Radiation planning technique safely reduces toxicity
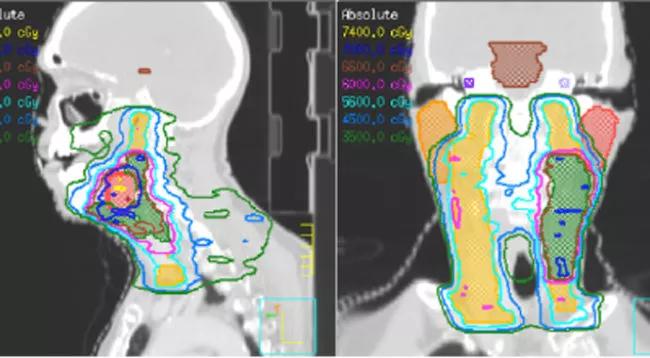
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/ed838ace-a859-4050-9bcf-4ef824bc8868/RTOG_690-x-380-650x358-1_jpg)
RTOG_690-x-380-650×358
Researchers from Cleveland Clinic and OhioHealth have published results from a first-in-human trial evaluating feasibility of Temporally Feathered Radiation Therapy (TFRT), which is designed to reduce the toxicity of radiation treatment.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
The research, appearing in Radiotherapy & Oncology, proved TFRT’s feasibility in clinical workflow. Additionally, assessments of treatment toxicities and radiation dosage comparisons to a standard radiotherapy plan were described.
TFRT is a novel technique for the planning and optimization of radiotherapy that considers the nonlinear aspects of normal tissue repair to manage toxicity. The technique is designed to reduce radiation-induced toxicities by optimizing the time through which radiation is delivered and consequently improves normal tissue recovery. Radiation-induced toxicity is a major contributor to impacting a patients’ quality of life and often a dose-limiting factor in the treatment of cancer with radiation therapy.
“We are excited that the complex TFRT technique, which uses current planning systems, was able to be delivered safely and in a standard clinical workflow,” said Jacob G. Scott, M.D., DPhil, a Cleveland Clinic radiation oncologist and the inventor of TFRT. “A larger trial with toxicity as the primary endpoint will allow us to truly study the efficacy of the approach. Collaboration will be important as we work to integrate TFRT into planning systems to expand automation and wider adoption into clinical practice.”
In this study, five patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma were treated with TFRT. The primary endpoint was feasibility of TFRT planning as defined by radiation start within 15 days of treatment planning. Secondary endpoints included estimates of toxicity.
Advertisement
The primary endpoint was met when patients were successfully treated with TFRT techniques without causing delays in radiation commencement. For patients who received TFRT, the median time from treatment planning to radiation start was 10 business days – not outside of standard timelines. The average time required for radiation planning was six days. The organs feathered included oral cavity, each submandibular gland, each parotid gland, supraglottis, and posterior pharyngeal wall. There were no significant deviations from standard planning, and toxicity was no more than expected – but we expect a larger trial to show reductions in toxicity without effecting cure rates.
“Radiation oncologists and physicists have made amazing advances in shaping the radiation dose to organs and tissue near a patient’s tumors, leading to effective treatments with less toxicity,” added Shireen Parsai, M.D., a radiation oncologist at OhioHealth who led this research during her residency at Cleveland Clinic. “TFRT takes advantage of the differential repair of tumors vs. healthy tissue by modulating how the dose is delivered to nearby tissue over time. This approach gives normal tissue more time to heal, allowing us, in theory, to deliver the same curative doses of radiation with less detriment to the patient’s quality of life.”
Advertisement
Advertisement
Goal-of-care discussions drive earlier hospice access
Clinical trials and de-escalation strategies
Combination therapy improves outcomes, but lobular patients still do worse overall than ductal counterparts
Bringing empathy and evidence-based practice to addiction medicine
Supplemental screening for dense breasts
Combining advanced imaging with targeted therapy in prostate cancer and neuroendocrine tumors
Early results show strong clinical benefit rates
The shifting role of cell therapy and steroids in the relapsed/refractory setting