Otolaryngologists discuss a complex case
A 22-year-old male with an unusually large mass of his soft palate was referred to the Department of Otolaryngology–Head and Neck Surgery at Cleveland Clinic. The mass, nearly the size of a tennis ball, had begun compromising his sleep, voice, breathing, and swallowing. Previously diagnosed as a mucocele, it had been known to the patient for over 10 years, growing slowly over time.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Recent changes in the tumor’s progression invoked concern about the potential for malignant transformation. Further workup characterized the tumor as a pleomorphic adenoma (PA), a benign salivary gland neoplasm, most often found in the parotid gland. PAs are characterized by a high rate of recurrence if not completely resected.
Due to the patient’s youth and symptomatic presentation, the surgeons recommended a complete resection and radial forearm free flap reconstruction. The complex, 10-hour procedure was led by Joseph Scharpf, MD and Dane Genther, MD, both staff in Cleveland Clinic’s Head & Neck Institute.
Dr. Scharpf, a head and neck surgical oncologist, who led the resection, notes that marginal removal on the tumor was challenging because of its outsized shape. “We had limited space to manipulate some of the critical anatomy, while also preserving the critical blood vessels and nerves in this complex region.”
Once the tumor was excised and margins tested negative, Dr. Scharpf and his team established vessels in the neck in preparation for the microvascular free flap reconstruction, the second part of the procedure led by Dr. Genther, a facial plastic and microvascular reconstructive surgeon.
Dr. Genther harvested tissue from the patient’s forearm to rebuild the palate, then grafted skin from the patient’s thigh to cover the forearm defect. The decision to utilize a forearm flap was straightforward. “It’s a thin and pliable tissue with a long vascular pedicle. A bulkier flap can impede speech and swallowing, making this the best choice for a soft palate reconstruction,” remarks Dr. Genther. The flap was inset to reconstruct the defect through a trans-oral approach.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic’s Head & Neck Institute has six microvascular surgeons and offers training in free flap reconstruction through the head and neck surgical oncology and reconstructive surgery fellowship.
Figure 1. Soft palate tumor in situ
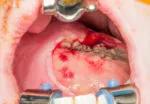
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/bec36efc-4eaa-40d7-a115-e09e3790d85a/19-ENT-5062-Patient-Palate-Reconstruction-TennisBallSized-Mass-1_650x450-150x104_jpg)
Figure 2. Soft palate tumor excised
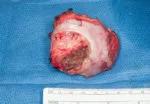
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/dbf5bc8c-abaa-4704-be0d-8f07e7286723/19-ENT-5062-Patient-Palate-Reconstruction-TennisBallSized-Mass-2_650x450-150x104_jpg)
Figure 3. Soft palate tumor excised, alternative view
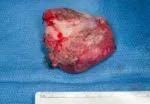
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/58bb40da-bfbe-4118-8c94-cb23b6758538/19-ENT-5062-Patient-Palate-Reconstruction-TennisBallSized-Mass-3_650x450-150x104_jpg)
Figure 4. Soft palate defect
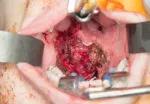
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/32a708f6-83bc-4788-97fe-cff2091c65bf/19-ENT-5062-Patient-Palate-Reconstruction-TennisBallSized-Mass-4_650x450-150x104_jpg)
Figure 5. Soft palate defect with retraction
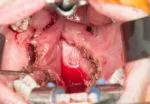
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/56a9a072-d98d-4743-8f7a-b27e92fb0c7a/19-ENT-5062-Patient-Palate-Reconstruction-TennisBallSized-Mass-5_650x450-150x104_jpg)
Figure 6. Soft palate reconstructed with radial forearm free flap
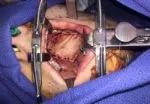
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/526261a5-b6ab-48fc-916f-99aaff653f31/19-ENT-5062-Patient-Palate-Reconstruction-TennisBallSized-Mass-6_650x450-150x104_jpg)
The patient was discharged after five days of postoperative care, which is typical for this type of procedure. Soon after the surgery, the patient’s sleep apnea and hypernasal speech resolved. At his four-month follow-up appointment, he reported a significantly improved quality of life with no remaining symptoms. Given the severity of the patient’s presentation and the complexity of the surgery, the patient will remain in close follow up for the next several years.
While this case was unusual given the age of the patient and the size of the tumor, Cleveland Clinic’s team of head and neck surgeons routinely treat a high volume of complex reconstructive cases. Additionally, the otolaryngologist-head and neck surgeons stress the importance of knowledge of and adherence to clinical and surgical guidelines of neoplasms such as PAs. Finally, a collaborative approach among surgeons and care teams is vital for a seamless implementation of surgical and post-surgical care to optimize patient outcomes.
Advertisement
Advertisement
Analysis of HNSCC patients shows HPV status to be predictive of higher abundance of oncobacteria within the tumor
Case study illustrates the potential of a dual-subspecialist approach
Evidence-based recommendations for balancing cancer control with quality of life
Study shows no negative impact for individuals with better contralateral ear performance
HNS device offers new solution for those struggling with CPAP
Patient with cerebral palsy undergoes life-saving tumor resection
Specialists are increasingly relying on otolaryngologists for evaluation and treatment of the complex condition
Detailed surgical process uncovers extensive middle ear damage causing severe pain and pressure.