Ruling out a common diagnosis and identifying an elusive condition
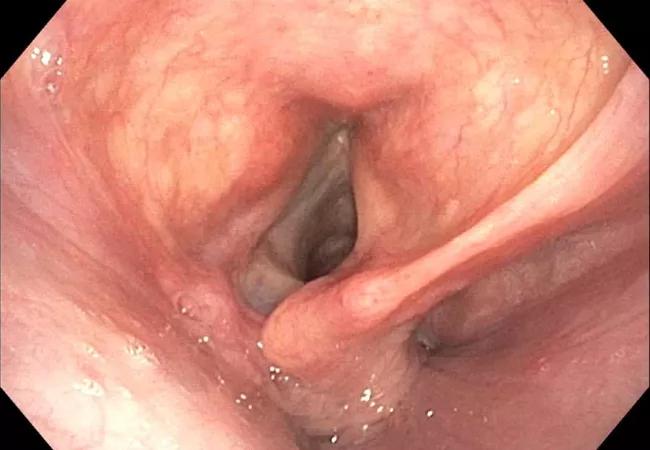
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/d1fcf718-2774-4191-8011-2348b08de675/21-PUL-2223308_Fig3B-650x450-hero_jpg)
21-PUL-2223308_Fig3B 650×450-hero
By Adriano Tonelli, MD, and Anthony Cucci, MD
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
An obese 51-year-old man with obstructive sleep apnea presented with progressive dyspnea for one year. Extensive evaluations revealed mild restriction on pulmonary function tests with normal diffusing capacity for carbon monoxide and normal lung parenchyma on a CT of the chest. An echocardiogram showed normal left and right ventricular systolic function. A right heart catheterization noted postcapillary pulmonary hypertension (PH) (pulmonary artery wedge pressure [PAWP] of 25 mm Hg). The patient was treated with diuretics without clinical improvement.
The patient underwent invasive cardiopulmonary exercise testing, given the persistent dyspnea with minimal activities. During the test we noted the presence of postcapillary PH with an end-expiratory PAWP of 26 mm Hg. We suspected a high intrathoracic pressure given obesity and pronounced respiratory oscillation with positional changes of his pulmonary pressures. Esophageal manometry revealed an end-expiration supine pressure of 18 mm Hg (Figure 1), hence the adjusted PAWP was normal at 8 mm Hg. In addition, the PAWP/cardiac output slope was normal (< 2 Wood units) during the exercise test and therefore not supportive of postcapillary PH with activities.
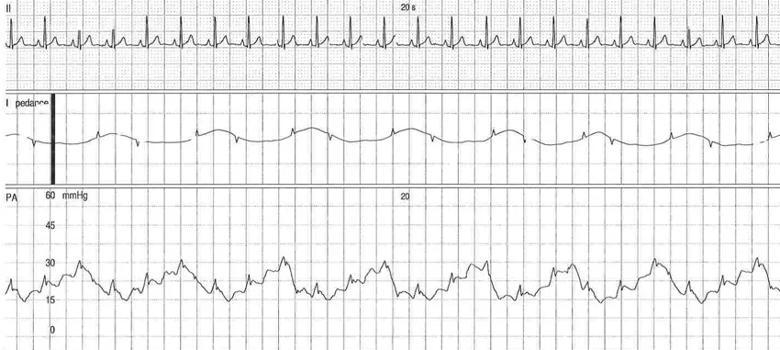
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/3549cde0-2324-4d75-824f-6c3cd4646aad/21-PUL-223308-Fig1a-inset_jpg)
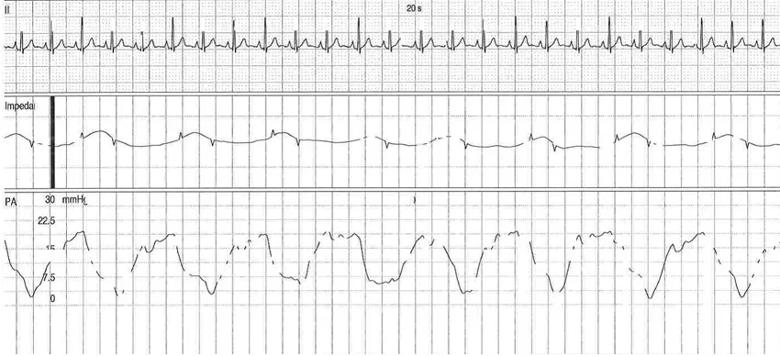
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/e6825b38-e400-46a9-a91b-114066ed0671/21-PUL-223308-Fig1b-inset_jpg)
Figure 1. End-expiratory PAWP (A) and intrathoracic pressures (B) in supine position.
