New study aims to assess a potential new indication for the technology
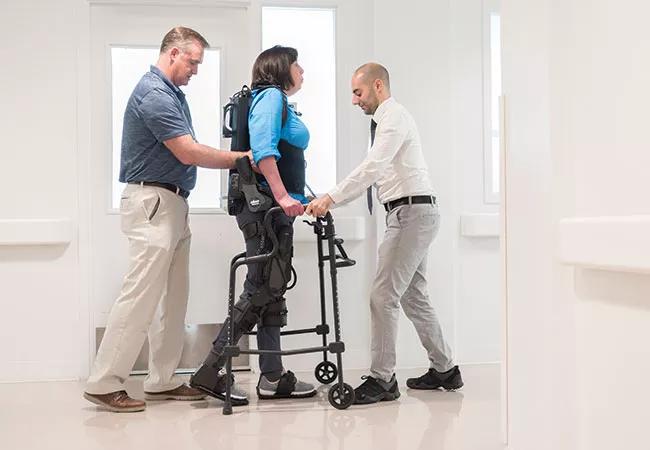
Cleveland Clinic is launching a pilot study designed to explore the extension of powered exoskeletons to a new application: assistance with gait rehabilitation in people with multiple sclerosis (MS).
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
“Powered exoskeletons are currently approved by the FDA to aid rehabilitation of patients with spinal cord injury and post-stroke hemiplegia,” says Francois Bethoux, MD, Chair of Cleveland Clinic’s Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation and principal investigator of the new study. “To our knowledge, there has been only one small study to date in the United States that has assessed the use of these devices in MS rehabilitation. We plan to build on that experience in our investigation, with the aim of gauging the feasibility and safety of this technology for gait training in individuals with relapsing or progressive MS who experience severe mobility limitations.”
The new investigation will be an uncontrolled pre-/post-intervention study using the EksoGT™ powered exoskeleton for eight weeks of gait training in up to 15 participants with MS, with the goal of study completion by at least five participants.
One prior reported study of a powered exoskeleton in MS (Kozlowski et al, Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2017;98:1300-1307) enrolled 13 patients with MS and Expanded Disability Status Scale (EDSS) scores of 5.5 to 7.0. That pilot study used the ReWalk® Rehabilitation 2.0 exoskeleton. Five of the 13 enrollees were able to tolerate the device, with skin issues being the most common adverse event. Those who used the exoskeleton consistently demonstrated qualitative improvements in sitting, standing and walking posture.
The new Cleveland Clinic pilot study will be one of the first assessments of the EksoGT exoskeleton in the setting of MS. This adjustable device consists of a fitted metal brace supporting the legs, feet and torso (see patient photo above). It manipulates the patient’s legs and waist to facilitate standing up, walking on a level surface and sitting down. Battery-powered motors drive the knee and hip joints, with the patient gaining support for balance and body positioning through use of a cane, a walker or crutches. A trained physical therapist operates the device and monitors the patient to ensure proper balance. The exoskeleton can be operated in various modes to trigger steps in different scenarios to meet patients’ differing needs and ability levels.
Advertisement
To be eligible for the study, individuals must have MS with moderate to severe walking disability, defined as an EDSS score of 5.5 to 7.5. Rehabilitation treatment involves three 60-minute sessions per week for eight weeks. Sessions consist of stretching, overground gait training and gait training with the exoskeleton device.
Patients are assessed at baseline, at the end of the eight-week treatment course and at follow-up evaluation four to six weeks after treatment ends. An additional assessment by phone several weeks into the treatment course is done to review adverse events, treatment adherence and any participant concerns.
Safety evaluation involves assessment for adverse events during or between treatment sessions, with special vigilance for falls and musculoskeletal pain, along with gauging of pain severity. Acceptability is assessed by the assistive device subscale of the Quebec User Evaluation of Satisfaction with Assistive Technology, version 2.
Feasibility assessment is based on the share of patients who complete at least 75% of the treatment sessions and how many patients drop out of the study. Efficacy is evaluated in terms of the following, all assessed without the patient wearing the device:
“Our aim with this pilot study is to assess the feasibility and safety of EksoGT exoskeleton use in individuals with MS and to collect preliminary efficacy data on gait and walking outcomes,” explains Dr. Bethoux, who also serves as Director of Rehabilitation Services in Cleveland Clinic’s Mellen Center for Multiple Sclerosis Treatment and Research. “Encouraging findings would support the design of a larger clinical trial of this device for gait training in people with MS.”
Advertisement
Advertisement

An argument for clarifying the nomenclature

An expert talks through the benefits, limits and unresolved questions of an evolving technology

Recommendations on identifying and managing neurodevelopmental and related challenges

Phase 2 trials investigate sitagliptin and methimazole as adjuvant therapies

Aim is for use with clinician oversight to make screening safer and more efficient

Rapid innovation is shaping the deep brain stimulation landscape

Study shows short-term behavioral training can yield objective and subjective gains

How we’re efficiently educating patients and care partners about treatment goals, logistics, risks and benefits