How to tell the difference and why it matters
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/ce776106-c038-424f-a506-0796e05a2f34/16-RHE-871-Calabrese-Hero-Image-650x450pxl_jpg)
16-RHE-871-Calabrese-Hero-Image-650x450pxl
By Rula Hajj-Ali, MD, and Leonard Calabrese, DO
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Primary angiitis of the central nervous system (PACNS) is a devastating disease in which exclusive inflammation and destruction of vessels in the CNS cause progressive, debilitating neurological deficits. Prognosis improves greatly with proper treatment, but with nonspecific tests and many confounding mimics, diagnosis can be tricky.
One of PACNS’s closest mimics is reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome (RCVS). The distinguishing characteristic of this group is the “thunderclap” headache — sudden, severe and with or without neurological deficits. Originally, rheumatologists treated RCVS as benign angiopathy of the CNS. In 2007, Calabrese et al set forth RCVS as a concept encompassing several syndromes with unifying clinical, laboratory and radiologic features. The clinical features and diagnostic criteria described in that paper have been considered the standard since its publication.
Distinguishing between RCVS and PACNS is critical because the treatment protocol is so vastly different. Misdiagnosing PACNS as RCVS can deprive a patient of medications that prolong survival and improve outcomes. These conditions are close mimics, but the astute clinician has several tools in her armamentarium to distinguish between them. We offer a brief overview of differences in clinical presentation below. Future posts will discuss differences in test results and management.
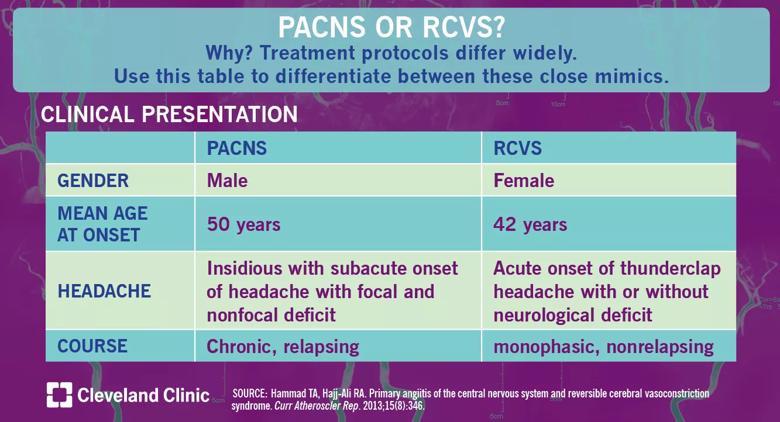
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/de9ba078-ae7c-41ee-895d-735825fb3f39/18-RHE-1077-PACNS-or-RCVS-Visual-Abstract-1200x650pxl_04_10_2018_01b_jpg)
Patients with PACNS are more commonly male and trend older with a mean age of 50 years at onset, while patients with RCVS are more likely to be female and a bit younger. Patients with both conditions almost always present with headaches, but the differences in onset and type are important to distinguish between the mimics. Patients with PACNS experience subacute onset of headaches with focal and nonfocal deficits; a patient with sudden-onset, severe, “thunderclap” headaches should be considered for RCVS whether or not neurological deficits are present. RCVS is monophasic, but patients with PACNS will experience these symptoms chronically.
Advertisement
When patients present with these symptoms, diagnostic tests can help eliminate the mimics and narrow towards a precise diagnosis.
Dr. Hajj-Ali is Associate Director of the Center for Vasculitis Care and Research in the Department of Rheumatic and Immunologic Diseases. Dr. Calabrese is Director of the R.J. Fasenmyer Center for Clinical Immunology.
Advertisement
Advertisement
Guidance from the largest cohort of SEEG-confirmed insular epilepsy patients reported to date
Ethical guidance provides guardrails so medical advances benefit patients
OCEANIC-STROKE results represent long-sought advance in secondary stroke prevention
Two studies from Cleveland Clinic may help advance the technology toward broader clinical use
Distinct MRI signature includes lesions beyond the corpus callosum, features predictive of vision and hearing loss
An argument for clarifying the nomenclature
An expert talks through the benefits, limits and unresolved questions of an evolving technology
Recommendations on identifying and managing neurodevelopmental and related challenges