Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/d600b117-da24-4bdc-90c9-5f015a770b1e/650x450-Open-Partial-Nephrectomy_jpg)
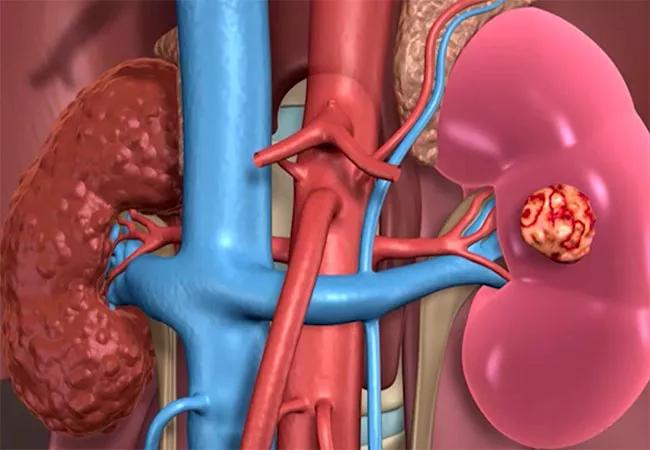
650×450-Open-Partial-Nephrectomy
By Steven C. Campbell, MD, PhD; Moshe C. Ornstein, MD, MA; and Nityam Rathi
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Is there a role for partial nephrectomy (PN) for some patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma (mRCC)? Arguing in favor of this strategy has traditionally been challenging given the limited survival for patients with mRCC, ongoing controversies about cytoreductive or consolidative surgery for mRCC, and the fact that most patients under consideration for such procedures have larger and complex tumors that are not amenable to PN. However, substantial improvements in clinical mRCC outcomes now afford opportunities for novel or unconventional treatment approaches in select patients, including PN for mRCC.
The prognosis for patients with mRCC has improved substantially over the past five years, primarily because of the ascendance of various immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) in combination or along with tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs). Before 2017, when TKIs ruled the roost, five-year overall survival for patients with mRCC was only 14%. In the four-year follow-up for CheckMate 214 (ipilimumab/nivolumab vs sunitinib in treatment-naïve mRCC), 53% of patients who received ipilimumab/nivolumab were still alive at 48 months compared to 43% of patients treated with sunitinib. At this four-year minimum follow-up, a complete response was experienced by 10.7% of patients on nivolumab/ipilimumab versus only 2.6% on sunitinib.1 These results highlight the durability of responses to therapy. Similar findings were noted in patients treated with ICI/TKI combinations.2 For example, in the CLEAR trial of lenvatinib/pembrolizumab versus sunitinib, the response rate (71% vs 36%), complete response rate (16% vs 4%), progression-free survival (23.9 vs 9.2 mo), and overall survival (hazard ratio for death 0.66; p = 0.005) all favored the ICI/ TKI combination.3 In short, patients with mRCC have better long-term outcomes with ICI-based therapy and thus there may be a role for consolidative surgery after an initial response to systemic treatments.4
Advertisement
What would this consolidative approach be? Classically, the strategy has been radical nephrectomy (RN), as most renal primary tumors in patients with mRCC are large and not amenable to PN. However, PN can provide strong local control for many patients, even some with large or complex tumors, and many of these cases can now be performed robotically with a short length of stay and a relatively low risk of major perioperative morbidity.5 The main advantage is better renal function, presuming that there is enough ipsilateral parenchyma to be saved after tumor excision and reconstruction. Does this really matter for patients with lethal cancer? This is a difficult question, but some of these patients may experience prolonged survival and future systemic therapies may rely on good renal function for safe administration. Even with our current regimens, dose reduction and interruption of therapy are more common in patients with chronic kidney disease.6 The ‘‘window of opportunity’’ for PN may be relatively narrow: if the residual renal tumor is really small (< 4 cm), then ablative approaches might be a better choice than PN in the mRCC setting.7
What about addressing the primary tumor upfront with cytoreductive surgery before systemic therapy? The primary tumor is of course the original source of the metastases and its removal might improve outcomes. Removal of the primary tumor in some patients might also substantially reduce the overall burden of disease and improve the likelihood that the metastases will respond to systemic therapies. Previous studies in the cytokine era suggested that cytoreductive nephrectomy would on average extend survival by approximately 50%,8 but more recent studies have called this into question.9 SURTIME and CARMENA suggest that upfront