Growing tumor sparks concern for melanoma

Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/7322b744-2ae2-47c3-b1de-22447146ff85/GettyImages-517380591_jpg)
Mystery Eye
A 16-year-old girl presented to Cleveland Clinic with a growing pigmented lesion of the left iris that was initially noted 5 years earlier. The girl’s visual acuity was 20/20 in the left eye, but her examination was remarkable for a 2- x 1.2- x 1-mm pigmented lesion in the 5 o’clock position with pupillary margin involvement.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
The ongoing growth of the lesion was confirmed by comparing the appearance of the affected eye with earlier photographs of the patient.
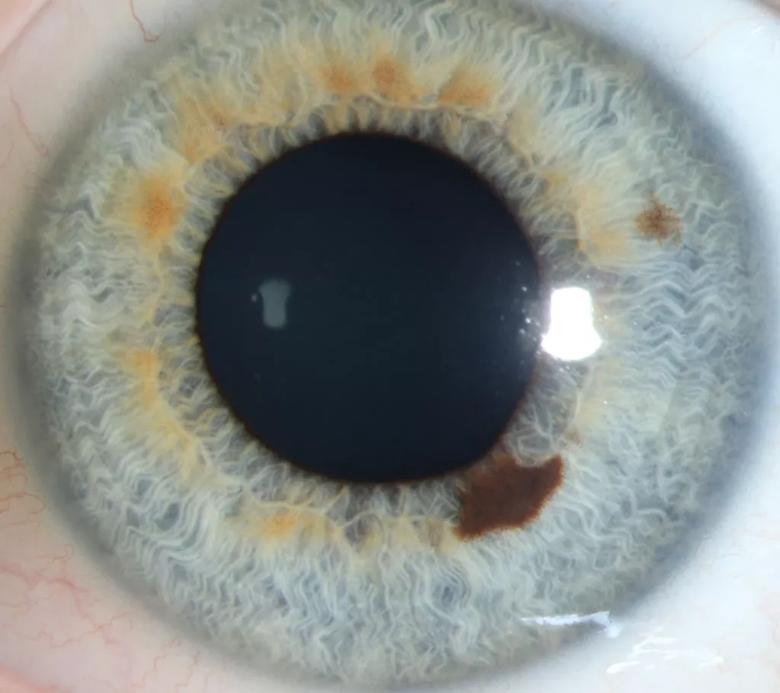
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/516d0f30-0d68-4c4e-ba54-a81033ed01f5/A_-Casey-Thornburg-Preop-photo-1024x910_jpg)
Initial examination reveals a pigmented lesion with pupillary margin involvement.
“The examination findings and changing appearance of the nevus were concerning for iris melanoma, a diagnosis that must be confirmed by biopsy,” explains Arun Singh, MD, Director of the Department of Ophthalmic Oncology in the Cole Eye Institute. “In this case, our principal challenges included removing the tumor completely and with clear margins, protecting the patient’s vision and appearance, reconstructing the pupil and restoring ocular function.”
Following a discussion of treatment options, the patient agreed to undergo an excisional biopsy of the lesion. Using a minimally invasive approach, Dr. Singh performed an iridectomy and pupilloplasty to reconstruct the delicate tissue of the iris and recreate an appropriately sized pupil.
Conventionally, iris resection for a suspected malignancy has involved a large incision in the cornea and sclera and the removal of 25% or more of the iris. This sector iridectomy has been associated with increased risk of wound-related complications, tumor seeding and recurrence, and photophobia due to iris defects.
Approximately 15 years ago, Dr. Singh developed a new technique: small-incision guarded hydroaspiration (SINGH procedure). Instead of one large incision, this approach involves multiple small incisions. After excising the tumor, plastic tubing containing a sodium hyaluronate solution is inserted into the anterior chamber. Using a syringe, the excised lesion is pulled into the tube, where it is isolated and removed safely as the tube is withdrawn from the anterior chamber. This prevents the tumor from being pulled across the wound, possibly shedding cells and seeding the edges of the wound.
Advertisement
The next step, pupilloplasty, restores the iris to a near-normal shape using a suturing slip-knot technique. This restoration of the iris not only repairs the cosmetic defect but also helps prevent photophobia.
“The larger incisions required by conventional techniques led to a number of risks that can now be avoided,” says Dr. Singh. “This minimally invasive approach results in faster healing and much better functional and cosmetic outcomes.”
Histopathology demonstrated a densely pigmented lesion with a fair amount of cytoplasm and no mitotic activity. These findings were consistent with melanocytoma, a benign, deeply pigmented tumor that most commonly arises on or adjacent to the optic nerve head. Such growths most commonly arise on or adjacent to the optic nerve head; however, they often appear on the iris of younger patients.
