Recommendations for temporary protective ileostomy based on risk stratification
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/778d581a-747d-4b8c-93fa-2a4873517b8f/Holubar_-j-pouch)
Dr. Holubar
Treating Crohn’s disease can be very complicated, especially on the operating room table. Even when physicians try to optimize patients before surgery, some may be at high risk for an anastomotic leak (AL). Patients who develop an AL after Crohn’s surgery require additional intervention, often operative, which results in added, potentially avoidable morbidity.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
To mitigate the complications associated with an AL, Cleveland Clinic surgeons may perform a temporary ileostomy. The benefits of an ileostomy for rectal cancer surgery or ulcerative colitis are well known. Outside of Cleveland Clinic, however, ileostomies are not widely used to treat Crohn’s patients. Cleveland Clinic researchers decided to develop a way of predicting AL risk for Crohn’s patients that could be used by other hospitals.
Under the leadership of Stefan Holubar, MD, MS, Director of the Inflammatory Bowel Disease Multidisciplinary Conference at Cleveland Clinic, researchers created a model and a score for predicting AL risk in Crohn’s patients, indicating when an ileostomy should be used. Dr. Holubar presented the details of the study Monday at the 2018 ASCRS Annual Scientific Meeting.
“This is the largest, best-designed study to date for predicting AL risk in Crohn’s patients,” notes Dr. Holubar. “According to our research, one in four Crohn’s patients are at high risk for an AL and thus may benefit from a temporary diverting ileostomy, suggesting a shift in surgical practice.”
Cleveland Clinic treats the highest volume of inflammatory bowel disease patients in the world. These include complicated, end-stage Crohn’s patients who have had multiple failed surgeries and are often on their fourth- or fifth-line medications.
“Because we’re seeing so many high-risk Crohn’s patients, we tend to have a lower threshold for diverting them with an ileostomy and perform this procedure more frequently than most hospitals,” explains Dr. Holubar. “While we knew that physicians tend to underestimate AL risk in Crohn’s disease, we didn’t have much data to justify the use of ileostomy in patients with Crohn’s.”
Advertisement
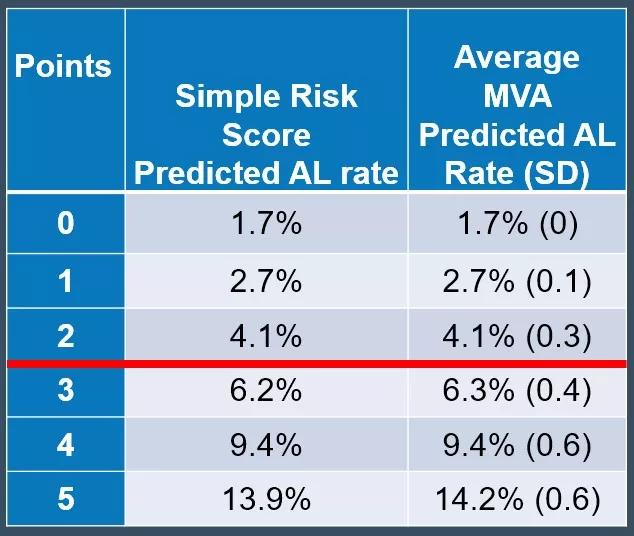
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/a2ba7585-e1e2-4721-83a4-1a5eb2c01fd6/Simple_risk_score_validation_jpg)
The study analyzed nationwide data collected from over 4,000 patients from 2012 to 2016. To develop the model, Dr. Holubar’s team performed a univariate and forward stepwise multivariable logistic regression analysis to identify independent risk factors.
The researchers used the unique “Colectomy Module”, which includes AL as one of the end points, from the National Surgical Quality Improvement Program. The Colectomy Module provided specific variables, or risk factors, relevant to colectomy and AL, considering whether the patient was on steroids, bowel prep or antibiotics. The module also analyzed the rate of ileus, the rate of leak and how the leaks were managed. (Prior to this study, no one had used the module to analyze AL risk and Crohn’s disease.) The team constructed a simple score by assigning each risk factor one point to see if that score was as accurate as the more complicated multivariable base score.
The researchers reported the following results:
Advertisement
“Our research suggests that nationally, surgeons are underestimating the AL rate in Crohn’s patients,” notes Dr. Holubar. “While our data clearly indicate that the leak rate increases with each risk factor, this information should add to and not replace clinical judgment.”
Before operating on a Crohn’s patient, the surgeon should risk stratify each patient as an individual to determine if the patient has a low or high risk of developing an AL. If the patient has three or more risk factors, the surgeon should consider diverting the patient, because the leak rate is predicted to be greater than 5 percent. “We know that the major complication rate of ileostomy reversal surgery is 5 percent,” explains Dr. Holubar. “So if you have a predicted leak rate of less than 5 percent, you don’t need an ileostomy.”
“We’re trying to provide a tool to help surgeons make better decisions, considering whether the benefits outweigh the risks of ileostomy,” says Dr. Holubar. “Our scientific model should also reassure patients that we’re making surgical decisions based on the highest quality scientific data available.”
Additional research may be used to analyze data from Cleveland Clinic patients as well as other national databases with the goal of triangulation. For example, Dr. Holubar’s team will repeat this study using additional data sources to further validate the findings.
Advertisement
Advertisement
Benefits of neoadjuvant immunotherapy reflect emerging standard of care
Multidisciplinary framework ensures safe weight loss, prevents sarcopenia and enhances adherence
Study reveals key differences between antibiotics, but treatment decisions should still consider patient factors
Key points highlight the critical role of surveillance, as well as opportunities for further advancement in genetic counseling
Potentially cost-effective addition to standard GERD management in post-transplant patients
Findings could help clinicians make more informed decisions about medication recommendations
Insights from Dr. de Buck on his background, colorectal surgery and the future of IBD care
Retrospective analysis looks at data from more than 5000 patients across 40 years