Research has clear implications for future of prostate cancer imaging
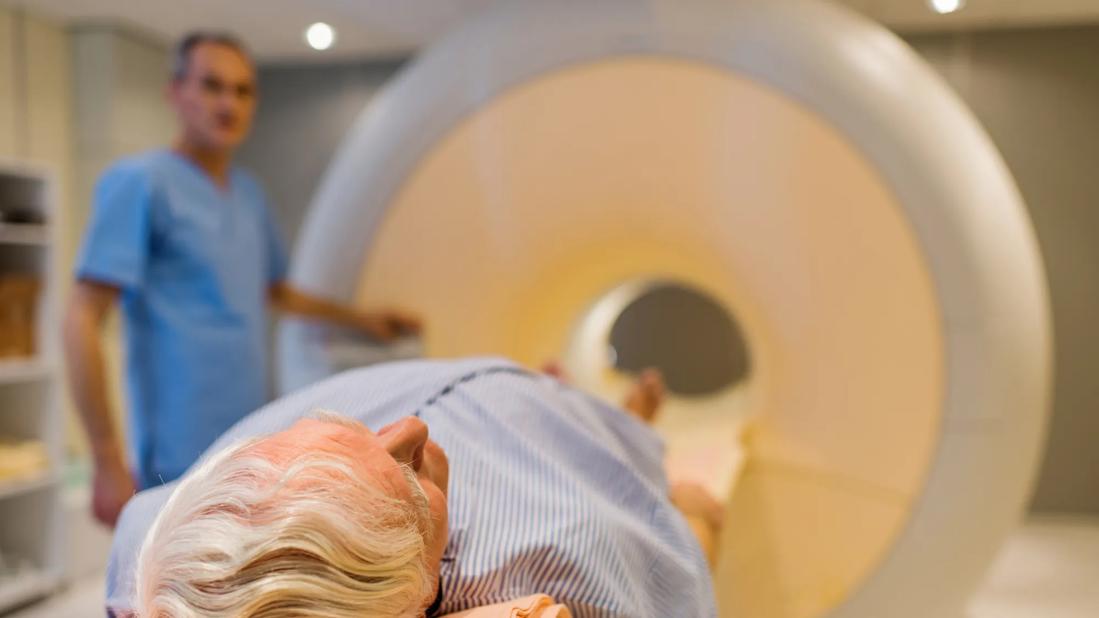
Cleveland Clinic researchers have successfully used positron emission tomography (PET) imaging to visualize biochemical changes within mouse prostate tumors that indicate advancement of disease. The proof-of-concept study, published in the Journal of Biological Chemistry, establishes the feasibility of using noninvasive PET to predict which prostate tumors are likely to resist standard androgen deprivation treatments.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Findings from the study, which was led by Nima Sharifi, MD, of the Lerner Research Institute, were two-fold. Dr. Sharifi’s team, including first author Ziqi Zhu, PhD, first discovered a metabolic “switch” that occurs when prostate cancer cells transition from being sensitive to androgen deprivation to being resistant to the treatment.
The lab’s earlier research established that when some aggressive prostate tumors are depleted of their androgen supply, their metabolic machinery adapts to produce endogenous androgens, allowing the tumors to continue to thrive despite external androgen deprivation. When this transition occurs, prostate cancer is said to be “castration-resistant.”
In the new study, Dr. Sharifi found a previously undiscovered step in the pathway to castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC). In typical prostate cancer cells, the amount of tumor androgens is kept under control. Specifically, the enzymes UGT2B15 and UGT2B17 bind to the androgen dihydrotestosterone (DHT), rendering it unavailable for use by the tumor and keeping androgen receptors in an inactive state. However, Dr. Sharifi’s team showed that in CPRC, this DHT coupling is absent, allowing free DHT to accumulate and activate androgen receptors. This change is a key step in the road to treatment resistance.
After making this discovery, Dr. Sharifi’s team hypothesized that they could differentiate between coupled and free DHT using PET, which could help distinguish between treatment sensitive and treatment resistant tumors. They radiolabeled tumors that had either intact or deficient (knockout) UGT2B15 and UGT2B17 activity. The tumors with intact machinery had both coupled and circulating DHT, which was evidenced by high uptake of the 18[F]-DHT radiolabel and resulting bright PET signal. The knockout tumors showed a much weaker signal.
Advertisement
These findings suggest a noninvasive method of monitoring the metabolic status of prostate tumors in real time and have clear implications for the future of prostate cancer imaging. “Today, PET imaging is only used clinically to locate and measure the size of prostate tumors,” Dr. Sharifi says. “We hope to use PET to monitor what is happening inside the tumor as well so we can better predict outcomes and tailor treatments.” Functional imaging to identify impending castration resistance would enable physicians to potentially change treatment course and avert full-blown resistance.
This study was performed in collaboration with nuclear medicine specialists in Cleveland Clinic’s Imaging Institute and imaging specialists from Case Western Reserve University’s Department of Biomedical Engineering.
Dr. Sharifi holds the Kendrick Family Chair for Prostate Cancer Research at Cleveland Clinic. He directs the Cleveland Clinic Center for Genitourinary Malignancies Research and co-directs the Cleveland Clinic Center for Excellence in Prostate Cancer Research. He has joint appointments in the Glickman Urological and Kidney Institute and Taussig Cancer Institute. In 2017, he received the national Top Ten Clinical Achievement Award from the Clinical Research Forum for earlier discoveries linking genetic variants with poor prostate cancer outcomes.
This project was supported by grants from the Howard Hughes Medical Institute, Prostate Cancer Foundation, and National Cancer Institute (part of the National Institutes of Health).
Advertisement
Advertisement

First full characterization of kidney microbiome unlocks potential to prevent kidney stones

Researchers identify potential path to retaining chemo sensitivity
Large-scale joint study links elevated TMAO blood levels and chronic kidney disease risk over time
Investigators are developing a deep learning model to predict health outcomes in ICUs.

Preclinical work promises large-scale data with minimal bias to inform development of clinical tests

Cleveland Clinic researchers pursue answers on basic science and clinical fronts

Study suggests sex-specific pathways show potential for sex-specific therapeutic approaches

Cleveland Clinic launches Quantum Innovation Catalyzer Program to help start-up companies access advanced research technology