Maximum exercise showed a mildly decreased peak oxygen consumption at 78% of predicted with normal anaerobic threshold. The flow-volume loops during exercise revealed inspiratory and expiratory flattening suspicious for an airway pathology (Figure 2).
Advertisement
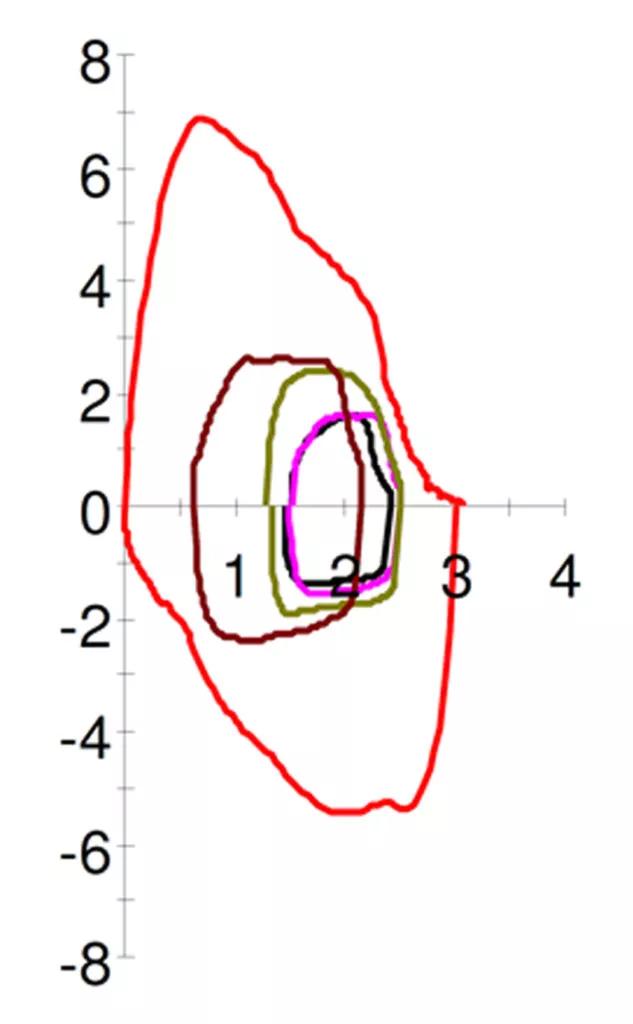
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/345a304a-67ee-4614-942e-c48166004499/21-PUL-223308-Fig2-inset-633x1024_jpg)
Figure 2. Flow-volume loops at rest (red line) and during exercise (other colors). Figure shows inspiratory and expiratory flow flattening with exercise.
We performed flexible laryngoscopy during exercise and noted a right vocal cord paralysis with redundant arytenoid tissue that reduced the glottis. The patient was able to exercise better while on continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) adjusted to his intrathoracic pressure, with better glottis opening during flexible laryngoscopy.
A dynamic CT of the chest showed no significant tracheal stenosis or tracheobronchomalacia. However, a bronchoscopy revealed a right arytenoid fold that almost completely occluded the airway under deep respiration (Figure 3), with evidence of severe expiratory dynamic airway collapse (Figure 4) that extended to the segmental bronchial level.
