Locations:
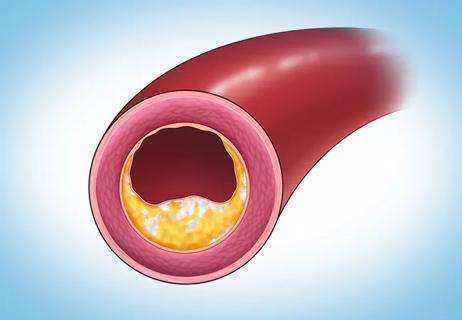
Observational study supports adding CAC score to traditional risk factors for precision medicine approach
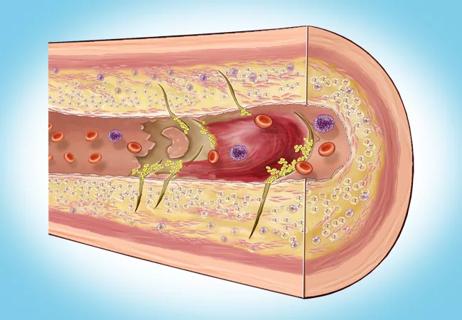
Inflammation found more predictive of events than LDL-C in pooled analysis of RCTs

Randomized controlled study undercuts unsubstantiated ‘heart health’ claims

Honored for multiple discoveries in atherosclerosis, including role of the gut microbiome
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Advertisement
Advertisement