Disorganization of retinal inner layers lends insights
By Amy S. Babiuch, MD, and Rishi P. Singh, MD
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Can we predict how a patient will respond to therapy? In previous studies, the disorganization of retinal inner layers (DRIL) has demonstrated its ability to help determine visual acuity (VA) prognosis in diabetic macular edema that requires treatment.
Given this association, the research group at Cole Eye Institute studied how DRIL may affect VA outcomes in patients with retinal vein occlusion (RVO) undergoing treatment for secondary macular edema with anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) agents.
DRIL is defined as the extent to which there is a failure in the recognition of any of the demarcations between the ganglion cell-inner plexiform layer complex, inner nuclear layer and outer plexiform layer on optical coherence tomography (OCT). This is demonstrated in Figure 1, where yellow lines course through the areas of normal demarcation and stop at those areas with poor demarcation.
Our researchers performed a retrospective study of eyes from patients with treatment naïve RVO and a minimum of 12 months follow-up. The study included patients with central retinal vein occlusion (CRVO), hemi-retinal vein occlusion (HRVO) and branch retinal vein occlusion (BRVO). Baseline DRIL was identified in 61.9 percent of all eyes (91/147).
DRIL burden was followed throughout the treatment course using a presence or absence approach to score DRIL across three regions (Figure 1) on the horizontal OCT line scan at baseline, 6 months and 12 months. At 6 and 12 months, DRIL scores were further evaluated for stable, increasing or decreasing DRIL burden.
Advertisement
Based on the results of the study, our group concluded that the presence of DRIL at baseline in BRVO patients is associated with worse baseline VA. Increasing DRIL burden in CRVO and HRVO patients is associated with reduced VA gains.
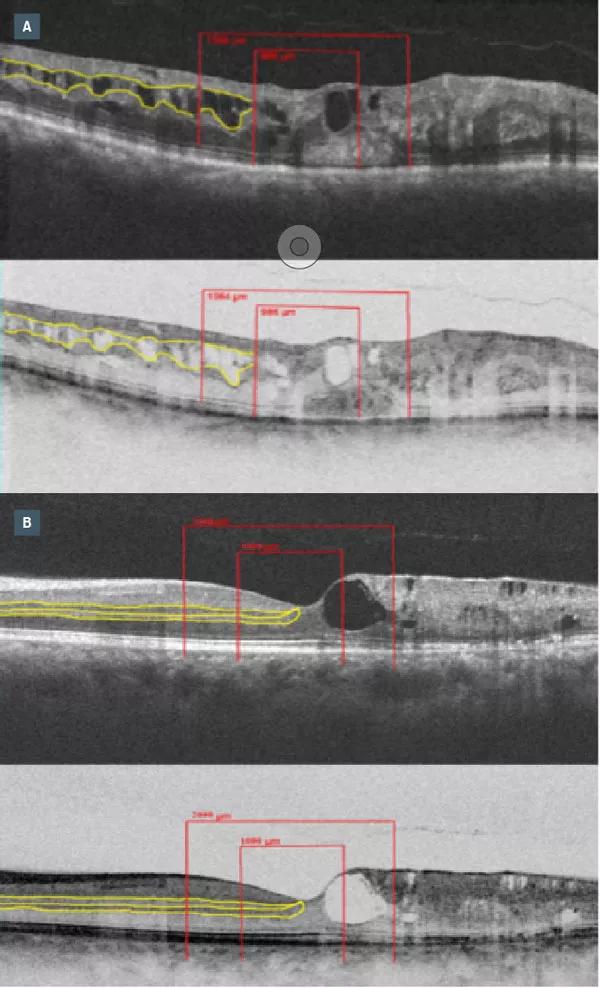
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/a4c6b00a-3f47-4d50-be2f-7251c787c7be/18-EYE-4342-Babiuch-CQD-Inset_jpg)
Figure 1: Representation of disorganization of retinal inner layers (DRIL) on SD-OCT and reverse gray-scale SD-OCT. The yellow lines highlight the inner retinal layer interfaces, which disappear in the areas of DRIL. The red lines demonstrate the three regions where DRIL was scored. (A) Patient with a branch retinal vein occlusion (BRVO) exhibiting intraretinal fluid and DRIL . (B) Patient with a central retinal vein occlusion (CRVO) exhibiting intraretinal fluid and DRIL.
For patients undergoing treatment with anti-VEGF agents, it’s important to identify biomarkers that might influence overall visual acuity outcomes. In this series of RVO patients, a modest increase in DRIL detection was observed in months 6 through 12, and when this was compared to the number of anti-VEGF injections delivered, the average number of injections decreased by about half during those months as compared to the first six months. This decline in treatment with anti-VEGF agents may have allowed for progression of disease.
These results demonstrate how using OCT to identify novel biomarkers such as DRIL in RVO helps to guide treatment with anti-VEGF therapy, and is a useful prognostic indicator for VA in RVO patients.
This work allows clinicians to better forecast how patients will progress with treatment.
Advertisement
Dr. Babiuch presented this study on the podium at the 2018 American Society of Retina Specialists (ASRS) Annual meeting and it has been accepted by JAMA Ophthalmology.
Advertisement
Advertisement

Motion-tracking Brillouin microscopy pinpoints corneal weakness in the anterior stroma

Registry data highlight visual gains in patients with legal blindness

Prescribing eye drops is complicated by unknown risk of fetotoxicity and lack of clinical evidence

A look at emerging technology shaping retina surgery

A primer on MIGS methods and devices

7 keys to success for comprehensive ophthalmologists

Study is first to show reduction in autoimmune disease with the common diabetes and obesity drugs

Treatment options range from tetracycline injections to fat repositioning and cheek lift