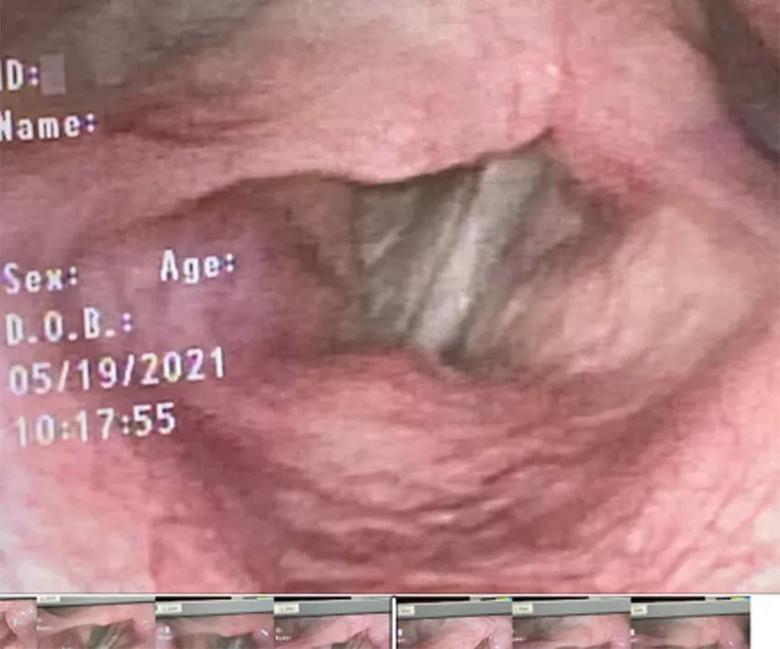
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/67399177-b561-4c2c-92e3-4d98ea7879bd/21-PUL-2223308_Fig3A-inset_jpg)

Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/22b44e5a-1abe-4c66-983c-e1e0ee5088b4/21-PUL-2223308_Fig3B-inset_jpg)
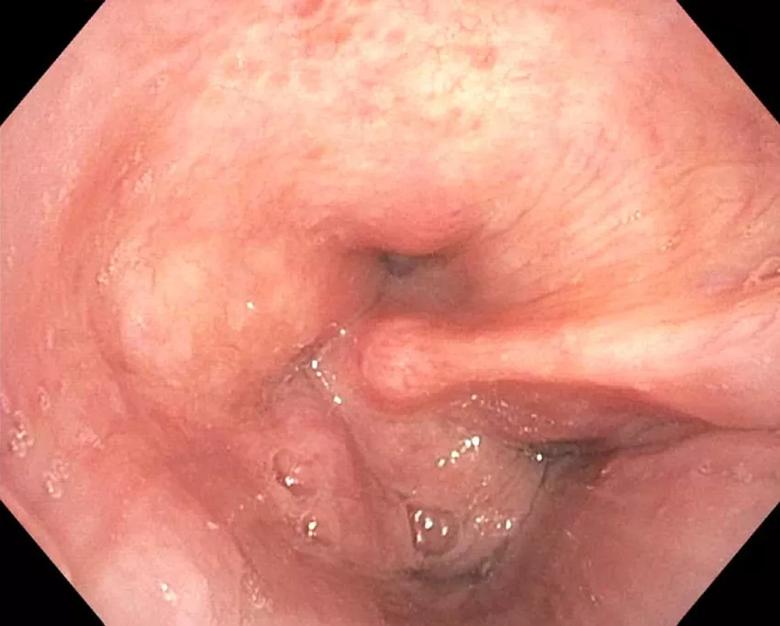
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/92c7a66a-150f-4bbb-b28c-0eb941bae238/21-PUL-2223308_Fig3C-inset_jpg)
Figure 3. Flexible laryngoscopy during exercise (A) and bronchoscopy evaluation (B [inhalation], C [exhalation]). Figures show right vocal cord paralysis, redundant right arytenoid fold with narrowing/occlusion of the glottis.
