Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/8367edbb-c654-4463-a6f9-7a2324d77e1c/SGRT_jpg)
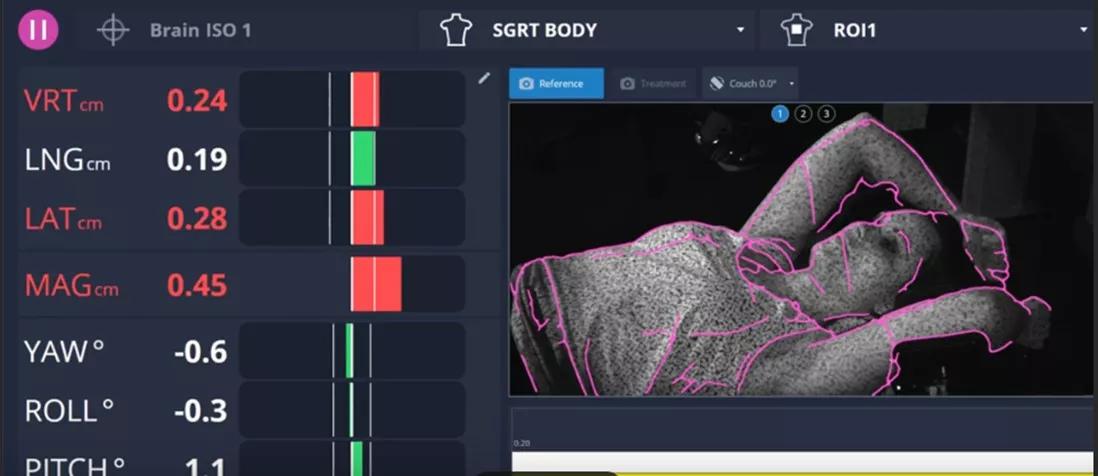
Surface Guided Radiation Therapy
Surface guided radiation therapy (SGRT) uses non-ionizing, 3D camera technology to capture real-time surface data in six degrees of freedom to position and monitor patients during radiation treatments. Unlike other image-guided approaches, it requires no external markers and does not add dose to the patient.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Today the radiation oncology team at Cleveland Clinic Weston Hospital uses the surface-guided approach for initial positioning and continuous monitoring in cases of stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS), stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT), and intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) for all body sites.
“Now that we are using SGRT for all of our patients, we’ve achieved faster setup times, more accurate positioning with less patient shifting, and a reduction in the amount of imaging needed for special procedures,” says Eva Suarez, MD, a board-certified radiation oncologist with Cleveland Clinic’s Maroone Cancer Center, Florida’s only designated Center of Excellence for the most widely used SGRT system in the world.
Dr. Suarez recently presented at the SGRT Community annual conference in June where she shared many of the benefits achieved when using SGRT for deep inspiration breath hold (DIBH) breast treatments. She also shared the findings of an internal study Cleveland Clinic Weston Hospital conducted to evaluate the efficiency and accuracy of surface-guided setup versus tattoo-based imaging setup.
“The SGRT system uses non-ionizing light emitted from specialized camera units in the treatment room to align a patient’s skin surface to the planned position,” explains Dr. Suarez. “This eliminates the need to mark the body as required with traditional laser imaging.”
In the 2020 study, the radiation oncology team alternated setups between SGRT and tattoo-based setup, with 20 patients per arm and each consisting of an equal mix of body sites — breast, chest, abdomen/pelvis, and head and neck. The timer started when the patient was laid on the table to the moment the therapists approved the position for cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT).
Advertisement
“We found patient positioning with tattoo-based setup was 19 seconds faster in head and neck cases but was more accurate with the surface-guided approach,” says Dr. Suarez. “As a result, the need to re-image and reposition head and neck patients was virtually eliminated with SGRT, saving time, CBCT exposure, and patient discomfort.”
While abdomen/pelvis cases were also faster, by 8 seconds, when using tattoo-based setup, surface-guided setup was 10 seconds faster for chest and breast cases. “An added benefit of SGRT in breast cases was eliminating the need for radiation therapists to manually calculate patient coordinates and then compare them to the radiation plan to determine if patient repositioning is needed and how the patient should be moved, as this process is now automated,” says Dr. Suarez.
When the SGRT arm of the study was repeated in 2022, data showed improvement in setup times across all body sites. According to Dr. Suarez, reduced setup times were achieved in part by adjusting the region of interest (ROI) identified for treatment and leaving the patients more uncovered at the time of simulation and treatment, along with other workflow improvements.
“Our SGRT-based setup times are now shorter for abdomen/pelvic, breast, and chest cases, though they remain slightly longer for head and neck cases compared to tattoo-based setups,” she says. “Notably, however, our setup accuracy with SGRT has improved for all sites due to additional experience and is more accurate than tattoo/laser setups, which means fewer repeat CBCTs.”
Advertisement
In her June presentation, Dr. Suarez also explained another important benefit of SGRT specific to patients receiving radiation therapy for breast cancer. Improved accuracy with this approach minimizes radiation-induced cardiac toxicity associated with treatment of the left breast.
“Patients treated for left breast cancer are at an increased risk of radiation-induced coronary artery disease independent of existing, underlying disease,” says Dr. Suarez, noting research has shown the rate of major coronary events increases linearly by 7.4% per unit of ionizing radiation dose to the heart.
Cleveland Clinic Weston Hospital has been using SGRT for all breast cancer cases involving deep inspiration breath hold, including left breast cancer, regional nodal radiation, and accelerated partial breast irradiation (APBI) since 2018.
“We use the DIBH technique in conjunction with SGRT to move the heart away from the breast during therapy and to lessen the impact of respiratory motion,” says Dr. Suarez. “This real-time motion management is a cardiac and pulmonary dose-sparing technique that allows delivery of radiation with sub-millimeter accuracy.”
Dr. Suarez also points out that with the implementation of DIBH with SGRT, her team no longer uses a voluntary breath holding system that requires patients to wear a mouthpiece, nose clip, and video glasses during treatment.
“Eliminating the use of this equipment reduces setup time and improves patient comfort,” says Dr. Suarez. “I have found patients are less nervous and more compliant with DIBH when using SGRT.”
Advertisement
She notes that all SBRT, SRS, IMRT head and neck cases, and single fraction courses are now tattooless at Cleveland Clinic Weston Hospital. “Though not the only benefit, providing tattooless radiation therapy provides a cosmetic benefit and can reduce anxiety for patients, helping them focus on other aspects of their care,” she adds.
Advertisement
Advertisement
Goal-of-care discussions drive earlier hospice access
Clinical trials and de-escalation strategies
Combination therapy improves outcomes, but lobular patients still do worse overall than ductal counterparts
Bringing empathy and evidence-based practice to addiction medicine
Supplemental screening for dense breasts
Combining advanced imaging with targeted therapy in prostate cancer and neuroendocrine tumors
Early results show strong clinical benefit rates
The shifting role of cell therapy and steroids in the relapsed/refractory setting