Cutaneous complications common post-transplant
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
As use of lung transplant (LT) becomes more common, pulmonologists should be aware of post-transplant dermatologic complications. In a recent pictorial review in CHEST, my colleagues and I describe the pathogenesis, epidemiological characteristics and clinical manifestations of dermatologic complications found in lung transplant recipients. Here I will focus on squamous cell carcinoma (SCC).
The incidence of SCC in solid organ transplant recipients is approximately 3.6 percent at 36 months and 26.5 percent at 10 years post transplant. The risk increases with age, time from transplant, prior skin cancer diagnosis and male sex. The use of immunosuppressants in transplant recipients increases the proliferation of oncogenic viruses and tumor promotion. Several common post-transplant drugs, including cyclosporine and azathioprine, can spur cellular processes that promote cancer development and growth.
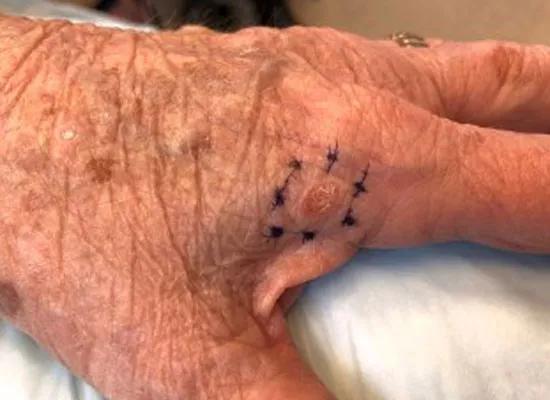
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/2c0f1f45-d1c2-4079-92a7-3ce0330c0ebf/fig-1_550x400_jpg)
There are several types of SCC. The above shows Bowen disease, or SCC in situ, in an LT recipient. Note the scaly erythematous plaque in an irregular shape. Bowen disease can progress to invasive SCC, which can metastasize.
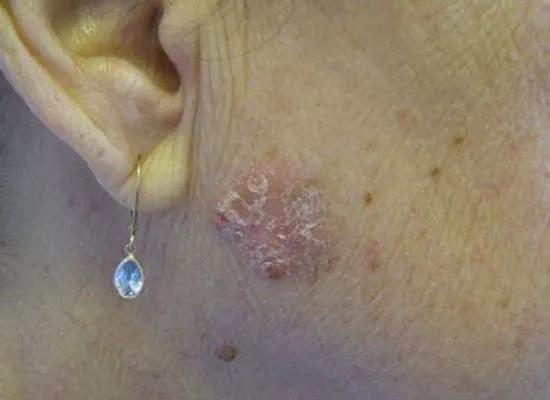
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/8c9dd717-736b-4371-b44b-2cb549622381/fig-2_550x400_jpg)
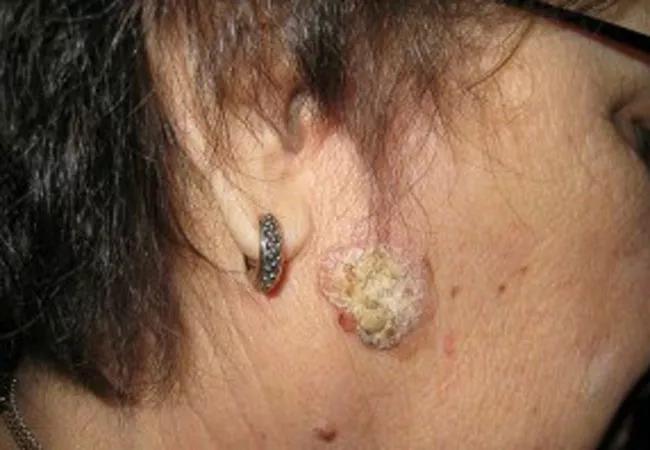
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/46bb2429-5f9b-4f9a-bc63-bec7d33f4316/fig-3_650x450_jpg)
Invasive SCCs, like the images above, are also scaly and erythematous but may be ulcerated, painful and symptomatic and present as cutaneous horns. The second image indicates five months of progression in the same patient.
Keratoacanthomas are dome-shaped variants of SCC that present as papules or nodules with a central keratin plug or ulcerations. They may regress spontaneously or proliferate despite treatment.
Advertisement
Patients with higher risk of developing SCC should be screened regularly and educated about the importance and proper application of skin surveillance and UV protection. I urge any transplant pulmonologist to incorporate counseling, treatment, education and referral to dermatology into their post-transplant visits. Early treatment for suspicious lesions is crucial, especially in this population.
Dr. Mehta is staff in the Department of Pulmonary Medicine.
Images are republished with permission from CHEST.
Advertisement
Advertisement
Family history may eclipse sun exposure in some cases
Consider secondary syphilis in the differential of annular lesions
Persistent rectal pain leads to diffuse pustules

Two cases — both tremendously different in their level of complexity — illustrate the core principles of nasal reconstruction
Stress and immunosuppression can trigger reactivation of latent virus

Low-dose, monitored prescription therapy demonstrates success

Antioxidants, barrier-enhancing agents can improve thinning hair