Novel protein-to-protein interactions that relate to key pro-fibrotic signals
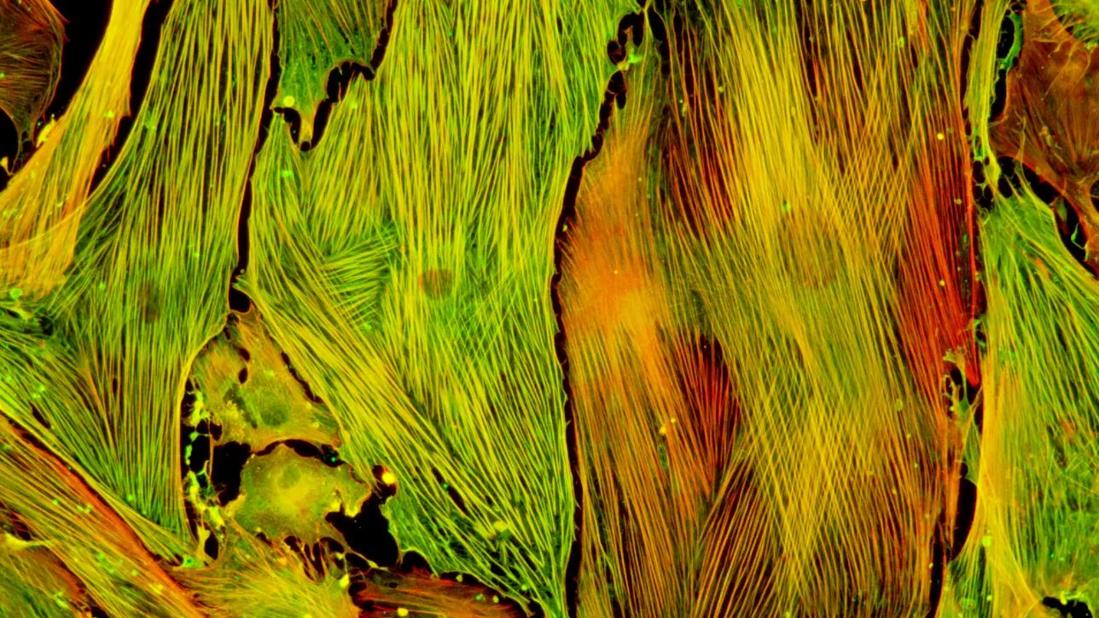
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/7632d9c7-dc20-4bc8-8b20-a244caec4c7d/Capture_jpg)
Lung fibroblasts isolated from a preclinical model were stimulated with TGF-β to induce myofibroblast differentiation
In a new study published in Science Signaling, Cleveland Clinic researchers have identified a novel target for new therapies that may help to treat or prevent a host of fibrotic conditions, which contribute to nearly half of overall mortality in the United States.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Fibrotic diseases are characterized by the overproduction of extracellular matrix (ECM), with resultant formation of scar tissue. Cells called myofibroblasts are thought to be the major producers of the scar tissue. Two key signals are needed to generate these myofibroblasts—active TGF-β (transforming growth factor-β) and a mechanical signal.
Previous research (published in the Journal of Clinical Investigation, 2014) led by Mitchell Olman, MD, a Cleveland Clinic physician-scientist and senior author of the current study, identified an ion channel called TRPV4 (transient receptor potential vanilloid) as the key transducer of the mechanical signal that leads to myofibroblast generation.
In the current study, research teams led by Dr. Olman and S.V. Naga Prasad, PhD, discovered that TRPV4 selectively binds to a kinase called PI3Kγ (phosphoinositide 3-kinase γ) to form an intracellular protein complex. This TRPV4-PI3Kγ complex—which is recruited by TGF-β—migrates from inside the cell to the plasma membrane and subsequently amplifies the actions of each individual protein, ultimately resulting in the differentiation of fibroblasts to myofibroblasts. Myofibroblasts produce and expel ECM outside of the cell, and contract the ECM to generate scar tissue—the hallmark of fibrotic diseases.
Taken together, these findings suggest that blocking TRPV4 and PI3Kγ binding may be an unexplored avenue for treating or preventing fibrotic conditions of many major organs. While additional research is necessary, this study provides promising support and rationale for a new treatment approach.
Advertisement
Lisa Grove, PhD, a postdoctoral fellow in Dr. Olman’s laboratory, is first author on the study, which was supported by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (part of the National Institutes of Health). Dr. Olman is a researcher in the Department of Inflammation & Immunity and a practicing pulmonologist. Dr. Prasad is a researcher in the Department of Cardiovascular & Metabolic Sciences.
Photo: Lung fibroblasts isolated from a preclinical model were stimulated with TGF-β to induce myofibroblast differentiation. The presence of yellow/orange in stress fibers indicates colocalization of phalloidin (F-actin, red) and alpha smooth muscle actin (αSMA, green), indicating incorporation of αSMA into stress fibers, which is a hallmark of myofibroblasts.
Advertisement
Advertisement
First full characterization of kidney microbiome unlocks potential to prevent kidney stones
Researchers identify potential path to retaining chemo sensitivity
Large-scale joint study links elevated TMAO blood levels and chronic kidney disease risk over time
Investigators are developing a deep learning model to predict health outcomes in ICUs.
Preclinical work promises large-scale data with minimal bias to inform development of clinical tests
Cleveland Clinic researchers pursue answers on basic science and clinical fronts
Study suggests sex-specific pathways show potential for sex-specific therapeutic approaches
Cleveland Clinic launches Quantum Innovation Catalyzer Program to help start-up companies access advanced research technology