A closer look at the innovative procedure
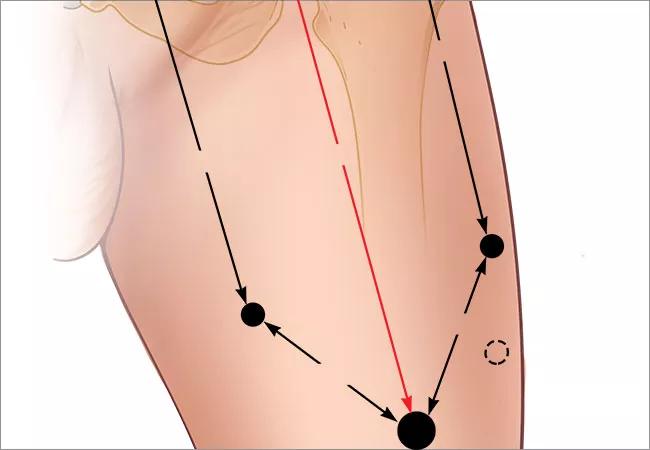
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/5bfdfa6c-7a59-45e7-ba03-36d9a4e85f2a/650x450-Inguinal-lymph-nodes_robotic-ports_20-URL-1830311_jpg)
650×450-Inguinal-lymph-nodes_robotic-ports_20-URL-1830311
Penile cancer is rare — it accounts for less than 1% of cancers in men in the United States — but its burden is no less insidious. It begins at the penis and advanced cases tend to spread into the inguinal lymph nodes located either superficially or deep within the groin.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
An inguinal lymph node dissection, or lymphadenectomy, has been the standard of care to diagnose, treat and prevent the spread of penile cancer. The procedure has been associated with a high complication rate including flap necrosis and lymphedema. In response, urologists have worked to minimize complications. Greater efforts have been made to improve early detection and develop less invasive surgical techniques.
Jayram Krishnan, DO, MBA, a urologic oncologist in Cleveland Clinic’s Glickman Urological & Kidney Institute, advocates for a robotic approach to inguinal node dissection. “Anecdotally, we see a significant reduction in postoperative complication, paired with a faster recovery, enabling patients to return to their daily activities sooner,” he says.
Adherence is given to all principles of the open surgical approach, but the robot allows surgeons to utilize smaller incisions, sparing the saphenous vein and limiting the area of dissection to superior-medial to the saphenofemoral junction — not performing a sartorious flap. Thus, this technique mitigates many of the risks for wound and edema complications.
“We will follow these modifications during robotic resection of the inguinal nodes. Nodes, both superficial and deep, can be approached in this fashion and both sides can be performed safely during one setting,” he says. He notes that laparoscopic access is obtained with the use of a spacemaker balloon. Once space is created, the robotic ports are placed, as shown below. The robot is placed in a “side dock” configuration on each side.
Advertisement
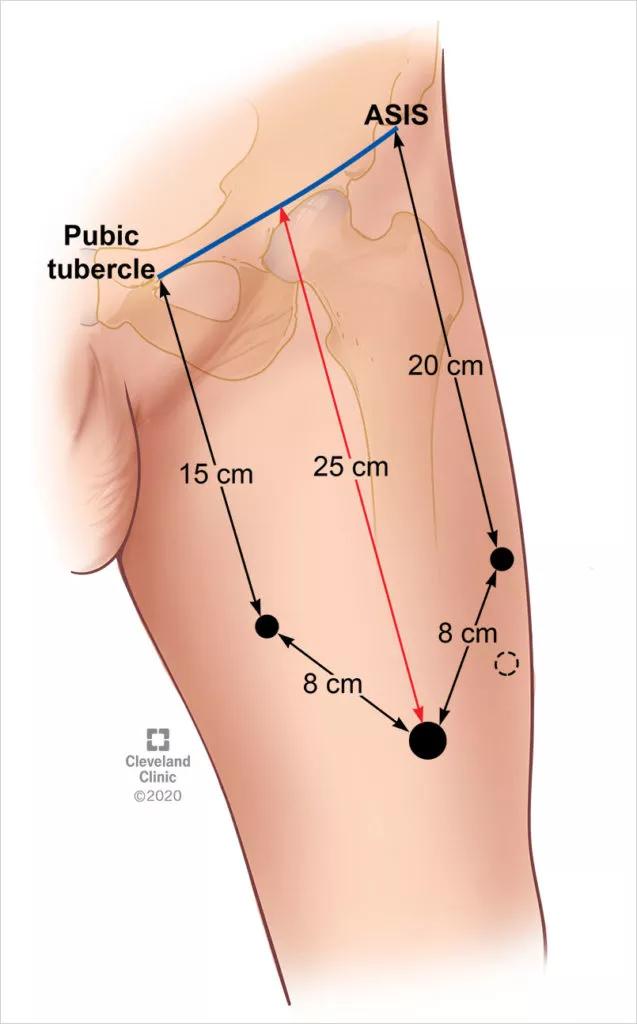
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/5ec2f381-6933-49dd-9cf9-247b06d9bd7a/805x-Inset-Inguinal-lymph-nodes_robotic-ports-637x1024_jpg)
Once in the space, the classic “split and roll” technique is used with the robotic instruments. Anatomic landmarks are used to aid in the dissection. Multiple small, medium and large clips can be used through the assistant port for control of lymphatic channels and small vessels.
Alternatively, a robotic vessel sealer can be used. A multi-use laparoscopic bag is used to collect and retrieve lymph node packets as they are liberated from the region. Once the robot is undocked, careful attention is given to wrapping the thighs tightly to prevent postoperative lymphoceles. This can be transitioned to compression stockings in the future. Patients are instructed to ambulate within the first 24 hours.
Dr. Krishnan has been incorporating this technique into his practice for the last six years, after completing an advanced urological robotic and laparoscopic fellowship training at Cleveland Clinic.
“Ultimately, our goal is to minimize pain and expedite recovery for patients. A robotic approach to inguinal node dissection has really contributed to these improved outcomes,” he says. “The future of this operation will, undoubtedly, be through the use of the robotic platform.”
Advertisement
Advertisement
Combination therapy improves outcomes, but lobular patients still do worse overall than ductal counterparts
Bringing empathy and evidence-based practice to addiction medicine
Supplemental screening for dense breasts
Combining advanced imaging with targeted therapy in prostate cancer and neuroendocrine tumors
Early results show strong clinical benefit rates
The shifting role of cell therapy and steroids in the relapsed/refractory setting
Radiation therapy helped shrink hand nodules and improve functionality
Standard of care is linked to better outcomes, but disease recurrence and other risk factors often drive alternative approaches