Apical-height dosing produces outcomes comparable to 5-mm dosing
Small choroidal melanoma needs less radiation to control than once thought. Conventional practice has been to apply radiation therapy to a minimum height of 5 mm, even for tumors smaller than 5 mm, as recommended by the Collaborative Ocular Melanoma Study (COMS). However, new research has found that applying treatment only to the actual height of the tumor, no matter how small — as recommended by the American Brachytherapy Society (ABS) — is just as effective.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
“COMS recommended treating up to 5 mm to prevent undertreatment of these small tumors,” says Arun D. Singh, MD, Director of Ophthalmic Oncology at Cleveland Clinic’s Cole Eye Institute. “But there’s also a risk of overtreatment, especially considering that many of these tumors are too small to biopsy and may not be melanoma at all.”
The more radiation, the higher likelihood of vision loss and other adverse effects. A lower dose may prevent those effects. Now, according to the study recently published in the British Journal of Ophthalmology and coauthored by Dr. Singh, findings show that a lower (apical) dose also offers patients the same excellent outcomes in visual acuity, recurrence, eye survival and metastasis as the higher (5 mm) dose.
Researchers reviewed the charts of 161 consecutive patients with small choroidal melanoma (apical height 1.0-2.5 mm, largest basal diameter < 16.0 mm) treated at Cole Eye Institute from 2004 to 2017. All patients were treated with 85 Gy of iodine-125 episcleral brachytherapy dosed to the apical height of the tumor.
At a mean follow-up of 40 months:
“Outcomes of this low dosing were very, very good, with a local control rate of 99.3%,” says Dr. Singh. “Treating these very small tumors to 5 mm may be unnecessary.”
Validation of apical-dose ABS guidelines for small and medium choroidal melanoma was recently published in Brachytherapy.
Advertisement
In that study, the actual apical-height radiation dosing in more than 300 patients was compared with simulated 5-mm dosing. Mathematical models indicated that patients had received 34% less radiation to their lens, 40% less radiation to their optic disc and 41% less radiation to their fovea than if they had received 5-mm dosing.
