New research sheds light on a potentially devastating condition that is reversible when properly managed
Podcast content: This podcast is available to listen to online.
Listen to podcast online (https://www.buzzsprout.com/2243576/14744064)
Cerebral amyloid angiopathy is a cerebrovascular disorder characterized by accumulation of amyloid proteins in small blood vessels of the brain and leptomeninges, leading to fragile vessel walls and subsequent brain bleeds. A subset of people with the disorder develop an inflammatory reaction to the amyloid deposition known as cerebral amyloid angiopathy-related inflammation (CAA-RI), which causes progressive cognitive decline.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
“As devastating as CAA-RI can be — it can even lead to seizures and sometimes coma — it is still very treatable and reversible,” says Abbas Kharal, MD, a stroke neurologist and immunologist in the Cerebrovascular Center at Cleveland Clinic. “The inflammation is very reversible and treatable with steroids and other immunosuppressive agents.”
In the latest episode of Cleveland Clinic’s Neuro Pathways podcast, Dr. Kharal discusses the diagnosis and management of CAA-RI, delving into:
Click the podcast player above to listen to the 30-minute episode now, or read on for a short edited excerpt. Check out more Neuro Pathways episodes at clevelandclinic.org/neuropodcast or wherever you get your podcasts.
This activity has been approved for AMA PRA Category 1 Credit™and ANCC contact hours. After listening to the podcast, you can claim your credit here.
Podcast host Glen Stevens, DO, PhD: What percentage of people who have cerebral amyloid angiopathy will get the inflammation?
Dr. Kharal: That's an excellent question. And the answer is that we don’t know! That is what our research paper tried to explain. We talk about cerebral amyloid angiopathy-related inflammation as it comes to attention when patients present with rapid cognitive decline, seizures, headaches or other signs of edema. And we pick it up on imaging and conclude that the patient has either known cerebral amyloid angiopathy before, or a new diagnosis, and a pattern that fits with edema — either vasogenic edema or T2 FLAIR hyperintensity in areas of cerebral microbleeds that is much more than what you’d expect from microbleeds alone. But I still don't think we understand the true prevalence, so our study tried to look at asymptomatic and symptomatic CAA-RI together.
Advertisement
There is a term that we put out in the literature, “radiological cerebral amyloid angiopathy-related inflammation.” It basically is cerebral amyloid angiopathy-related inflammation that radiographically meets criteria for CAA-RI that may not manifest symptomatically — may not present with the headaches or the cognitive decline or seizures yet — versus the clinico-radiographic CAA-RI, which is clinically manifesting and has radiographic evidence.
In our study we showed that CAA-RI was prevalent in about 10.8% of 511 patients with cerebral amyloid angiopathy that we reviewed. That percentage represents those who had at least radiological CAA-RI, some of whom also had clinical radiographic evidence as well. But if we looked specifically at the subgroup of patients with CAA with white matter disease of any type, the prevalence of CAA-RI was as high as 28%.
Advertisement
Advertisement

Exploring new tools and techniques to improve the diagnosis and treatment of concussions.

Training, tools and resources lead to safer, more compassionate care

Cleveland Clinic researchers collaborate with Microsoft to create a product ready for the field
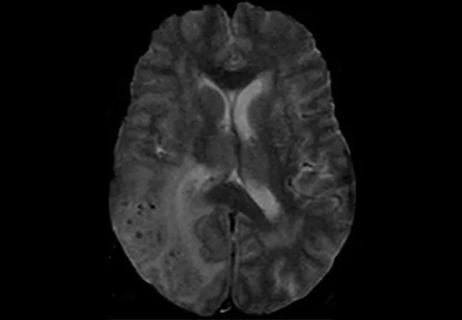
Vigilant MRI evaluation needed for prompt care of potentially reversible inflammation, study finds

Machine learning study associates discrete neuropsychological testing profiles with neurodegeneration
Q&A with Brain Trauma Foundation guideline architect Gregory Hawryluk, MD, PhD

An argument for clarifying the nomenclature

An expert talks through the benefits, limits and unresolved questions of an evolving technology