Treatments differ widely in these mimics
By Rula Hajj-Ali, MD, and Leonard Calabrese, DO
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Distinguishing between reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome (RCVS) and primary angiitis of the central nervous system (PACNS) is critical because the treatment protocol is so vastly different. Misdiagnosing PACNS as RCVS can deprive a patient of medications that prolong survival and improve outcomes. Prognosis improves greatly with proper treatment. We offer a brief overview of differences in management techniques below. See these posts for differences in clinical presentation and imaging and test results.
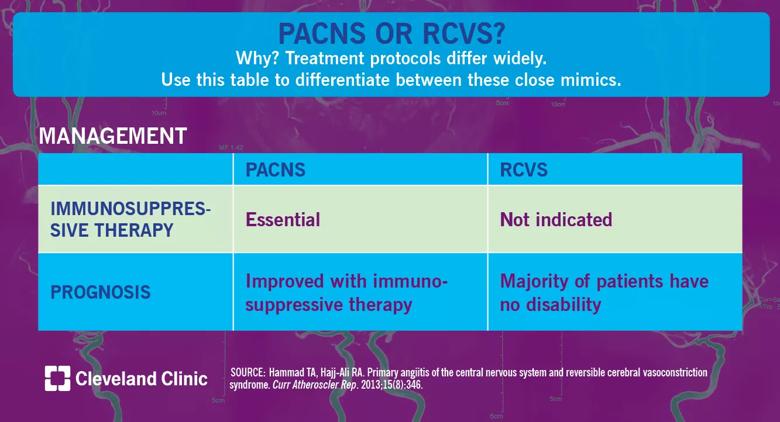
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/f088a773-4051-4470-a0d3-73877cfb127e/18-RHE-1077-PACNS-or-RCVS-Visual-Abstract-1200x650pxl_04_10_2018_03b_jpg)
Before the advent of immunosuppressive therapies, the prognosis for PACNS was dismal. Survival improves with aggressive therapy. The use of immunosuppressive therapy in not indicated in RCVS, as the pathogenetic mechanisms are related to vasospasm and not inflammation; calcium channel blockers are commonly used to control headaches.
We have recently elucidated functional capabilities, quality of life and frequency of depression for our strong cohort of patients with PACNS in the longest reported follow-up in the literature to date and the first evaluation of the quality of life and incidence of depression in these patients. Of 78 patients, 27 responded to the questionnaires (34.6 percent). Mean follow-up was 5.5 years (± 4.7). Seventy percent had mild disability, and 5 percent had severe disability. Around half of the patients had no mobility problem and no problems with usual activities, and two-thirds had no problems with self-care. Physician assessment with the Modified Rankin Scale showed that the majority of PACNS patients had mild long-term disability with a median disability score of one. Approximately 70 percent of patients had minimal or no depression. Mortality was 11 percent.
Advertisement
As our experience with and knowledge of PACNS and RCVS has grown, rheumatologists and neurologists alike grow closer toward demystifying these mimics and providing precise diagnoses for affected patients. Much work remains to be done to assess the pathogenesis and etiologies of both conditions. At the RJ Fasenmyer Center for Clinical Immunology’s CNS Vasculopathy Program, we are currently looking for biomarkers in CSF to better elucidate these mechanisms.
Dr. Hajj-Ali is Associate Director of the Center for Vasculitis Care and Research in the Department of Rheumatic and Immunologic Diseases. Dr. Calabrese is Director of the R.J. Fasenmyer Center for Clinical Immunology.
Advertisement
Advertisement

Aim is for use with clinician oversight to make screening safer and more efficient

Rapid innovation is shaping the deep brain stimulation landscape

Study shows short-term behavioral training can yield objective and subjective gains

How we’re efficiently educating patients and care partners about treatment goals, logistics, risks and benefits

An expert’s take on evolving challenges, treatments and responsibilities through early adulthood

Comorbidities and medical complexity underlie far more deaths than SUDEP does

Novel Cleveland Clinic project is fueled by a $1 million NIH grant

Tool helps patients understand when to ask for help