Visual acuity of 20/50 or better after three years was found in 56% of these patients. According to estimates, that number would have been only 31% had patients had 5-mm dosing.
With proper treatment, patients diagnosed with small melanoma can expect good local control (Figures 1 and 2) and a negligible risk of mortality. The British Journal of Ophthalmology study indicated overall survival of 97% and metastatic-free survival of 100% at three years.
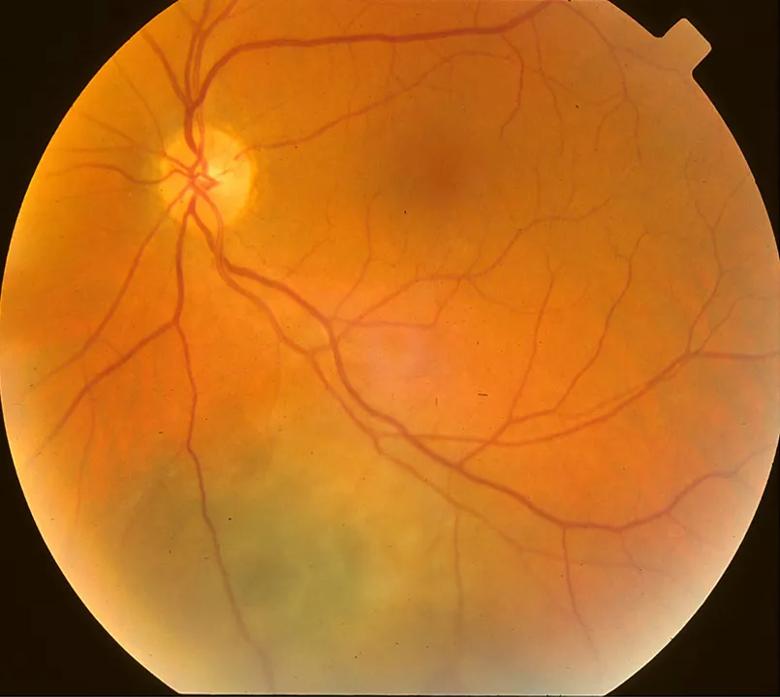
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/729dace2-a8f1-43fe-9058-75b616a06d20/21-EYE-2317711-CQD-Melanoma-Brachytherapy_Arun-Singh_fig1-inset_jpg)
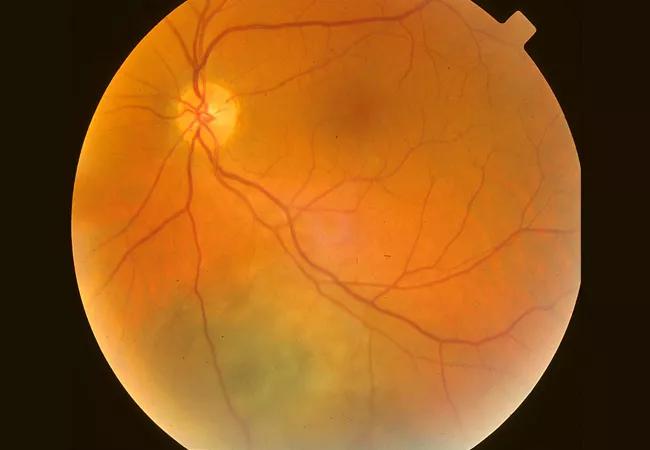
Figure 1. A 60-year-old male presented with a choroidal melanoma (12 mm x 9 mm x 3 mm) close to the optic disc and fovea in the left eye.
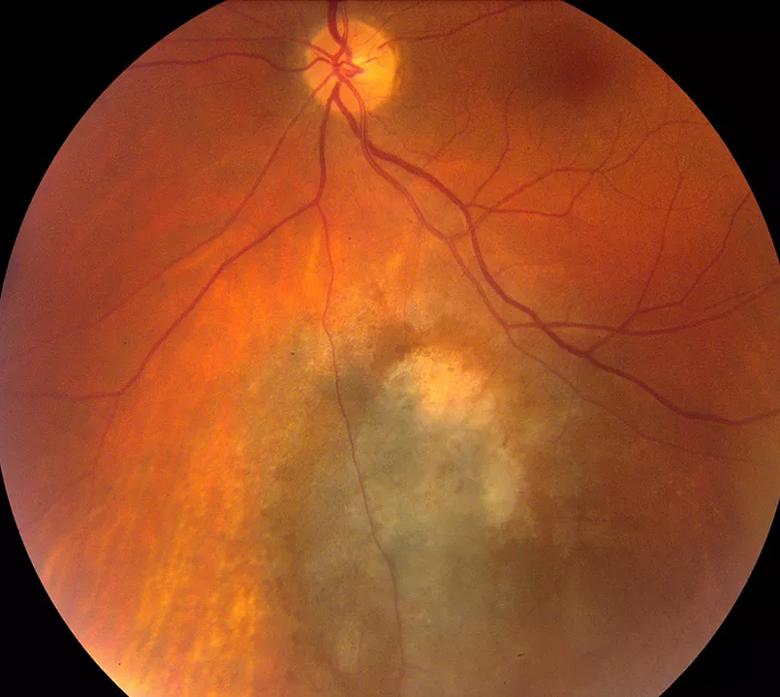
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/f3e78903-d39c-4b06-af82-801f048ba0ed/21-EYE-2317711-CQD-Melanoma-Brachytherapy_Arun-Singh_fig2-inset_jpg)
Figure 2. Ten years following episcleral brachytherapy (prescribed per ABS guidelines), the tumor was regressed with preserved visual acuity (20/20) and absence of metastasis.
“This was the first study to evaluate all four key clinical outcomes, things that patients with choroidal melanoma most want to know: Will the treatment stop the cancer from coming back? Will I keep my eye? Will I preserve my vision? Will I save my life?” says Dr. Singh. “We now can feel confident about answering yes to all those things.”
Advertisement
Advertisement

Radiation therapy helped shrink hand nodules and improve functionality

Standard of care is linked to better outcomes, but disease recurrence and other risk factors often drive alternative approaches

Phase 1 study demonstrates immune response in three quarters of patients with triple-negative breast cancer

Multidisciplinary teams bring pathological and clinical expertise

Genetic variants exist irrespective of family history or other contributing factors

Study shows significantly reduced risk of mortality and disease complications in patients receiving GLP-1 agonists

Structured interventions enhance sleep, safety and caregiver resiliency in high-acuity units

Addressing rare disease and challenging treatment course in an active young patient