nephrectomy may no longer be indicated, but these studies were underpowered or flawed in other ways.10,11 Most in the field still believe in the cytoreductive paradigm for RCC, presuming very careful patient selection. We believe that patients who meet all of the following criteria should still be considered for cytoreductive surgery: (1) good performance status; (2) mRCC with good or intermediate International mRCC Database Consortium prognostic risk; (3) most of the disease burden ( > 90%) is within the ipsilateral kidney and retroperitoneum and can be readily and safely resected; and (4) metastatic sites should generally not include the brain or liver.12 On the basis of the third criterion, most cytoreductive nephrectomies will require RN, but the literature suggests that approximately 1%–2% of such cases can be considered for PN.13 Perhaps this percentage is somewhat higher in the current era given advances in renal surgery and the better efficacy of systemic therapies, as discussed above.
Advertisement
There is another group of mRCC patients for whom PN may be considered: patients with isolated or oligometastatic disease. Many of these patients should be managed with surgical or focal ablative modalities to all identifiable sites, an aggressive approach that may yield five-year cancerfree status in up to 20%–40% of carefully selected patients. Adjuvant ICI may also be considered in such patients to optimize long-term outcomes, especially considering the benefit seen in the M1-NED subset of KEYNOTE-564.14 How many of these patients would be better off with their primary tumor managed with PN rather than RN or tumor ablation is unknown, but again it is likely to be less than half.
After taking into account all of these considerations, it is likely that only a fraction of patients with mRCC will qualify for PN, with one recent meta-analysis suggesting that this may only apply to approximately 1%–2% of cases.6 Nevertheless, this cohort of patients can and should be carefully considered for PN, taking into account all of the risks and benefits related to their age, comorbidities, and individual functional and oncologic factors.
Editor’s note: This review was published as part of the Open Debate Series in European Urology Open Science. For con and referee perspectives, visit:
Kuusk T, Bex A. Partial Nephrectomy for Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma: Con. Eur Urol Open Sci. 2022 Aug 30;44:81-83. doi: 10.1016/j.euros.2022.07.011.
Minervini A, Grosso AA, Di Maida F. Partial Nephrectomy for Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma: Referee. Eur Urol Open Sci. 2022 Aug 30; 44:78-80. doi: 10.1016/j.euros.2022.08.007.
Advertisement
*This article is published under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0). To access the originally published version, please see: Campbell SC, Ornstein MC, Rathi N. Partial Nephrectomy for Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma: Pro. Eur Urol Open Sci. 2022 Aug 30;44:92-93. doi: 10.1016/j.euros.2022.05.019.
Conflicts of interest: Moshe C. Ornstein has a consulting/advisory role for Pfizer, Eisai, Exelixis, Merck, AVEO, and Bristol-Myers Squibb, participates in speaker bureaus for Exelixis and Bristol-Myers Squibb; has received research funding from Bristol-Myers Squibb and Pfizer; and has received travel and accommodation expenses from Exelixis and Bristol-Myers Squibb. Steven C. Campbell has received an honorarium from Fujifilms for a presentation related to parenchymal volume analysis. Nityam Rathi has nothing to disclose.
References
Advertisement
Advertisement
Goal-of-care discussions drive earlier hospice access
Clinical trials and de-escalation strategies
Combination therapy improves outcomes, but lobular patients still do worse overall than ductal counterparts
Bringing empathy and evidence-based practice to addiction medicine
Supplemental screening for dense breasts
Combining advanced imaging with targeted therapy in prostate cancer and neuroendocrine tumors
Early results show strong clinical benefit rates
The shifting role of cell therapy and steroids in the relapsed/refractory setting