“We always approach these kinds of cases with caution because the goal is to remove the entire tumor without compromising the patient’s vision,” explains Dr. Singh. “In this particular case, the stakes were somewhat elevated because the patient was so young, and our ability to restore the external appearance of the eye was one of her chief concerns.”
At one-week follow-up, the patient’s eye was healing well, and her visual acuity was 20/20 in the left eye.
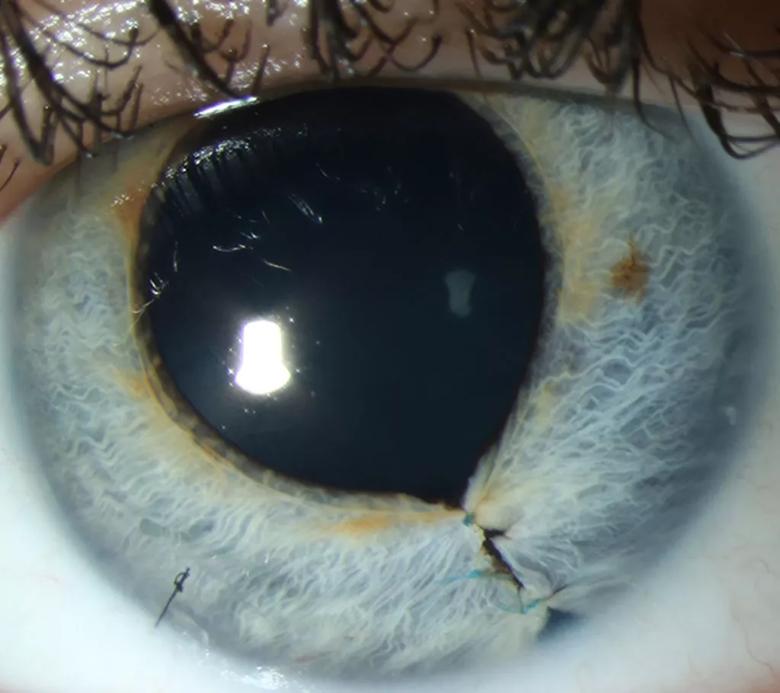
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/4ff4cf35-286d-4eeb-9f8a-6cfaab9b147f/B_-Casey-Thornburg-Post-op-photo-1024x910_jpg)
Stitches are still visible at one-week follow-up, but the patient’s eye appeared to be healing properly.
At three month follow-up, the patient’s visual acuity and ocular pressures were stable, and her eye had a normal cosmetic appearance.
Advertisement
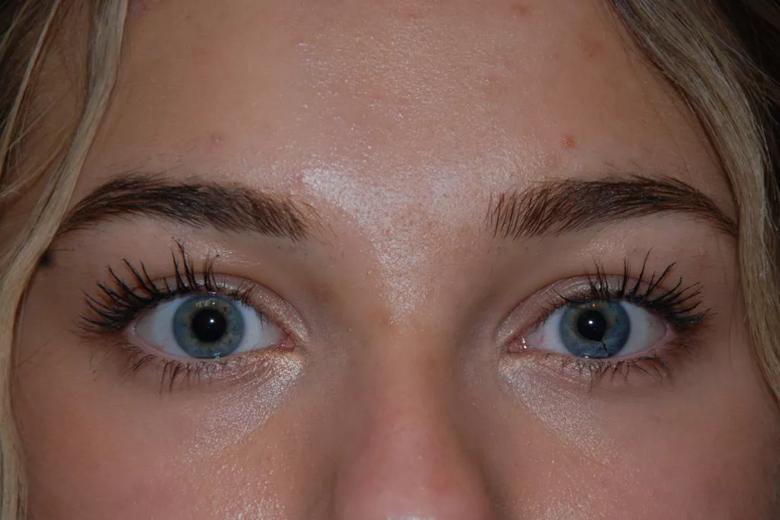
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/83465ec7-cac8-479a-9bdc-b71452bdd304/C_-Casey-Thornburg-external-photo-1024x683_jpg)
Virtually no signs of the tumor were visible three months after the procedure.
“If this patient would have come to us two decades ago, our best option would be to simply watch the lesion while hoping to avoid a big surgery,” says Dr. Singh. “Thanks to the development of these minimally invasive techniques, we were able to treat her safely and with great success.”
Advertisement
Advertisement
Goal-of-care discussions drive earlier hospice access
Clinical trials and de-escalation strategies
Combination therapy improves outcomes, but lobular patients still do worse overall than ductal counterparts
Bringing empathy and evidence-based practice to addiction medicine
Supplemental screening for dense breasts
Combining advanced imaging with targeted therapy in prostate cancer and neuroendocrine tumors
Early results show strong clinical benefit rates
The shifting role of cell therapy and steroids in the relapsed/refractory setting