Using “opportunistic imaging” to identify significant comorbidities such as cardiovascular risk and bone health
By Nishant Patel, MD; Ryan Ward, MD; Juan Calle, MD; Erick Remer, MD; and Manoj Monga, MD
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Noncontrast computed tomography (NCCT) scans remain the most accurate imaging modality to detect kidney stones and to direct management. NCCTs provide a reliable measure of stone burden, stone location, stone density and skin-to-stone distance. It is well known that vascular calcifications, also detectable through NCCT, are associated with nephrolithiasis. Kidney stones are also associated with hypertension, bone loss, atherosclerosis, diabetes, cardiovascular disease and obesity.
We recognized that the NCCT scans we regularly perform on kidney stone patients could be mined for additional useful information to help us manage patients.
“Opportunistic imaging” is a term used for evaluating other conditions using an existing image. In two unique studies published in the Journal of Endourology and The Journal of Urology, we evaluated the ability of NCCT scans obtained during a kidney stone work-up to contribute to a better understanding of patient comorbidities and the potential causes of their stones.
In this collaboration between Cleveland Clinic departments of Urology and Radiology, CT scans were evaluated for visceral obesity, hepatic steatosis, abdominal aortic calcifications and vertebral bone mineral density.
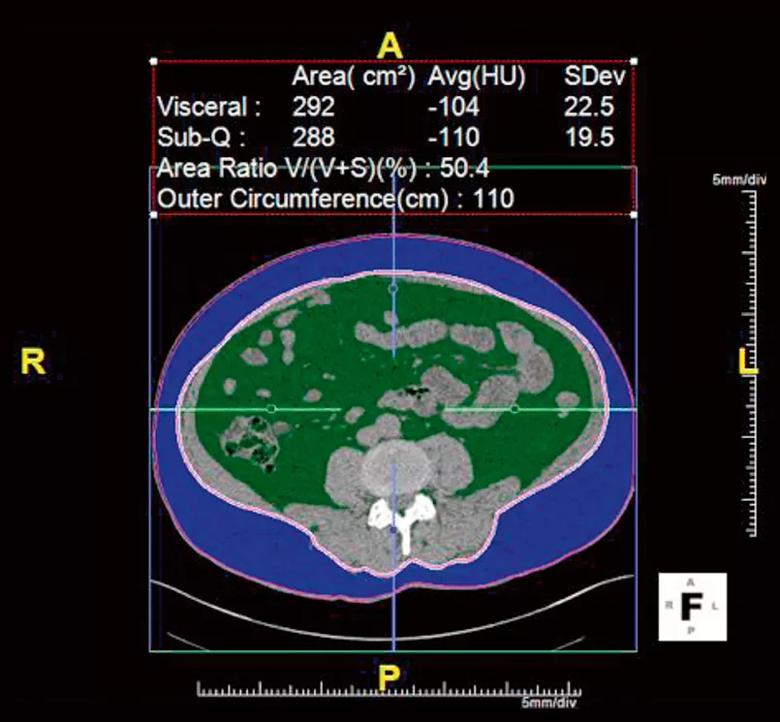
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/a06c17ca-7155-4fc8-80d9-3ba67ee1eead/805x-Noncontrast-CT-Scans-for-Kidney-Stones_jpg)
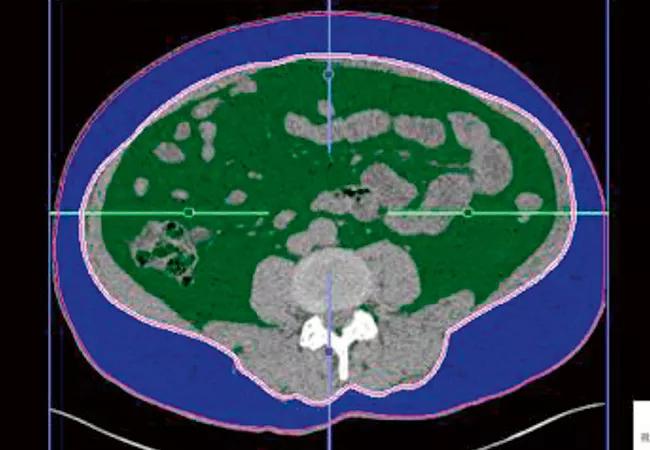
Figure 1. Visceral fat area (VFA) shown in green; subcutaneous fat area in blue. This CT scan shows VFA was 50.4 percent.
We found that visceral obesity and hepatic steatosis were associated with a low urine pH. We also noted that visceral obesity proved a better predictor than body mass index when identifying those with a low urine pH and uric acid stones. Indeed, 90 percent of uric acid stone patients had a high visceral fat area on CT scan. This information can be used to identify patients in whom dissolution therapy may be valuable.
Advertisement
We identified an association between abdominal aortic calcifications and a higher risk of low urine pH and hypocitraturia.
Patients with low vertebral bone mineral density on CT were more likely to have large stone volumes, hypercalciuria and hypocitraturia.
If a CT scan is ordered, we should put it to good use. Opportunistic CT imaging does not add cost or radiation exposure, nor does it require additional equipment. It can identify potentially significant comorbidities that may require further evaluation and management (e.g., cardiovascular risk, bone health). It can predict underlying metabolic abnormalities, suggest kidney stone preventive strategies and identify those best suited for a trial of dissolution therapy.
The prevalence of nephrolithiasis in the United States is approximately 9 percent and the disease carries significant burden to patients and the health care system. Our future studies will evaluate the impact of medical approaches to stone prevention (e.g., using thiazides or citrates) on bone mineral density. The goal is to maximize the “opportunity” our imaging provides.
Dr. Patel, a former fellow, is now an assistant professor at UCLA Health in Los Angeles. Dr. Ward is a diagnostic radiology resident.
Advertisement
Advertisement

Pediatric urologists lead quality improvement initiative, author systemwide guideline

Fixed-dose single-pill combinations and future therapies

Reproductive urologists publish a contemporary review to guide practice

Two recent cases show favorable pain and cosmesis outcomes

Meta-analysis assesses outcomes in adolescent age vs. mid-adulthood

Proteinuria reduction remains the most important treatment target.

IgA nephropathy is a relatively common autoimmune glomerular disease that can be diagnosed only by biopsy

Oncologic and functional outcomes are promising, but selection is key