Novel three-drug regimen used to manage life-threatening developments
In April 2021, a 42-year-old man reached out to Brian Hill, MD, PhD, for a second opinion after being diagnosed with hairy cell leukemia following a bone marrow biopsy at a healthcare facility in northwest Ohio.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
“At the time of diagnosis, he was getting easily fatigued and couldn’t exercise,” explains Dr. Hill, Director of the Lymphoid Malignancies Program at Cleveland Clinic’s Taussig Cancer Institute. “He was experiencing a slow-moving progression of symptoms.”
Standard front-line therapy for hairy cell lymphoma –an indolent B-cell lymphoproliferative disease – is the chemotherapy medication cladribine. Dr. Hill recommended the patient begin the drug, typically administered daily for five days or via a continuous pump for seven days, but the situation quickly pivoted.
“When I met the patient for a virtual second opinion, I recommended he get vaccinated against the coronavirus before beginning treatment,” says Dr. Hill. “Within two weeks, however, he was hospitalized with COVID-19 pneumonia.”
The patient was admitted to his local hospital with fever and shortness of breath. He tested positive for COVID-19, and within a few days, his breathing became more labored. He was transferred to Cleveland Clinic’s main campus.
“His critical illness was exacerbated by neutropenia from his leukemia,” says Dr. Hill. “Once he was admitted to our ICU, he rapidly deteriorated. Within a few days, the patient was intubated and put on mechanical ventilation. His oxygenation levels were so poor that he was placed in the prone position and underwent pharmacologic paralysis.”
Unfortunately, the patient’s severe COVID-19 had severely compromised his immune system. “The only way to improve his neutrophil and white blood cell counts was to get the cancer cells out of the bone marrow,” says Dr. Hill. However, the oncology team quickly realized that the standard chemotherapy approach for hairy cell leukemia could prove detrimental.
Advertisement
“He would not likely survive short-term worsening of his neutropenia caused by the administration of traditional chemotherapy with cladribine,” explains Dr. Hill.
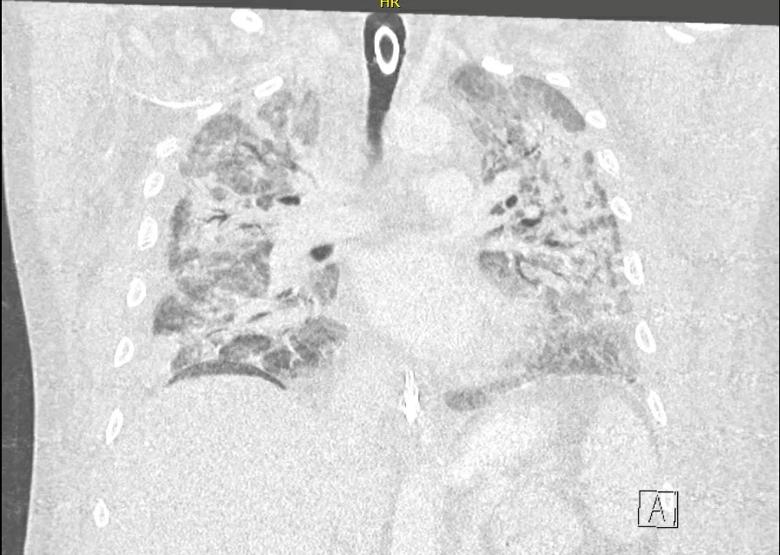
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/69a0fa0b-d0ff-40ea-b9ca-087dc517bdc0/Hairy-Cell-Leukemia-Case_png)
Coronal chest CT image taken while the patient was hospitalized for severe COVID-19 pneumonia. Extensive bilateral infiltrates and air bronchograms are seen; an endotracheal tube can also be visualized.
After discussions with other oncologists and the patient’s critical care team, including pulmonology specialists, Dr. Hill began to administer vemurafenib, an FDA-approved tablet medication for treating melanoma that targets mutations in the BRAF gene.
Approximately 90% of hairy cell leukemia cases also have this same BRAF mutation, says Dr. Hill. Although vemurafenib is not as effective as cladribine for hairy cell leukemia, the drug has proven to be an effective second-line treatment.
Twice a day for more than two weeks, caregivers crushed a 960-mg tablet of vemurafenib and administered it to the patient through a nasogastric tube. He also was treated with remdesivir for COVID-19.
Gradually, the patient’s neutrophil count recovered, his breathing improved and his fever abated. He was weaned off high levels of oxygen.
“His COVID finally turned the corner,” says Dr. Hill. “I give most of the credit to our medical ICU nurses, pharmacists and physicians whose great work kept him going through all this.”
During his time in the hospital, the patient suffered numerous complications, including bacteremia and ventilator-associated pneumonia. He also lost some function in his left hand from neurologic compression of his brachial plexus.
Advertisement
After two months in the medical ICU, the patient was transferred to a medical-surgical unit in mid-June and was later discharged from the hospital July 1. His treatment journey for hairy cell leukemia continued throughout.
“While vemurafenib is a good drug, it wasn’t good enough in his case,” says Dr. Hill. “He stopped making progress while in the hospital, so we gave him a 70% dose of cladribine.” Once discharged, the patient received a standard dosage of the monoclonal antibody medication rituximab, which was necessary due to ongoing cytopenias.
“It was a balancing act to provide enough treatment against the hairy cell leukemia, but not so much as to set him back in terms of infectious complications,” explains Dr. Hill.
A year after his hairy cell leukemia diagnosis, the patient is in remission. His only residual medical deficit is impaired inflection of his left wrist, for which he is undergoing physical therapy. The patient is back at home with his family, including his wife and three children. He hopes to return to work within the next few months.
“For patients like this one with rare diseases who have atypical treatment courses, it’s important to think outside the box to get the best outcomes. Cleveland Clinic excels at that,” says Dr. Hill. “In this case, we could not wait for the patient to get better from COVID to treat the cancer. We had to address both at once.”
Advertisement
Advertisement

Radiation therapy helped shrink hand nodules and improve functionality

Standard of care is linked to better outcomes, but disease recurrence and other risk factors often drive alternative approaches

Phase 1 study demonstrates immune response in three quarters of patients with triple-negative breast cancer

Multidisciplinary teams bring pathological and clinical expertise

Genetic variants exist irrespective of family history or other contributing factors

Study shows significantly reduced risk of mortality and disease complications in patients receiving GLP-1 agonists

Structured interventions enhance sleep, safety and caregiver resiliency in high-acuity units

Addressing rare disease and challenging treatment course in an active young patient