An international consensus statement on a subtype of a rare disease
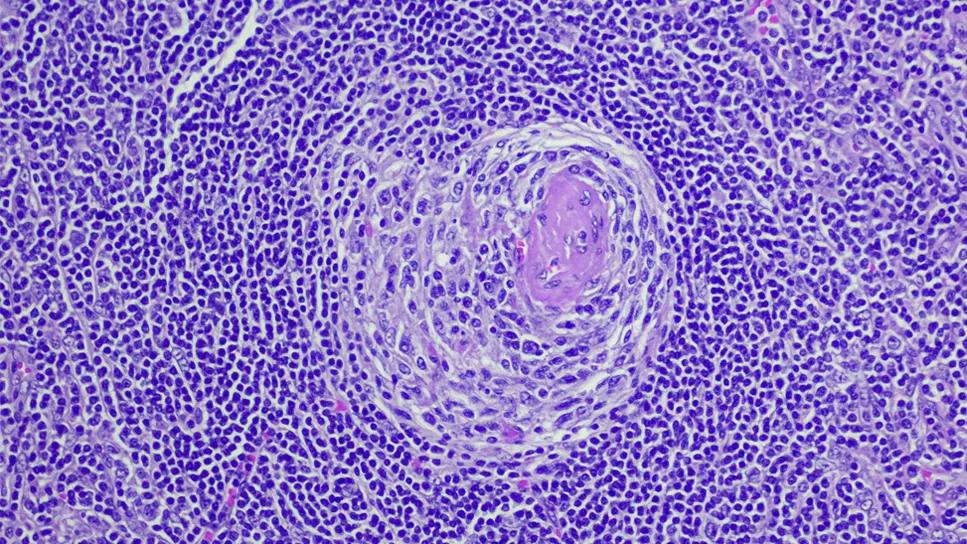
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/4fe0b888-0044-4a6f-b647-d5e789a11409/burden-of-imcd-in-us-mukherjee)
Castleman disease
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Our understanding of Castleman disease (CD) has evolved substantially in recent years, with the establishment of an international registry (ACCELERATE) in 2016 and diagnostic criteria for the idiopathic multicentric version of CD (iMCD) in 2017. A recent international effort published in Blood proposes treatment guidelines for iMCD, an important step forward in improving treatment outcomes in this rare, orphan disease.
Castleman disease comprises a heterogeneous group of lymphoproliferative disorders that affect the lymph nodes and related tissues. Characteristic histopathology features in CD lymph nodes include plasmacytic, hyaline vascular and mixed variants. Unicentric CD involves a single region of enlarged lymph nodes, whereas multicentric CD (MCD) usually affects multiple lymph node regions, a variable degree of systemic inflammatory response, cytopenias and occasionally multiple organ failure. Human herpes virus 8 (HHV-8) has been implicated in the causation of approximately 50 percent of MCD cases, but the etiology of the HHV-8-negative MCD remains unknown – hence the idiopathic label.
Treatment of iMCD presents significant challenges not only because its incidence is 21-25 cases per million person-years but also because of varied clinical severity ranging from patients with mild constitutional symptoms, to some presenting in critical condition with multiorgan failure resulting from a cytokine storm notably including interleukin-6 (IL-6). Subtypes also exist, including TAFRO syndrome, which presents with thrombocytopenia (T), anasarca (A), fever (F), reticulin fibrosis of the bone marrow (R) and organomegaly (O) but with typically normal gamma-globulin levels.
Advertisement
I was part of a working group of 42 experts from 10 countries convened by the Castleman Disease Collaborative Network. Our goal was to establish consensus-, evidence-based treatment guidelines for iMCD in order to help physicians determine the severity of disease and the most appropriate therapeutic option, thereby improving outcomes for patients.
Patients with two of the following five criteria have severe iMCD, which often presents with the TAFRO subtype.
