Patient climbs Mount Kilimanjaro 8 months after surgery
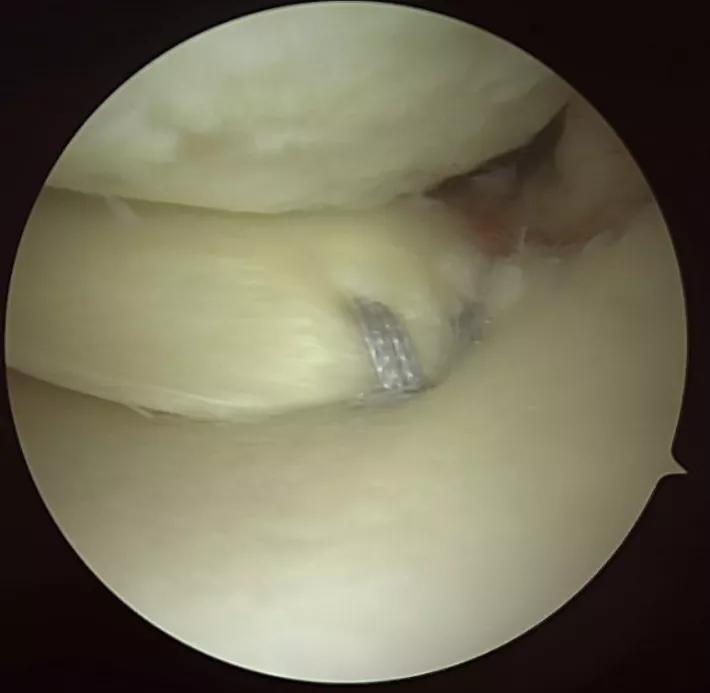
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/75fca456-44b2-4729-861e-29445d807a29/medial-meniscus-root-tear-feature2)
A torn meniscal root with sutures
A 47-year-old woman presented at Cleveland Clinic with severe pain on the medial side of her knee and some pain in the knee’s posterior aspect. The patient was active in sports, weightlifting and hiking, and was preparing for an upcoming trip to climb Mount Kilimanjaro.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
The pain had occurred suddenly while the patient was walking in a parking lot. She reported feeling a large pop in her knee before experiencing pain that she rated a 9 out of 10.
Following an MRI scan, the patient was diagnosed with a medial meniscal root tear.
“We used to wait to order an MRI until physical therapy and other conservative treatments failed,” says Lutul D. Farrow, MD, Executive Director of Cleveland Clinic Sports Medicine. “Now we can have a high-index suspicion of the diagnosis based on patient history, so we do the MRI right away.”
Less than 10 years ago, conventional treatment for meniscal root tears mirrored treatment for osteoarthritis: physical therapy, cortisone injection, bracing and weight-bearing modifications, he says.
“The treatments usually were unsuccessful for meniscal root tears. I found that most of these patients weren’t getting better. In some cases, they couldn’t return to work or daily activities. Eventually arthritis would progress, and the patients would get relief after having a total knee replacement.”
Newer understanding of these injuries has led to better treatments and outcomes, notes Dr. Farrow, who says meniscal root repair accounts for a growing part of his surgical practice. He estimates seeing 20-30 patients with meniscal root tears each year in addition to patients with more common meniscal tears.
Nearly 90% of his patients with root tears are white females, usually age 45 to 65 and often overweight. Patients frequently report doing a low-risk activity (e.g., getting up from a chair, stepping off a curb) before feeling or hearing a pop and experiencing excruciating pain. Many cannot bear weight after the injury. Some patients report feeling moderate pain in the back of the knee for weeks or months before the injury. Arthritis is a common comorbidity.
Advertisement
“Signs of more common meniscal tears, like knee popping, clicking, locking or giving way, usually are not present before root tears,” Dr. Farrow says. “There are no smaller tears or other issues leading up to the injury. People tend to go from OK to not OK very quickly.”
The patient had started physical therapy but reported no improvement before seeing Dr. Farrow.
“I immediately recommended surgical repair since the success rate of conservative therapies is pretty dismal for these injuries,” Dr. Farrow says. “Her mountain-climbing trip was about nine months out, so we had limited time to repair and rehabilitate the knee. Patients typically are not fully weight-bearing until two months after surgery and then have many more months of rehab.”
Degenerative meniscal root tears are typically a medial compartment issue, he says, involving the medial meniscus as well as medial articular cartilage. However, every surgical repair starts with a diagnostic arthroscopy to assess the rest of the knee, including the cartilage in the patellofemoral joint and the lateral compartment.
“If the patient has stage 4 osteoarthritis, we don’t seek to repair the meniscus because the clinical outcome will not be favorable,” Dr. Farrow says. “Instead, we do a partial meniscectomy to remove the torn tissue and then refer the patient for knee replacement if they do not improve.”
The patient in this case had only mild arthritis in her knee, so the surgical team proceeded with repairing the meniscal root.
The surgical procedure was done arthroscopically in less than one hour. Dr. Farrow offers these clinical pearls:
Advertisement

Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/d02926ac-699f-4ae6-b1c8-eefcc8560eb8/medial-meniscus-root-tear-inset)
A. Coronal MRI image demonstrating root tear (arrow); B. Medial meniscus root tear (triple arrow); C. Sutures placed into the root prior to reduction and fixation of the root; D. Root sutures tensioned and meniscus root repaired to footprint.
For six weeks after surgery, the patient was not weight-bearing on her surgical leg and had restricted range of motion. She then wore a medial unloader brace until two months after surgery, when her physical therapist slowly introduced impact activities.
“While we were unable to simulate exactly what her climbing trip would entail, she worked on hiking at various inclines and declines, gradually increasing duration,” says Cleveland Clinic physical therapist Amy Bell. “We’d break down her actions into parts, so that she could work on individual movements, like drills.”
The patient also worked on regaining endurance through aerobic activities, like cycling and elliptical workouts.
Her total recovery time was approximately six months.
At eight months postsurgery, the patient successfully completed an eight-day, 47-mile hike to the summit of Mount Kilimanjaro.
“I advised her to wear a knee brace during her climb, which she did,” Dr. Farrow says. “The climb to the summit is rigorous and can be challenging for someone with healthy knees. To do it after a surgery and with limited recovery time was no small feat.”
Today, the patient no longer requires a knee brace and does not require follow-up care.
Dr. Farrow offers four takeaways from this case:
Advertisement
Advertisement
Multidisciplinary care can make arthroplasty a safe option even for patients with low ejection fraction
Self-care may be just as effective for some patients
Most return to the same sport at the same level of intensity
Higher than 5-year rates for prostate cancer and melanoma and about the same as breast cancer
Insights to help orthopaedic practices comply with the 2025 CMS mandate
Dr. Piuzzi wins 2025 Kappa Delta Young Investigator Award for pioneering work
Largest cohorts to date reveal low rates of major complications
More report a clinically meaningful change in function at 90 days compared to patients with lower BMI