Why precise diagnosis matters
By Rula Hajj-Ali, MD, and Leonard Calabrese, DO
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
An extensive workup is required to rule out primary angiitis of the central nervous system (PACNS), a devastating disease in which exclusive inflammation and destruction of vessels in the CNS cause progressive, debilitating neurological deficits. Prognosis improves greatly with proper treatment, but with nonspecific tests and many confounding mimics, diagnosis can be tricky.
One of PACNS’s closest mimics is reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome (RCVS). Distinguishing between RCVS and PACNS is critical because the treatment protocol is so vastly different. Misdiagnosing PACNS as RCVS can deprive a patient of medications that prolong survival and improve outcomes. We offer a brief overview of differences in the results of diagnostic tests below. See this post for differences in clinical presentation. A future post will focus on management.
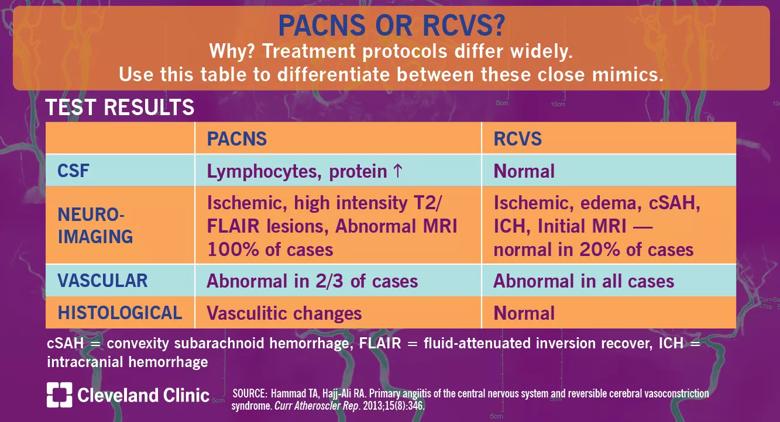
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/1e15f7c7-253c-4e7f-a6bd-3aa092789f9b/18-RHE-1077-PACNS-or-RCVS-Visual-Abstract-1200x650pxl_04_10_2018_02b_jpg)
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) analysis is essential in the differentiation between PACNS and RCVS and in excluding infections and malignancies. PACNS cases will show lymphocyte-predominant pleocytosis, elevated protein levels and normal glucose levels. In RCVS, normal CSF is the rule, unless the CSF is contaminated by subarachnoid or parenchymal hemorrhages.
Neuroimaging in PACNS cases is always abnormal. Ischemic infarctions are the most common lesions and are often multiple and bilateral. Nonspecific high-intensity lesions are also common in PACNS as visualized on T2-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) with a fluid-attenuated recovery sequence. RCVS is usually but not always abnormal on neuroimaging. Upon initial presentation, 20 percent of patients may have normal neuroimaging. Edema is a common finding, and computed tomography can show convexity subarachnoid hemorrhage or intracranial hemorrhage, both more common in RCVS.
Advertisement
Cerebrovascular imaging is always abnormal in RCVS and usually abnormal in PACNS. Stenosis and dilation visualized by direct or indirect angiography are not specific to either condition. Involvement of vascular beds in RCVS is usually bilateral and affecting multiple territories which may not be true in PACNS. Further, the cerebrovascular abnormalities in RCVS are dynamic and improve over time.
In the lab, both PACNS and RCVS will test normal for C-reactive protein, erythrocyte sedimentation rate, complete blood count and complete metabolic profile. Serologic tests for rheumatologic, autoinflammatory, autoimmune, malignant and infectious diseases are negative in PACNS and RCVS.
Advances in neuroimaging such as the use of 3-Tesla high resolution MRI specifically to assess the vessel wall hold promise in differentiating between both entities. The vessel walls in RCVS do not show enhancement while in PACNS enhancement occurs.
Brain biopsy is the often-feared, underutilized gold standard in the diagnosis of PACNS. An open-wedge procedure is considered low risk, and an experienced neurosurgeon working as part of a multidisciplinary team can perform a biopsy with greater than 80 percent sensitivity and 90-100 percent specificity. Finding inflammation in the vessel wall is characteristic of PACNS, while brain biopsies are normal in RCVS.
Dr. Hajj-Ali is Associate Director of the Center for Vasculitis Care and Research in the Department of Rheumatic and Immunologic Diseases. Dr. Calabrese is Director of the R.J. Fasenmyer Center for Clinical Immunology.
Advertisement
Advertisement
Advertisement
Ethical guidance provides guardrails so medical advances benefit patients
OCEANIC-STROKE results represent long-sought advance in secondary stroke prevention
Two studies from Cleveland Clinic may help advance the technology toward broader clinical use
Distinct MRI signature includes lesions beyond the corpus callosum, features predictive of vision and hearing loss
An argument for clarifying the nomenclature
An expert talks through the benefits, limits and unresolved questions of an evolving technology
Recommendations on identifying and managing neurodevelopmental and related challenges
Phase 2 trials investigate sitagliptin and methimazole as adjuvant therapies