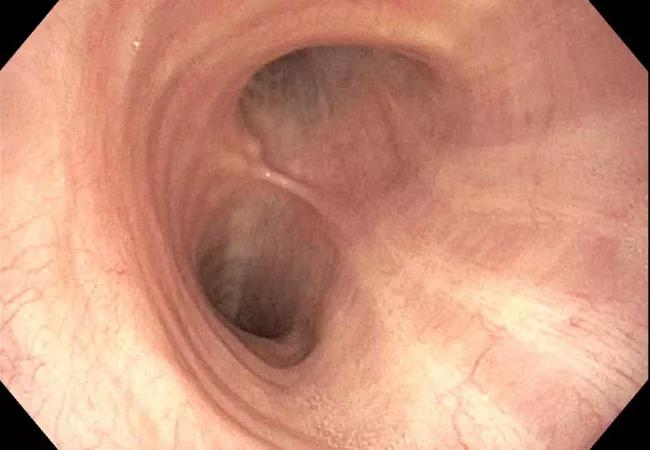
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/b0537a08-e307-4905-a1ef-4622aa4cc78f/21-PUL-2223308_Fig4A-inset_jpg)
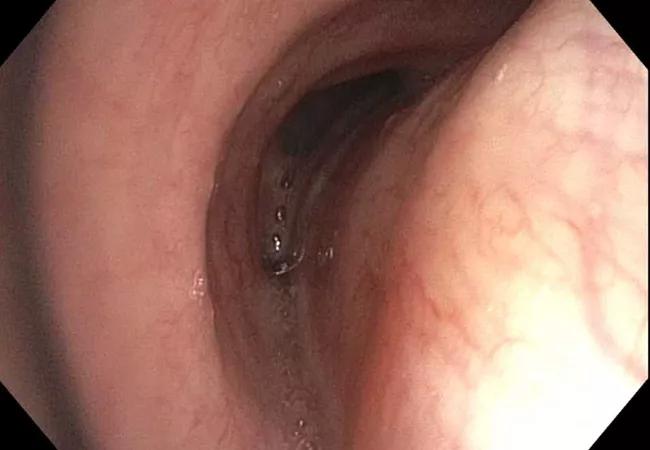
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/07e423ff-c55f-4ea2-8dc8-3af2433dfe43/21-PUL-2223308_Fig4B-inset_jpg)
Figure 4. Bronchoscopy showing expiratory dynamic airway collapse (A [inspiration], B [exhalation]).
This case illustrates the value of an adequate hemodynamic evaluation in patients with PH. An increase in intrathoracic pressure is directly transmitted to the pulmonary vessels leading to a high PAWP and the inadequate diagnosis of postcapillary PH, as in this case. This change in diagnosis was supported by the lack of clinical response and worsening of renal function when the patient was treated with diuresis. A careful recording of flow-volume loops allowed us to detect the flattening of inspiratory and expiratory flows. This abnormal finding was further explored with flexible laryngoscopy and then bronchoscopy, leading to the final diagnosis of exercise-induced laryngeal obstruction with expiratory dynamic airway collapse.
Advertisement
Adriano Tonelli, MD, is staff in the Department of Pulmonary Medicine within Cleveland Clinic’s Respiratory Institute. Anthony Cucci, MD, is staff in the Department of Critical Care Medicine within Cleveland Clinic’s Respiratory Institute.
Advertisement
Advertisement
Takeaways from the most recent annual meeting centered around clinical advances, AI integration and professional development
Recent breakthroughs have brought attention to a previously overlooked condition
A review of treatment options for patients who may not qualify for surgery
Looking at the real-world impact and the future pipeline of targeted therapies
The progressive training program aims to help clinicians improve patient care
New breakthroughs are shaping the future of COPD management and offering hope for challenging cases
Exploring the impact of chronic cough from daily life to innovative medical solutions
How Cleveland Clinic transformed a single ultrasound machine into a cutting-edge, hospital-wide POCUS program