One of the largest series in adults finds outcomes comparable to those in children
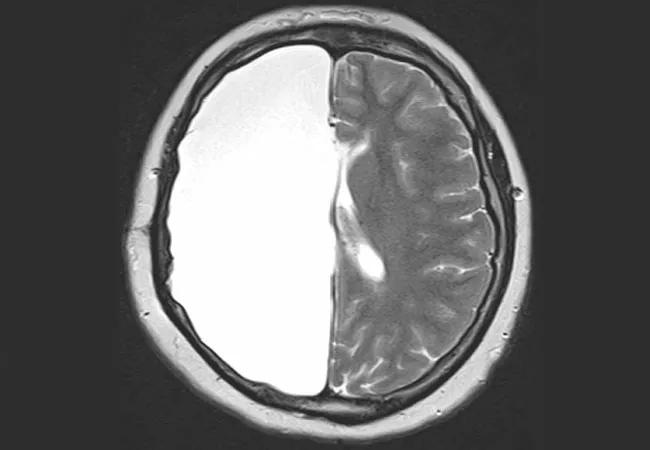
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/42a1e48f-f1b4-424c-af59-7c068fb12779/19-NEU-6053-hemispherectomy-650x450_jpg)
hemispherectomy
Long-term freedom from seizures and functional outcomes for adults following hemispherectomy are similar to those reported in patients undergoing the surgery during infancy or childhood. So finds a newly reported review of Cleveland Clinic experience with the procedure in adults, which also revealed prognostic indicators of postoperative outcomes.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
“Hemispherectomy is rarely performed after childhood for refractory epilepsy, when it is feared that risks to language, cognition and motor skills may be too high,” says Cleveland Clinic epileptologist Ahsan N. V. Moosa, MD, primary investigator of the study, which was published in Epilepsia (2019 Nov 2 [Epub ahead of print]) and presented on December 7 at the American Epilepsy Society’s 2019 annual meeting. “But we found that this surgery is also safe and effective after age 16, and we identified factors that can inform preoperative counseling.”
When indicated for refractory epilepsy secondary to a large, unilateral hemispheric lesion, hemispherectomy is usually performed in infancy or childhood to take advantage of the time of optimal neural plasticity. Long-term seizure freedom rates following hemispherectomy in childhood are reported to be about 66% to 80%. Because the procedure is so uncommonly performed in older age groups, less is known about immediate outcomes in this setting, and no longitudinal data were available.
This study reviewed 47 consecutive patients who were at least 16 years old when they underwent hemispherectomy between 1996 and 2016 at Cleveland Clinic’s Epilepsy Center. Preoperatively, 93% of patients had seizures either daily or weekly.
The mean age at surgery was 26.4 years, with age cohorts breaking down as follows:
Most patients acquired their epileptogenic lesion well before the surgery, as follows:
Advertisement
Nearly half of etiologies (47%) were attributed to perinatal stroke. Other causes included malformations of cortical development (15%) and other acquired conditions (30%), including Rasmussen encephalitis, trauma and encephalitis.
The following outcomes were found over mean postsurgical follow-up of 5.4 years (median, 2.9 years):
Advertisement
Multivariate analysis revealed two factors associated with seizure recurrence after hemispherectomy:
Although acute postoperative seizures are often regarded as transient and attributable to perioperative stresses, Dr. Moosa notes that they may be a predictor of poorer prognosis, especially in patients with severe epilepsy preoperatively. None of the patients who had Engel class I outcomes showed epileptic activity in the contralateral hemisphere postoperatively.
Nevertheless, Dr. Moosa emphasizes, bilateral or generalized epileptiform discharges seen on preoperative EEG should not disqualify a patient from consideration for hemispherectomy; such features were found in one-third of the patients who became seizure-free postoperatively.
In general, better preoperative motor function — and lack of cerebral peduncle atrophy on preoperative MRI (which was usually associated with it) — correlated with worsened motor function postoperatively. This was true for both ambulatory status and hand function.
According to Dr. Moosa, it is perhaps not surprising that outcomes of adult hemispherectomy were similar to those of hemispherectomy performed in childhood because most of the adult patients in this cohort experienced their brain injury in childhood.
“One might regard most of these patients as pediatric hemispherectomy candidates who had their surgery in adulthood,” he explains. “Our results suggest that neural plasticity and language transfer across hemispheres are determined by the age at brain injury, not by when surgery is performed.”
Advertisement
Advertisement
A case study in pairing imaging acumen with subspecialty expertise to yield answers and symptom relief
Guidance from the largest cohort of SEEG-confirmed insular epilepsy patients reported to date
Ethical guidance provides guardrails so medical advances benefit patients
OCEANIC-STROKE results represent long-sought advance in secondary stroke prevention
Two studies from Cleveland Clinic may help advance the technology toward broader clinical use
Distinct MRI signature includes lesions beyond the corpus callosum, features predictive of vision and hearing loss
An argument for clarifying the nomenclature
An expert talks through the benefits, limits and unresolved questions of an evolving technology