Time to recurrence most predictive
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/8c4892b7-22d0-4adc-8453-a297ae9d483b/ovarian-cancer-GettyImages-486784816)
Ovarian-CA_650x450
Numerous past studies have shown that patients with ovarian cancer who respond to chemotherapy but then recur within six months generally live another 10 months. Survival for patients with ovarian cancer who respond to chemotherapy but recur later, however, is more variable. The advice given to such patients is usually just an average of how long all patients with recurrent ovarian cancer survive, 21 months.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Average survival times, however, do not provide much specific information to individual patients. Recently, a group of physicians from the NRG/Gynecologic Oncology Group analyzed clinical prognostic factors for survival after recurrence of high-grade, advanced-stage ovarian-peritoneal-tubal carcinoma. They then developed a nomogram to predict individual survival after recurrence.
“Patients want more specifics about their individual survival because it allows them to better plan for the future,” says Peter Rose, MD, who was first author on the study that was recently published in the journal Obstetrics and Gynecology.
The retrospective study included 4,739 patients, of which 84 percent had stage III and 16 percent had stage IV ovarian carcinoma. At a median follow-up of 88.8 months, the vast majority of patients (89.4 percent) had died. The median survival after recurrence was 21.4 months.
The investigators identified a number of significant prognostic factors, including: time to recurrence after initial chemotherapy, clear cell or mucinous histology, residual disease after primary surgery, performance status, stage IV disease and age. These factors are utilized to develop a nomogram to predict estimated survival for each patient.
Dr. Rose says the group’s analysis shows that time to recurrence was by far the strongest variable for determining how long a patient would survive (accounting for 85 percent of the model). Residual disease, histology and performance status were the next most significant factors affecting survival after recurrence.
Advertisement
All of the patients in the study were treated with primary surgery followed by chemotherapy. More recently, however, oncologists have used neoadjuvant chemotherapy followed by surgery in patients with ovarian cancer. “It has become more popular because a lot of older people get ovarian cancer and they don’t do well with aggressive surgery,” Dr. Rose notes.
Dr. Rose suggests that the study’s cohort could be used as a control group for future studies. Researchers could compare survival outcomes of patients using new treatments to those of this group to determine whether the new drug prolongs a patient’s survival significantly.
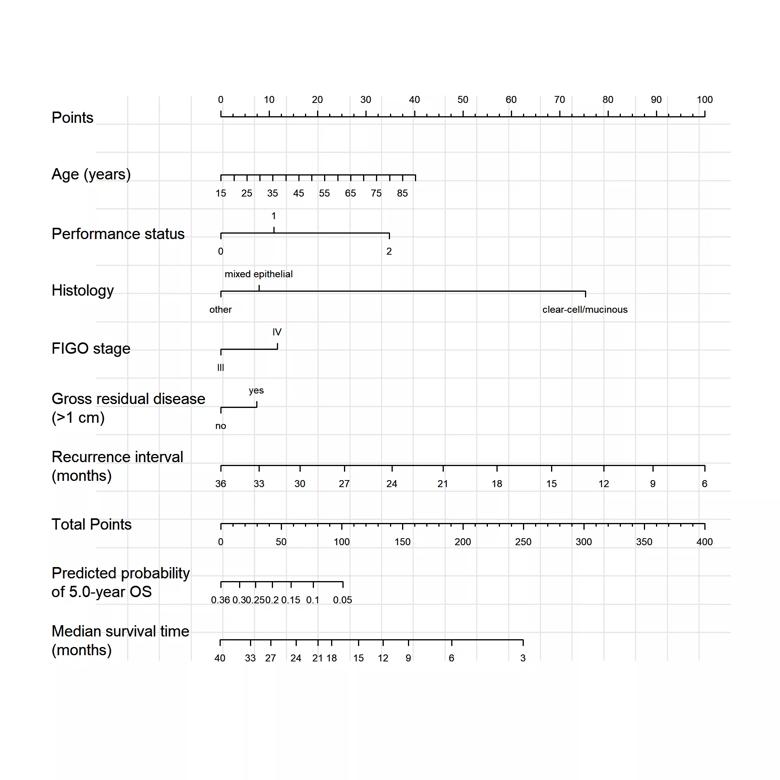
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/c0317738-acec-4e6b-851b-88a743704a41/Nomogram_png)
Nomogram for predicting median survival time after recurrence. To use, find the patient’s recurrence interval on the recurrence axis, then draw a straight line upward to the Points axis to determine how many points toward death the patient receives for her recurrence interval. Do this again for the other axes, each time drawing a straight line upward toward the Points axis. Sum the points received for each predictor and find the sum on the Total Points axis. Draw a straight line down to the median-survival axis to find the patient’s median survival time after recurrence of ovarian cancer.
Advertisement
Advertisement
Supplemental screening for dense breasts
Combining advanced imaging with targeted therapy in prostate cancer and neuroendocrine tumors
Early results show strong clinical benefit rates
The shifting role of cell therapy and steroids in the relapsed/refractory setting
Radiation therapy helped shrink hand nodules and improve functionality
Standard of care is linked to better outcomes, but disease recurrence and other risk factors often drive alternative approaches
Phase 1 study demonstrates immune response in three quarters of patients with triple-negative breast cancer
Multidisciplinary teams bring pathological and clinical expertise