Researchers hope it will lead to earlier, more accurate diagnosis
With support from a $7.2 million National Institutes of Health grant, a multicenter study is launching to evaluate whether the MRI-based biomarker known as the central vein sign (CVS) can serve as a sensitive and specific diagnostic marker for multiple sclerosis (MS). The study is funded through the National Institutes of Neurological Disorders and Stroke’s Clinical Validation of a Candidate Biomarker for Neurological Disease Program Announcement.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
“We hypothesize that determining whether a patient meets central vein sign criteria will promote earlier and more accurate diagnosis of MS,” says the study’s co-principal investigator, Daniel Ontaneda, MD, PhD, of Cleveland Clinic’s Mellen Center for Multiple Sclerosis Research and Treatment. “This, in turn, should reduce misdiagnoses and simplify clinical decision-making.”
The prospective study, referred to as CAVS-MS, will enroll 400 patients with typical or atypical presentations of MS at 11 participating centers in North America, with Cleveland Clinic serving as the coordinating center. The study is being conducted under the auspices of the North American Imaging in MS Cooperative and will be led by Dr. Ontaneda and Dr. Nancy Sicotte at Cedars-Sinai in Los Angeles.
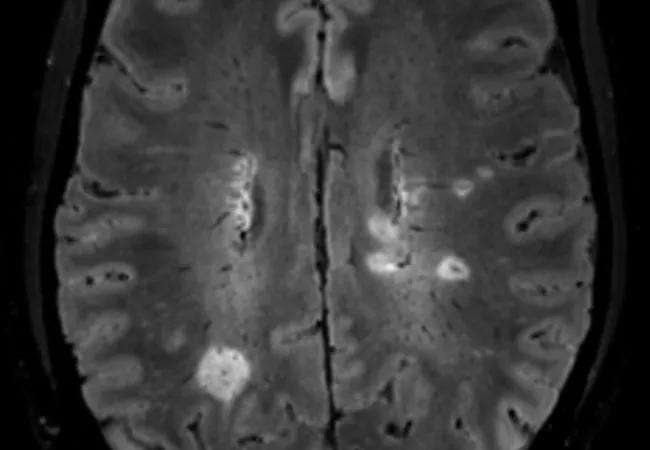
The CVS refers to a vein visualized inside a white matter lesion on T2* MRI sequences that appears as a hypointensity relative to the surrounding lesion. “The presence and pathophysiologic significance of a central vein in MS white matter lesions has been extensively described in both pathology- and MRI-based studies,” notes Dr. Ontaneda.
He adds that CVS criteria — i.e., scoring of a brain MRI based on the presence of the CVS — have been well validated as a sensitive and specific marker of MS in cross-sectional studies. “We are now conducting this large prospective study to definitively assess the central vein sign as a diagnostic biomarker for immediate translation into clinical care,” Dr. Ontaneda explains. “The hope is that this sign can improve sensitivity and specificity relative to current approaches and avoid the need for complicated and time-consuming clinical scoring methods.”
Advertisement
He adds that the grant application was the culmination of several years of preparatory work that included collaborations with the National Institutes of Health (Pascal Sati, PhD, and Daniel Reich, MD, PhD), University of Vermont (Andrew Solomon, MD), University of Pennsylvania (Russell Shinohara, PhD) and Cedars-Sinai (Nancy Sicotte, MD).
The need for improved diagnostic methods in MS is widely recognized. Although MRI is a longstanding tool for detecting MS lesions, diagnostic inaccuracies persist. Up to 20% of people diagnosed with MS (1 in 5) are later found not to have the disease, Dr. Ontaneda notes. “This is highly consequential, as more than two-thirds of misdiagnosed patients are unnecessarily exposed to risks from disease-modifying therapies, which in rare cases can be life-threatening,” he says.
Moreover, the current standard in MS diagnosis — the McDonald criteria, which combine clinical symptoms and MRI findings — were developed from studies in people with typical clinical presentations of MS. This reduces the specificity of these criteria, rendering them uninformative for the nearly half of MS patients who present to neurologists with atypical or nonclassical symptoms.
