the surgery as too risky and opt to wait until the infant is older. However, Dr. Najm says, that was not an option in this case. “He was low birthweight and had a severe leaky valve. There’s no way we would have been able to wait. He wouldn’t have been able to grow.”
Najm and colleagues reported the case in the August 2021 issue of JTCVS Techniques. “It’s a tough anomaly that is not easy to deal with. You really need to strategize before you tackle this,” he says.
Pulmonary artery banding is sometimes used as a palliative measure for unbalanced AVC defects, but the team determined that the long-term risk of worsening atrioventricular valve regurgitation would have outweighed the benefits. Instead, they went for a complete repair.
Cut-and-sew isthmus ablation was performed with an incision from the inferior vena cava to the RAVV rather than using cryoablation, since the freezing would likely have damaged the tiny baby’s heart.
Dr. Najm and colleagues provide six additional surgical technique pearls from this case, which may inform other complex valve repairs in small infants who are unsuitable for single-ventricle repair or pulmonary artery banding:
Advertisement
1) Division of the superior and inferior bridging leaflets, despite the absence of a ventricular septal defect, to allow identification of all abnormal leaflet attachments. “Dividing them will allow you to see what’s under there so you can do a proper repair and avoid obstruction of the left ventricular outflow tract,” Dr. Najm observes.
2) Use of a fresh autologous pericardial leaflet augmentation patch instead of direct leaflet approximation. “When you have leaflets that are deficient, you need to replace or add material. This is how you add autologous pericardium,” Dr. Najm notes.
3) Commisuroplasty for the double-orifice LAVV to prevent valvular incompetence. Surgeons will typically close the smaller orifice because it’s leaking, but Najm doesn’t think that’s a good technique. “I think the best thing is to do this annuloplasty or commisuroplasty, which are sutures on the annulus in order to improve the competency of the valve, without closing it. That way it’s still functional,” he explains.
4) Division of all valvular attachments except primary chords, to improve mobility of restricted RAVV leaflets and facilitate a better repair.
5) Approximation of RAVV papillary muscles with pledgeted suture to improve leaflet coaptation. “Not only working on the annulus, but working on the papillary muscle improves valve function,” Dr. Najm says.
6) Left atrial line placement for postoperative hemodynamic monitoring, particularly taking care to avoid hypertension, volume loading the heart, and early weaning to extubation.
Advertisement
“This is a very fine, delicate repair and if you allow the blood pressure to go up the repair can fall apart quickly because initially it’s flimsy. Eventually it will heal and won’t be an issue. But at least in the first 42-48 hours it’s important to keep the lines in to make sure we’re actually monitoring all this,” Dr. Najm says.
The decision to pursue an aggressive surgical approach and all of the preparation paid off: The boy is now over a year old and healthy. “He’s looking great. He’s growing up so well, and has had no further operations. A great success.”
Featured image: Intraoperative image from complex partial AVC repair in an infant with double orifice LAVV and significantly restricted RAVV. Reproduced with permission under the Creative Commons CC-BY-NC-ND license.
Advertisement
Advertisement
Findings hold lessons for future pandemics
One pediatric urologist’s quest to improve the status quo
Overcoming barriers to implementing clinical trials
Interim results of RUBY study also indicate improved physical function and quality of life
Innovative hardware and AI algorithms aim to detect cardiovascular decline sooner
The benefits of this emerging surgical technology
Integrated care model reduces length of stay, improves outpatient pain management
A closer look at the impact on procedures and patient outcomes