First retrospective study compares balloon and rigid bronchoplasty
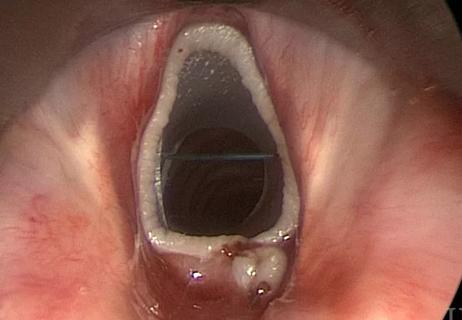
Benign subglottic and tracheal stenosis (SGTS) is a challenging airway disorder that is most often caused by prior intubation or tracheostomy. SGTS can significantly affect quality of life, causing difficulty breathing, wheezing, cough and frequent respiratory infections. While surgery remains the definitive treatment approach, some patients need a minimally invasive strategy or a more urgent intervention. Over the years, endoscopic management has been defined and become an integral part of SGTS therapy.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
The two endoscopic dilation approaches that enlarge the airway – balloon and rigid bronchoplasty –have their advantages and disadvantages. Balloon bronchoplasty may be easier to perform and, due to its progressive inflation, it has been hypothesized that it is more effective at reducing local tissue trauma and promoting organized mucosal healing. But disposable balloons are more costly than rigid bronchoplasty and, in some patients, they may lead to rapid drops in oxygen levels as they block the airway entirely for 30 to 60 seconds.
Rigid bronchoplasty may be preferable for patients with medical conditions, such as COPD, who may need ventilation or oxygenation at all times, and can protect patients from bleeding in certain situations. However, rigid bronchoplasty may lead to more temporary soreness immediately following the procedure; it has also been thought to injure tissue and result in earlier and more severe recurrences.
While both approaches are considered acceptable strategies, no data existed that suggested that one modality was more effective or safer than the other. To obtain this data, the Cleveland Clinic Respiratory Institute Department of Pulmonary, Allergy and Critical Care led the first cohort study to compare balloon and rigid bronchoplasty outcomes. “There has been a lack of evidence and comparative studies to guide practitioners in choosing the optimal endoscopic dilation approach,” says Francisco A. Almeida, MD, MS, a pulmonologist at Cleveland Clinic and study investigator.
Advertisement
The study cohort included 63 patients who were referred to the interventional pulmonary service for evaluation and management of benign SGTS between 2011 and 2020: 38 had balloon bronchoplasty and 25 rigid bronchoplasty. The severity of stenosis was defined according to the Cotton Myer classification system (grade 1: 0% to 50%; grade 2: 51% to 70%; grade 3: 71% to 99%; grade 4: no lumen). The mean stenosis grade was 2.89 and 3.0 in the balloon and rigid bronchoplasty groups, respectively.
Most participants (33 balloon and 16 rigid) had prior intubation; the remainder of cases were idiopathic or had prior tracheal resection or radiation. Nearly all patients (60) had electrocautery to make radial incisions in multiple quadrants of the stenotic lesion before endoscopic dilation. Concomitant treatment also included depomedrol (35 participants) and mitomycin C (20 participants).
At follow-up, balloon and rigid bronchoplasty were shown to be equally effective and safe in the early management of benign SGTS. In addition, no significant difference was found in the mean stenosis grade in the balloon and rigid groups: 1.97 and 2.2 respectively. All patients had an improvement in symptoms and in the airway cross-sectional area following their index endoscopy; no procedural-related complications were observed in either group.
The Cotton Myer grade shift between the index and follow-up procedure in both groups was similar (3 to 1; 3 to 2). Of the three patients in the rigid bronchoplasty group who did not undergo electrocautery incision before dilation, two had an improvement in their stenosis grade, and one had no change at follow-up.
Advertisement
“The data shows that it is safe to use rigid bronchoplasty which can cut costs at institutions where access to balloon dilation is difficult. At the interventional pulmonary service, we feel more confident using rigid bronchoplasty when there is a concern about ventilation or bleeding,” says Dr. Almeida.
The study appears in the Journal of Bronchology & Interventional Pulmonology.
New ablative therapies for SGTS are currently under investigation, including cryotherapy to complement endoscopic dilation and possibly reduce the need for repeated procedures for this airway restenosis. A randomized trial is actively recruiting participants and has the potential to change the treatment landscape of benign SGTS.
“We have been using cryotherapy and based on our early experiences, patients seem to have recurrences less often than with other therapies. We are hoping to do a comparative study and find out if this therapy can help patients and improve outcomes,” says Dr. Almeida.
Advertisement
Advertisement

First five-year prospective study provides valuable data to guide decision-making
A new study indicates high patient satisfaction with the Maddern Procedure, but the technique can be technically challenging for surgeons

Recent breakthroughs have brought attention to a previously overlooked condition

Case study illustrates the potential of a dual-subspecialist approach

Findings show profound muscle loss variance between men and women
New tools and protocols to improve care

Endoscopic balloon dilation during pregnancy helps optimize outcomes
For the first time, risk is shown after accounting for underlying contributions of pulmonary disease