It's not always a drug reaction
By Alok Vij, MD
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
A 25-year-old man being treated in the hospital for catatonia and flaccid paralysis developed fever and a lobar consolidation, prompting treatment with piperacillin-tazobactam. A dermatology consult was called 3 days later when the patient developed a rash on the forehead, cheeks, chin, and upper trunk, raising concern for a drug-related eruption.
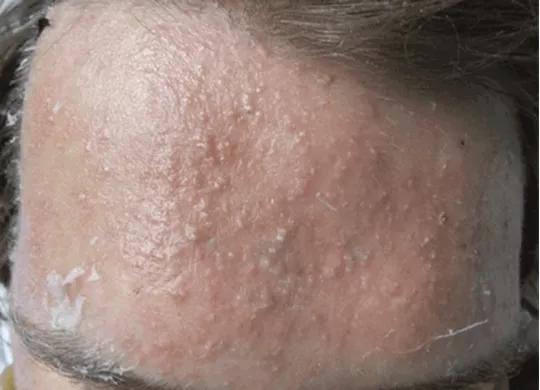
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/c65de6e2-47d4-4c4b-b832-7b9bb72ceace/fung-folic_png)
A brightly erythematous plaque on the forehead with monomorphic pustules was noted on day 3 of piperacillin-tazobactam infusion.
Close examination of the rash revealed bright red plaques studded with sheets of monomorphic pustules. Possible causes other than drug therapy were considered, including folliculitis, acneiform eruption, and pustular psoriasis. Bacterial culture of a pustule was negative, but punch biopsy of a pustule revealed an abundance of round and oval budding yeast forms consistent with Malassezia (formerly called Pityrosporum) “stuffing” the hair follicles and forming cleared spaces in the dermis surrounded by an exuberant lymphohistiocytic infiltrate. Special stains were negative for bacteria and mycelial forms. The clinicopathologic findings were diagnostic of Malassezia folliculitis with formation of dermal abscesses.
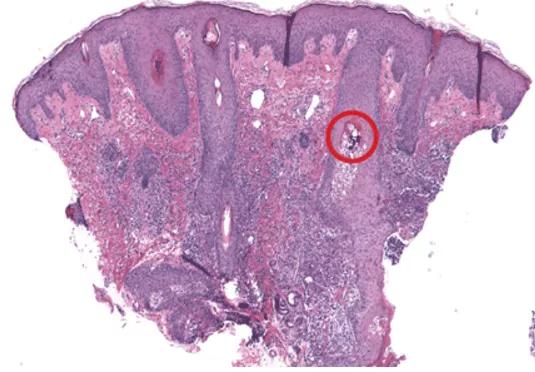
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/a67f0618-2393-4da3-8e26-c40138059be8/fungal-folic2_png)
Histologic sections reveal Malassezia folliculitis and abscess formation within the dermis. The red circle highlights yeast forms within the follicular epithelium (hematoxylin and eosin, × 4).
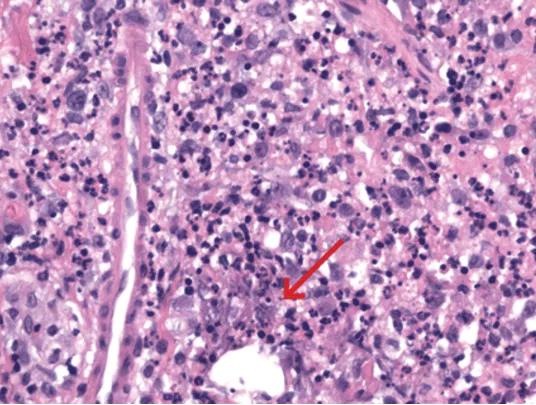
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/3a9d4f77-64d6-4fa5-a125-f8d5dd93a15f/fungal-folic3_png)
Histologic sections of a perifollicular dermal abscess show mixed inflammatory infiltrate including neutrophils and histiocytes centered on cleared-out spaces with small, grey-blue yeast forms (red arrow) (hematoxylin and eosin, x 100).
Advertisement
The patient was treated with intravenous itraconazole 200 mg daily for 7 days and topical benzoyl peroxide 5% gel, with ketoconazole 2% cream for maintenance therapy. The treatment brought improvement of the rash.
The appearance of sterile pustules after starting a new antibiotic raised suspicion for acute localized exanthematous pustulosis, a variant of acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis. It is a serious but uncommon adverse drug reaction, with a frequency of one to five cases per million per year. The eruption of erythematous plaques studded with sterile pustules classically appears 1 to 5 days after starting a drug. Piperacillin-tazobactam has been infrequently reported in association with acute exanthematous pustulosis, but antibiotics in general are among the most commonly reported culprits.
Although our concern for acute localized exanthematous pustulosis was warranted, the morphology and distribution of this patient’s exanthem also raised suspicion of fungal folliculitis, which is more common.
Malassezia folliculitis appears as a monomorphic papular and pustular eruption on the chest, back, and face, as in our patient. Differentiating fungal folliculitis from pustulosis is important, as each condition is treated differently: Malassezia folliculitis is treated with antifungals, and acute localized exanthematous pustulosis is managed with cessation of the offending drug, supportive care, and systemic or topical steroids.
Our experience with this patient was a reminder to consider fungal folliculitis in the differential diagnosis of a pustular eruption, so as to allow appropriate management and to avert discontinuation of potentially life-saving medications.
Advertisement
Dr. Vij is associate staff in the Dermatology and Plastic Surgery Institute.
This article originally appeared in Cleveland Clinic Journal of Medicine.
Advertisement
Advertisement
Family history may eclipse sun exposure in some cases
Consider secondary syphilis in the differential of annular lesions
Persistent rectal pain leads to diffuse pustules

Two cases — both tremendously different in their level of complexity — illustrate the core principles of nasal reconstruction
Stress and immunosuppression can trigger reactivation of latent virus

Low-dose, monitored prescription therapy demonstrates success

Antioxidants, barrier-enhancing agents can improve thinning hair