Staged reconstruction allows for easier reintervention if needed
By Nathan Mesko, MD and Lukas Nystrom, MD
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
The primary treatment for soft tissue sarcoma (STS) is the surgical resection of the cancer. In some instances when skin must also be resected with the tumor, reconstructive surgery (e.g., muscle flaps and/or split-thickness skin graft options), is necessary to cover the wound defects. However, the ideal timing of this reconstruction has yet to be identified.
At the 2019 Annual Meeting of the American Association of Orthopaedic Surgeons in Las Vegas, we presented outcomes data from 491 patients who underwent excision of an extremity or trunk STS at our facility over a 10-year period. Eighty-one of those patients had associated soft-tissue reconstruction: 26 had primary reconstruction on the same day as the tumor resection surgery, and 55 had staged or delayed reconstruction with wound vacuum temporization.
Perhaps one reason that ideal procedure timing has yet to be elucidated is that the indications for primary vs. staged reconstruction are not defined. Many times, in surgery for STS, we have to remove skin with the tumor or evacuate a large area of muscle leaving a large potential space. The remaining skin may not be able to stretch enough to adequately close the wound. In these patients, plastic surgery reconstructive options to cover the defect with a split-thickness skin graft or flap are essential. For primary reconstruction, the plastic surgeon would operate immediately following the excision, under the same episode of general anesthesia. In staged reconstruction, a wound vacuum is placed to temporarily cover the defect, and after margins are confirmed as negative (i.e., no cancer left) the plastic surgeon will bring the patient back at a later date for reconstruction. The question we sought to answer in this review was: “Is there a difference in surgical or oncologic outcomes between primary and staged reconstruction following STS excision?”
Advertisement
We found no significant difference in the surgical outcomes of patients who received primary or staged reconstruction. The mean time to reconstruction was 17±15 days in the staged group.
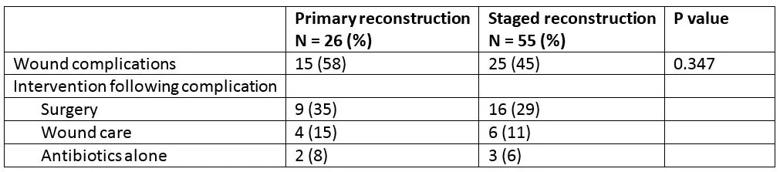
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/468e4503-eb3a-4756-840b-c2e78ec4523a/Table-1_jpg)
Table 1. Wound complications
Infection was the most common complication, with 10 superficial and 13 deep infections in the 81 surgeries. Forty-six percent of patients in the primary group and 53% of patients in the staged group had healed within three months. These differences were not statistically significant.
When analyzing oncologic outcomes, we found no significant difference between primary and staged reconstruction.
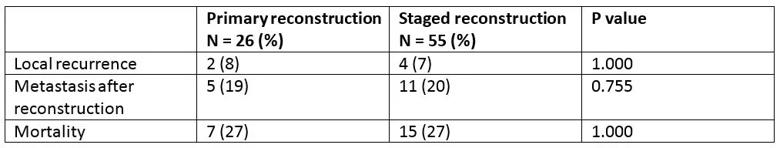
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/a3506449-a65e-4398-90f7-546f2fec87a4/Table-2_jpg)
Table 2. Oncologic outcomes
Significantly, 58% patients in the primary reconstruction group required admission to the surgical intensive care unit (SICU) compared with only 22% in the staged group. Length of SICU stay, however, did not differ between the groups.
The number of surgeries was higher, at 3.9±2.1 in the staged reconstruction group compared with 2.5±2.4 in the primary group. When we looked at the total number of surgeries after reconstruction, however, we found no difference between the cohorts. There was also no difference in total anesthesia time.
We performed a wide excision in a 63-year-old male with a high-grade STS of the proximal tibia underwent a wide excision with wound vacuum temporization. After confirming negative margins, we completed the staged reconstruction on postoperative day three.
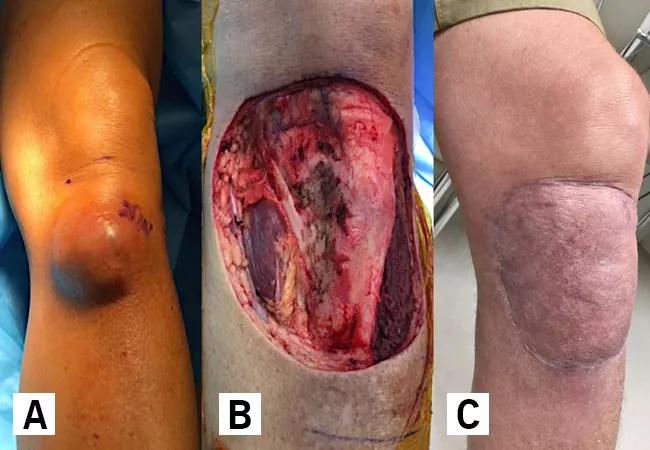
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/f9b11ddf-174b-43a7-8c0d-7d654363ddfa/19-ORT-1130-CQD-Inset_jpg)
A) preoperatively, B) during primary excision, and C) 3 months post soft tissue reconstruction with a rotational gastrocnemius flap + STSG.
Advertisement
Staging the reconstruction appears to have been beneficial in cases in which there were positive margins. Two patients in the primary group had positive margins, and neither underwent an additional re-excision procedure. Four patients in the staged reconstruction cohort had positive margins, and all four underwent further re-excision before reconstruction.
It can take up to a week after the initial excision to obtain an accurate margin evaluation. By staging reconstruction, we can confirm that the surgical margins are negative. Routinely, with direct partnership and communication with our sarcoma pathology team, margin turnaround can be in as little as 24-48 hours, creating fewer delays between excision and definitive coverage. In staged cases, a delayed reconstruction affords easy reintervention following positive margins, with little additional morbidity.
In addition to the improved ease of reintervention with staged reconstruction, our study shows that immediate and long-term outcomes were no different between the primary and staged cohorts. This was not a randomized study with a variety of indications used for staging that were surgeon specific. Further investigation to explore our outcomes would optimally involve collaborating with other institutions to build a larger patient cohort with multiple different surgeon practices.
Advertisement
Advertisement
Goal-of-care discussions drive earlier hospice access
Clinical trials and de-escalation strategies
Combination therapy improves outcomes, but lobular patients still do worse overall than ductal counterparts
Bringing empathy and evidence-based practice to addiction medicine
Supplemental screening for dense breasts
Combining advanced imaging with targeted therapy in prostate cancer and neuroendocrine tumors
Early results show strong clinical benefit rates
The shifting role of cell therapy and steroids in the relapsed/refractory setting