The technology could reduce complications by offering patients an alternative to open liver surgeries
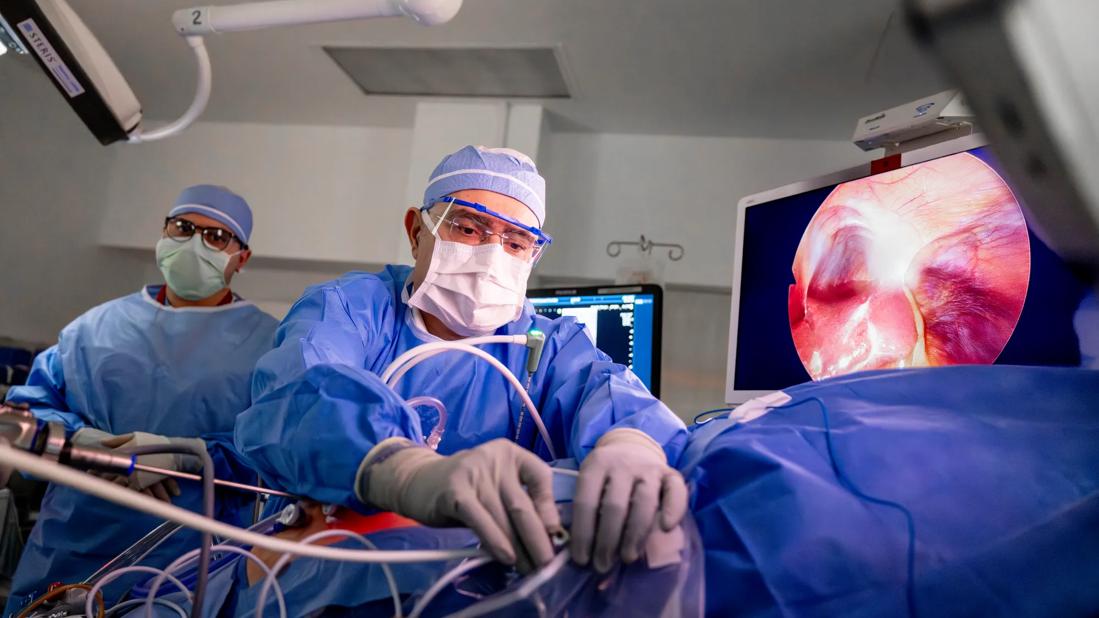
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/b84febf8-5606-4b48-b4cd-dfb5f0da0274/DDI_5499934_1-10-25_004_LDJ)
2015058_11-20-20_025_MK-Hero_650x450
Cleveland Clinic is the first hospital in the world to use a recently FDA-approved ablation technology that can destroy large liver tumors. The new device from Medtronic is called the Emprint™ HP Ablation System with Thermosphere™ Technology. The minimally invasive procedure uses a single needle connected to a powerful 150-watt microwave generator that can burn a malignant liver tumor as large as 2.4 inches (6 cm).
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Eren Berber, MD, Director of Cleveland Clinic’s Surgical Liver Tumor Ablation Program, led a team that successfully used the device in October to treat a patient who had a 2.4-inch liver tumor. Following the minimally invasive procedure, the patient is doing well and postoperative imaging shows no trace of the tumor. Since the first case in October at Cleveland Clinic, Dr. Berber’s team has treated four more patients with large liver tumors using the technology.
“We’ve been using the previous versions of this technology,” says Dr. Berber. “But the challenge was that with a single needle, we were only able to create 4-centimeter burns. This technology is able to utilize 150 watts of power compared to the 100 watts that we used before. We’re also now able to create 6- or 7-centimeter burns with a single stick. This allowed us to treat larger tumors more confidently.”
Cleveland Clinic has been using ablation technologies to treat smaller tumors up to about 1.5 inches (4 cm) in diameter and not amenable to liver resection. Dr. Berber and his team have treated close to 1,000 patients with ablation and more than 200 patients with microwave ablation. It was because of this extensive experience with the technique and device that Dr. Berber was selected as the first clinical user. “This microwave ablation technology is very powerful, and if you don’t use it well, you can cause damage to the liver, you can cause bleeding or you can disrupt the tumor,” says Dr. Berber. “As the technology becomes more advanced and more powerful, gaining ablation expertise through experience becomes even more important.”
Advertisement
To perform the procedure, a laparoscopic camera and an ultrasound probe are inserted in the abdomen through two small incisions. Then, a microwave needle is inserted through the skin into the liver tumor. When ready, the generator delivers heat to burn and destroy the lesion.
“Over the last six years, ablation technology evolved to incorporate microwave technology, which gives us a more homogeneous heating of the tissues by achieving higher temperatures,” explains Dr. Berber. “There is more balanced heating, and we can now reach higher tissue temperatures. Because of that, the success of ablation has greatly improved; the failure rate went down from 20% to 40% to about 10% or less.”
Dr. Berber notes that the best candidates for this procedure for treatment of large liver tumors are those with comorbidities which rendered them poor candidates for a major operation that would involve liver resection (cutting). This includes patients with multiple systemic diseases, heart problems, lung problems, or elderly patients who have decreased functional status who cannot tolerate a major operation. This procedure would be a good alternative for patients who would require surgery to remove a large portion of their liver. Open liver surgical procedures are associated with longer operative times and hospital stays, as well as higher incidence of complications.
“The goal is to offer the best treatment option for patients depending on their unique health condition,” says Dr. Berber In the hands of an experienced surgical team, the laparoscopic ablation technique benefits the patient, who experiences better postoperative recovery, less pain, a quicker return to normal life, and a lower risk of an incisional hernia compared with traditional open surgery.”
Advertisement
Dr. Berber has a consulting agreement with Medtronic and has received honoraria for consulting activities. He notes that his consulting agreements do not affect his choice of the best treatment option for his patients.
Advertisement
Advertisement
Combination therapy improves outcomes, but lobular patients still do worse overall than ductal counterparts
Bringing empathy and evidence-based practice to addiction medicine
Supplemental screening for dense breasts
Combining advanced imaging with targeted therapy in prostate cancer and neuroendocrine tumors
Early results show strong clinical benefit rates
The shifting role of cell therapy and steroids in the relapsed/refractory setting
Radiation therapy helped shrink hand nodules and improve functionality
Standard of care is linked to better outcomes, but disease recurrence and other risk factors often drive alternative approaches