A toolkit for primary care physicians seeking to decrease unintended pregnancy in this population
Unintended pregnancy in adolescents remains a public health problem in the U.S. even during a global pandemic; as 64% of pregnancies in 20-24 year olds, 77% in 18-19 year olds and 90% in 15-17 year olds are unintended and/or unplanned.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
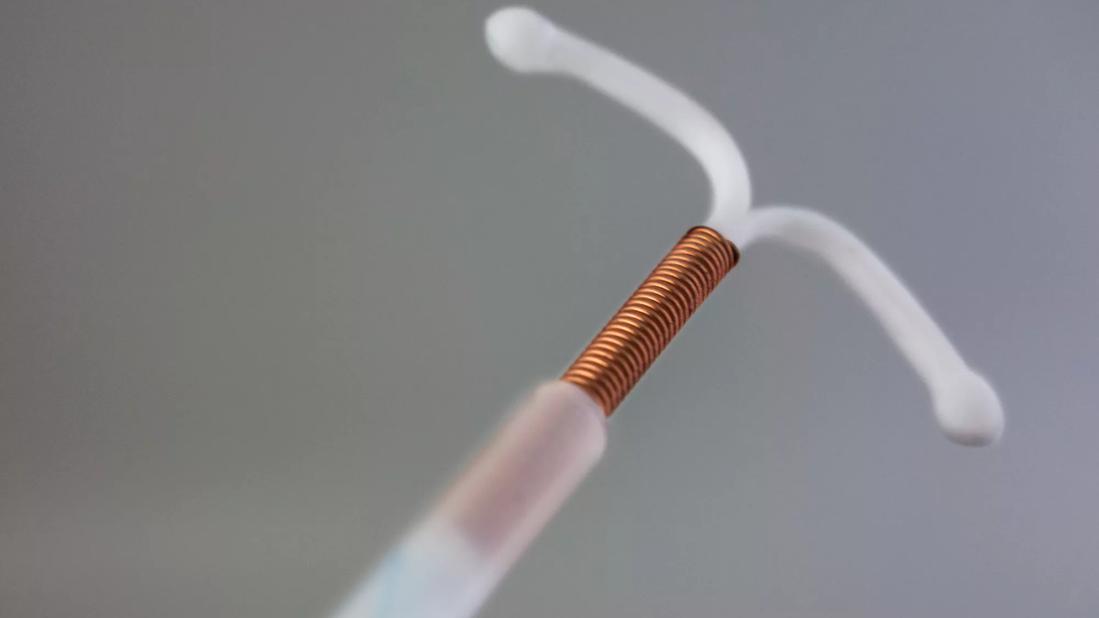
Teen pregnancy correlates with lower lifetime educational and economic achievement and a high likelihood of early parenting of their own offspring. Long-acting reversible contraceptives (LARCs) are recommended as the first-line, most effective contraceptive option according to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention1 and the World Health Organization.2 Pediatricians often feel ill-equipped to counsel youth adequately on all options, and same-day LARC access can be a challenge. Thanks to a $645,753 grant from Merck, Ellen Rome, MD, MPH, will be doing research to create a toolkit usable by primary care clinicians to decrease unintended teen/young adult pregnancies through greater LARC use with easier access.
Dr. Rome and collaborators will use an evidence-based implementation framework to conduct interviews with pediatric practices that currently offer high-volume LARC services to identify the processes necessary for scaling up LARC delivery, including staffing needs, essential training on insertion/removal, billing, contracts, stocking and supply chain. This toolkit can then be used to scale up care locally and nationally.
Advertisement
Advertisement

Uterine transposition cleared the field for radiation therapy

ACOG-informed guidance considers mothers and babies

Prolapse surgery need not automatically mean hysterectomy

Artesunate ointment shows promise as a non-surgical alternative

New guidelines update recommendations

Two blood tests improve risk in assessment after ovarian ultrasound

Recent research underscores association between BV and sexual activity

Psychological care can be a crucial component of medical treatment