Notch pathway inhibition preserves retinal neurons and promotes regrowth in zebrafish
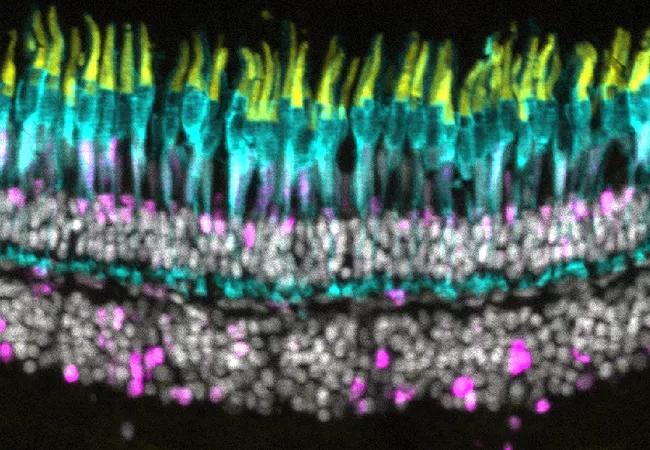
Unlike humans and other mammals, zebrafish have the ability to activate stem cells to regenerate retinal neurons killed by high-intensity light damage or injury. After being blasted with light, lost or damaged photoreceptors in zebrafish regrow. So, why doesn’t the same thing happen when zebrafish photoreceptors degenerate due to disease?
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
A team led by ophthalmic researcher Brian Perkins, PhD, of Cleveland Clinic Cole Eye Institute has discovered that it can. Their findings were published recently in the Journal of Neuroscience.
“Ours is one of the first studies that uses a disease model of progressive retinal dystrophy to understand retinal regeneration,” says Dr. Perkins. “Physicians typically aren’t seeing patients who forgot to wear sunglasses and stared at the sun for 20 minutes. They’re treating patients with retinitis pigmentosa; macular degeneration; and slow, progressive inflammatory responses and diseases.”
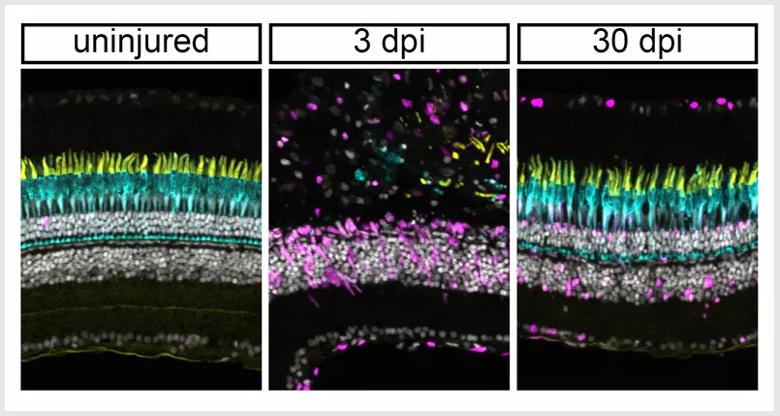
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/7ef3b746-dd95-45d1-99d4-612164142dac/22-EYE-3049477-New-findings-in-retinal-regeneration-Perkins-805-inset_jpg)
The retina in zebrafish regenerates following light damage. Cone photoreceptors are shown in yellow/cyan. Active stem cells are in magenta. At three days post injury (3 dpi), the photoreceptors have been completely destroyed. At 30 days post injury (30 dpi), they have been completely regenerated.
In a zebrafish model of inherited retinal dystrophy, Dr. Perkins’ team used single-cell RNA sequencing to dissociate cells in the retina and sequence genes that were turning on in individual cells.
“We found that in the Müller glia — which can act as endogenous stem cells in the retina — the expression of one particular gene called notch3 was enhanced,” Dr. Perkins explains. “Previous research had shown that following light damage, expression of notch3 was decreased.”
Those contrasting findings suggested that inhibiting the Notch pathway would send the regeneration process into overdrive. Dr. Perkins’ research team proved it by using a notch3-inhibiting drug to trigger regeneration, leading to a complete preservation of photoreceptors.
Advertisement
“In these disease models, it was the enhancement of Notch signaling that was preventing zebrafish from regenerating photoreceptors,” Dr. Perkins says.
The team also reported that immunosuppression mitigated the effects of retinal degeneration.
By breeding the zebrafish model of inherited retinal dystrophy with a second zebrafish mutant that lacked immune cells in the eye, the team developed fish that carried a mutation for retinal degeneration but no inflammation. In those fish, the photoreceptors did not degenerate despite having the mutation.
While there’s still debate about the utility of immunosuppressants in people with inherited retinal dystrophy, Dr. Perkins says his findings support the idea that reducing inflammation slows degeneration of photoreceptors.
Dr. Perkins plans to continue researching the link between inflammation and Notch signaling. He and his team hope to show similar findings in other disease models.
“There’s a lot left to explore,” he says. “We looked at one particular genetic model. We fully expect this to be generalized, but we need to confirm it.”
The team also intends to look more closely at single-cell RNA sequencing and uncover other gene expression changes that are occurring.
“We plan to further study how other pathways are responding differently in disease models compared to injury models,” says Dr. Perkins. “There’s a solid and deep foundation for what happens following light damage or acute injury, but that’s not necessarily transferable to a slow disease state.”
Advertisement
Advertisement

Motion-tracking Brillouin microscopy pinpoints corneal weakness in the anterior stroma

Registry data highlight visual gains in patients with legal blindness

Prescribing eye drops is complicated by unknown risk of fetotoxicity and lack of clinical evidence

A look at emerging technology shaping retina surgery

A primer on MIGS methods and devices

7 keys to success for comprehensive ophthalmologists

Study is first to show reduction in autoimmune disease with the common diabetes and obesity drugs

Treatment options range from tetracycline injections to fat repositioning and cheek lift