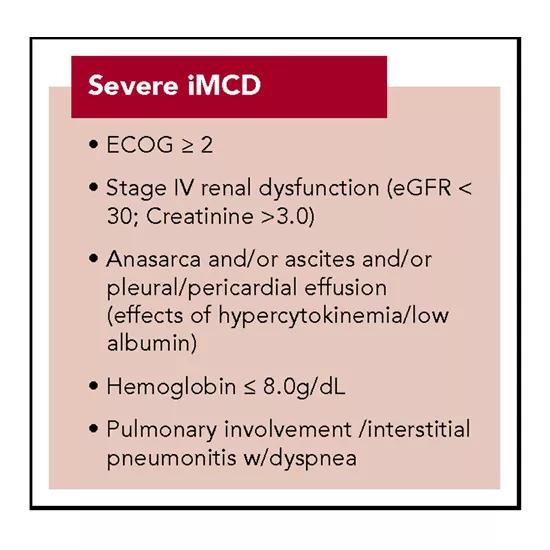
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/6919f618-b93b-4726-9010-70b0168fa010/SevereiMCD_550x550_jpg)
Based on the clinical severity, iMCD should receive different courses of treatment. Our group has proposed the following treatment algorithm:
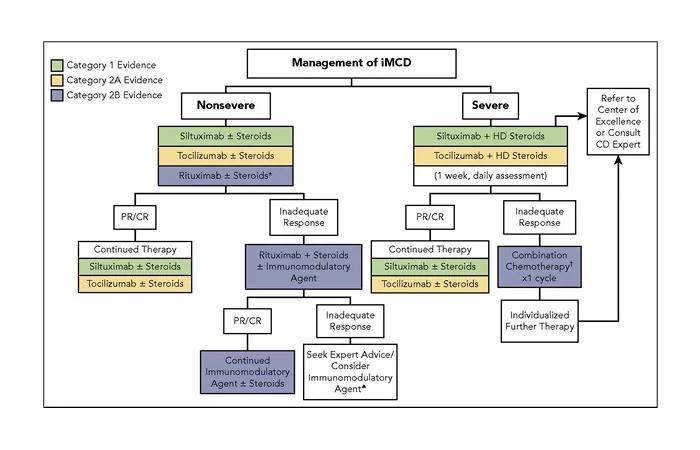
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/85a8912c-4e74-49aa-8938-3ac959d055d3/Management_700x450_jpg)
For all severe cases of iMCD, we recommend consultation with an expert in CD. Cleveland Clinic Cancer Center treats several patients with CD annually. We offer clinical and pathology expertise in diagnosing and managing these cases. We actively participate in Castleman Disease Collaborative Network patient registry and tissue collection efforts to better understand the natural history of these diseases. We also contribute to clinical and translational research to better understand pathogenesis and to develop therapeutic interventions. We are in the process of starting clinical trials in the immediate future.
Finally, we also sought to establish criteria for therapeutic response for iMCD. We based these criteria on evaluation of biochemical, lymph node and symptom response. Nonsevere patients with inadequate responses to therapy should also be referred to centers experienced in the treatment of CD.
Advertisement
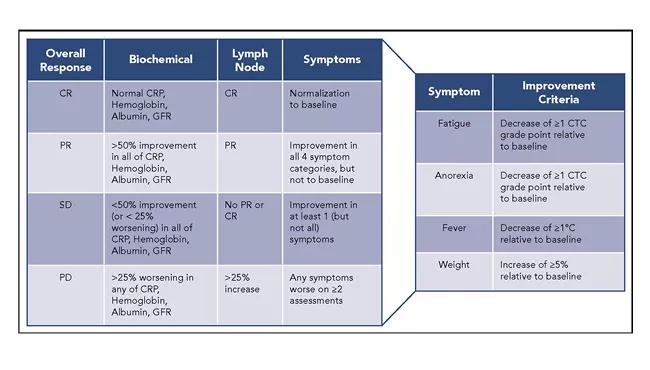
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/f1664588-115e-42f1-a7df-0e1158d08b1c/Response_650x370_jpg)
The establishment of stratification, treatment guidelines and therapeutic response criteria should provide physicians with guidance in choosing appropriate therapies and assessing responses in this rare disease. This is especially important for patients with severe iMCD, who may require rapid combination chemotherapy in order to avoid death.
The addition of these treatment guidelines to recently established diagnostic criteria takes us one step closer to better outcomes for our patients.
Dr. Mukherjee is staff in the Department of Hematology and Medical Oncology and is an expert in rare hematologic conditions and cancers, including Castleman disease.
Feature image: Photomicrograph of the excised lymph node mass showing a stroma-rich variant of hyaline-vascular Castleman’s disease with hyperplastic lymphoid follicles (arrowheads), regressed hyalinized germinal centers (thin arrow) and penetrating capillaries (thick arrow; hematoxylin and eosin; magnification, 100 ×). Republished with permission from Rice BL, Parambil JG, Farver CF, et al. Concomitant Castleman’s disease and sarcoidosis. Am J Med Sci. 2011;341(3)257-259.
Advertisement
Advertisement
Clinical trials and de-escalation strategies
Combination therapy improves outcomes, but lobular patients still do worse overall than ductal counterparts
Bringing empathy and evidence-based practice to addiction medicine
Supplemental screening for dense breasts
Combining advanced imaging with targeted therapy in prostate cancer and neuroendocrine tumors
Early results show strong clinical benefit rates
The shifting role of cell therapy and steroids in the relapsed/refractory setting
Radiation therapy helped shrink hand nodules and improve functionality