Timeliness of MS diagnosis is also key, as diagnostic delay is common in cases of relapsing-remitting MS and can carry severe and lifelong consequences.
The CAVS-MS study has been designed to assess whether CVS criteria can help address some of these unmet diagnostic needs. It will specifically explore the role of presentation type by enrolling across North America a mixed population of patients with typical clinical presentations (n = 200) and those with atypical presentations, including suggestive MRI findings in the absence of neurologic symptoms (n = 200).
Advertisement
Patients will be enrolled when presenting to an MS center for diagnostic referral, and they will undergo follow-up at prespecified intervals for 24 months. Brain MRI will be performed at baseline and 24 months, with scans scored on the basis of CVS criteria. T2-weighted fluid-attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) imaging will be combined with T2*-weighted segmented echo-planar imaging to enable simultaneous identification of white matter lesions and venous structures (Figure).
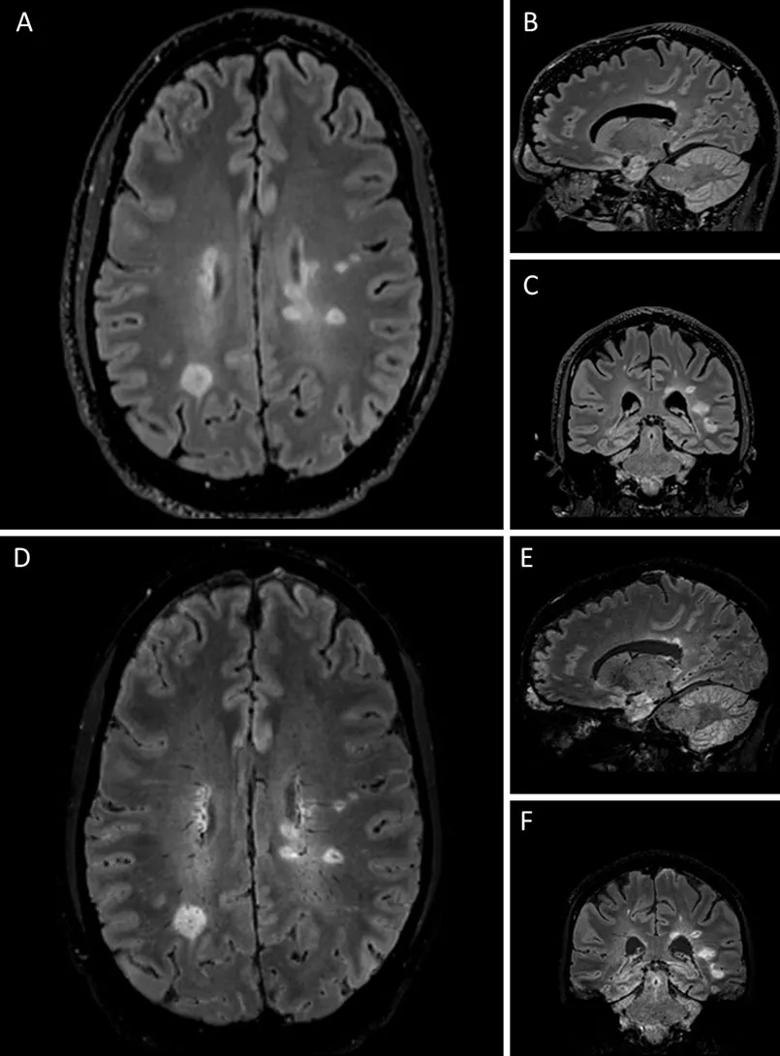
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/ea3352b2-9241-4db2-b185-533821218610/20-NEU-1845659-CQD-Ontaneda_Grant-to-study-central-vein-sign-in-MS_805x1090-Inset-A_jpg)
Figure. Representative central vein images in a research participant with multiple sclerosis. Hyperintense lesions are demonstrated on T2-FLAIR images shown in axial (A), sagittal (B) and coronal (C) views. Central veins are observed in a preponderance of lesions in the merged FLAIR and T2*-weighted images shown in axial (D), sagittal (E) and coronal (F) views.
The primary objective is to determine whether use of CVS criteria allows for an earlier accurate diagnosis of MS in patients who do not meet the McDonald criteria at baseline. “We aim to show that the CVS is a simple and reliable diagnostic biomarker that will show an increase in sensitivity while preserving specificity,” Dr. Ontaneda observes.
Secondary objectives include the following:
Advertisement
The researchers will also begin exploratory studies of optimal methods for integrating CVS findings into MS diagnostic criteria, along with any resulting healthcare-related cost savings. “These initial exploratory analyses will be important to how readily positive findings about the utility of CVS criteria can impact clinical practice,” says Dr. Ontaneda. The ultimate goal is to have the CVS incorporated into the MS diagnostic criteria, he adds.
Advertisement
Advertisement

An expert talks through the benefits, limits and unresolved questions of an evolving technology

Recommendations on identifying and managing neurodevelopmental and related challenges

Phase 2 trials investigate sitagliptin and methimazole as adjuvant therapies

Aim is for use with clinician oversight to make screening safer and more efficient

Rapid innovation is shaping the deep brain stimulation landscape

Study shows short-term behavioral training can yield objective and subjective gains

How we’re efficiently educating patients and care partners about treatment goals, logistics, risks and benefits

An expert’s take on evolving challenges, treatments and responsibilities through early adulthood