75% median reduction in seizures observed over 9 years of treatment
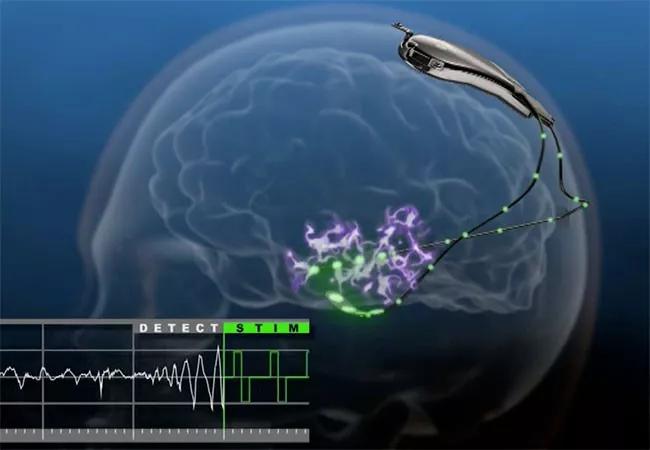
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/475fb0b9-6680-4640-a348-37865475f5f7/19-NEU-320-RNS-neurostimulation-650x450_jpg)
19-NEU-320-RNS-neurostimulation-650×450
Long-term responsive neurostimulation (RNS) therapy with the NeuroPace RNS® System is safe and associated with reductions in seizures that grow cumulatively over time, according to results of a nine-year prospective multicenter study of the device in patients with medically refractory epilepsy.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
The findings, from the Long-Term Treatment Trial of the RNS System, were reported in a platform presentation May 8 at the American Academy of Neurology’s 2019 annual meeting.
“In addition to further demonstrating that responsive neurostimulation is a safe and effective treatment, this study shows that its benefits keep accruing over time as therapy continues,” says study presenter and principal investigator Dileep Nair, MD, Section Head of Adult Epilepsy in Cleveland Clinic’s Epilepsy Center.
The RNS device is an implantable, closed-loop neuromodulation system that was approved by the FDA in 2013 to treat medically refractory partial-onset seizures in adults.
Dr. Nair’s presentation reflected the complete follow-up experience of 33 epilepsy centers participating in the study, which followed two previous studies that led to FDA approval of the RNS System.
Of the 256 patients participating in those earlier studies — a two-year feasibility study (n = 65) and the two-year randomized pivotal trial of the device (n = 191) — 230 continued for an additional seven years of open-label prospective follow-up in the Long-Term Treatment Trial. All were adults with medically intractable focal-onset seizures localized to one or two seizure foci.
These 230 patients had the following characteristics at baseline:
Approximately one-third of the patients had failed vagus nerve stimulation, and another third had been unresponsive to prior epilepsy surgery. “These patients had a very high seizure burden and represented some of the most intractable epilepsy cases any practice will see,” observes Dr. Nair.
Advertisement
Patients were followed for a total of nine years, representing 1,895 patient-years of follow-up. Key efficacy findings from the analysis included the following:
Additionally, comprehensive neuropsychological testing revealed no significant worsening in any of 14 measures assessed, as well as statistically significant improvements in verbal memory, particularly among patients with RNS in the mesial temporal lobe, and in naming ability among patients with RNS in the neocortex.
“We found that patients’ cognition and quality of life were maintained or improved throughout nine years of follow-up,” Dr. Nair observes.
There were 16 patient deaths during the nine-year follow-up, including two from suicide, one due to status epilepticus, four from definite SUDEP (sudden unexplained death in epilepsy), two from probable SUDEP and three from possible SUDEP.
No stimulation-related side effects were reported in the long-term study, which Dr. Nair says is likely due to the practice of adjusting stimulation parameters in the clinic. “We can tell right away, during the clinic visit, whether there are any stimulation-elicited effects, and we can adjust for them accordingly.”
Advertisement
He adds that RNS offers another potential benefit: “This technology provides clinicians with serial neural recordings that can be used to personalize therapy.”
Dr. Nair discloses that he is a paid consultant to NeuroPace, which markets the RNS System.
Image at top courtesy of NeuroPace, Inc.
Advertisement
Advertisement
A case study in pairing imaging acumen with subspecialty expertise to yield answers and symptom relief
Guidance from the largest cohort of SEEG-confirmed insular epilepsy patients reported to date
Ethical guidance provides guardrails so medical advances benefit patients
OCEANIC-STROKE results represent long-sought advance in secondary stroke prevention
Two studies from Cleveland Clinic may help advance the technology toward broader clinical use
Distinct MRI signature includes lesions beyond the corpus callosum, features predictive of vision and hearing loss
An argument for clarifying the nomenclature
An expert talks through the benefits, limits and unresolved questions of an evolving technology