Cutaneous complications common post-transplant
As use of lung transplant (LT) becomes more common, pulmonologists should be aware of post-transplant dermatologic complications. In a recent pictorial review in CHEST, Atul Mehta, MD, staff in the Department of Pulmonary Medicine, and colleagues describe the pathogenesis, epidemiological characteristics and clinical manifestations of dermatologic complications found in lung transplant recipients. The below images focus on actinic keratosis (AK) or solar keratosis.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
AK is caused by the abnormal proliferation of keratinocytes due to UV radiation. This premalignant skin lesion can potentially become squamous cell carcinoma (SCC). Classic AK appears as large, scaly, thin, erythematous papules; hypertrophic AK is thicker and sometimes manifests with cutaneous horns. Atrophic AK lacks scaling, and in pigmented AK, the scaly papules are pigmented. Actinic cheilitis and conjunctival AK are also possible.
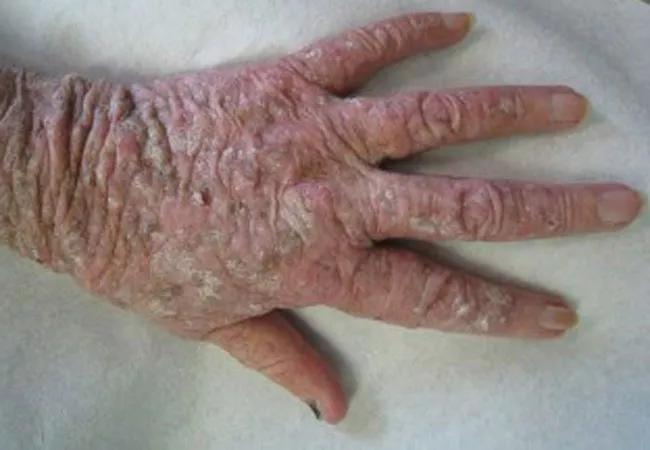
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/c498453f-f736-4e14-a3d2-3724c74d382a/19pul073-fig-1_650x450_jpg)
The patient above experienced photodamage and severe actinic keratosis. The image below shows voriconazole-induced phototoxicity.
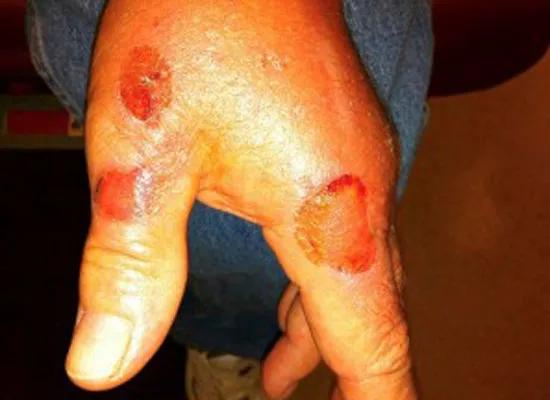
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/9dacf4cf-2db2-40d0-99d3-b187d574eb65/19pul073-fig-2_550x400_jpg)
The reported prevalence of AK in patients with LT is high, and increased risk of malignancy is a major concern. Because AK can transform into SCC, patients with higher risk should be screened regularly and educated about the importance of skin surveillance and proper application of UV protection including sunscreen application, sun-safe clothing and avoidance.
Dr. Mehta notes that he urges any transplant pulmonologist to incorporate counseling, treatment, education and referral to dermatology into their post-transplant visits. Early treatment for suspicious lesions is crucial, especially in this population.
The pictorial review also examines herpes virus, Kaposi sarcoma, malignant melanoma and post-transplant squamous cell carcinoma.
Images are republished with permission from CHEST.
Advertisement
Advertisement
Family history may eclipse sun exposure in some cases
Consider secondary syphilis in the differential of annular lesions
Persistent rectal pain leads to diffuse pustules
Two cases — both tremendously different in their level of complexity — illustrate the core principles of nasal reconstruction
Stress and immunosuppression can trigger reactivation of latent virus
Low-dose, monitored prescription therapy demonstrates success
Antioxidants, barrier-enhancing agents can improve thinning hair
A hybrid approach