Provides option for patients previously deemed anatomically unsuitable
Cleveland Clinic interventional cardiologists and imaging specialists have developed a novel transseptal procedure for transcatheter replacement of a failing prosthetic mitral valve. Known as CLEVE (Clearance of the Leaflet to Eliminate Valve Excursion), the procedure employs a leaflet modification technique that mitigates the risk of left ventricular outflow tract (LVOT) obstruction during valve-in-valve (ViV) transcatheter mitral valve replacement (TMVR).
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
“In some patients, the deployed transcatheter heart valve displaces the surgically placed prosthetic valve leaflet, pushing it toward the LVOT and limiting outflow to the body through the aorta,” explains Amar Krishnaswamy, MD, Section Head of Invasive and Interventional Cardiology. “We found that by creating a perforation at the base of the anterior prosthetic mitral valve leaflet and dilating it with a balloon, we can separate the leaflet from the prosthetic valve frame and then deploy the transcatheter heart valve into that space, pushing away the entire surgical leaflet. This creates a much larger opening and alleviates the risk of neo-LVOT obstruction.” Key steps in the procedure are shown in the Figure.
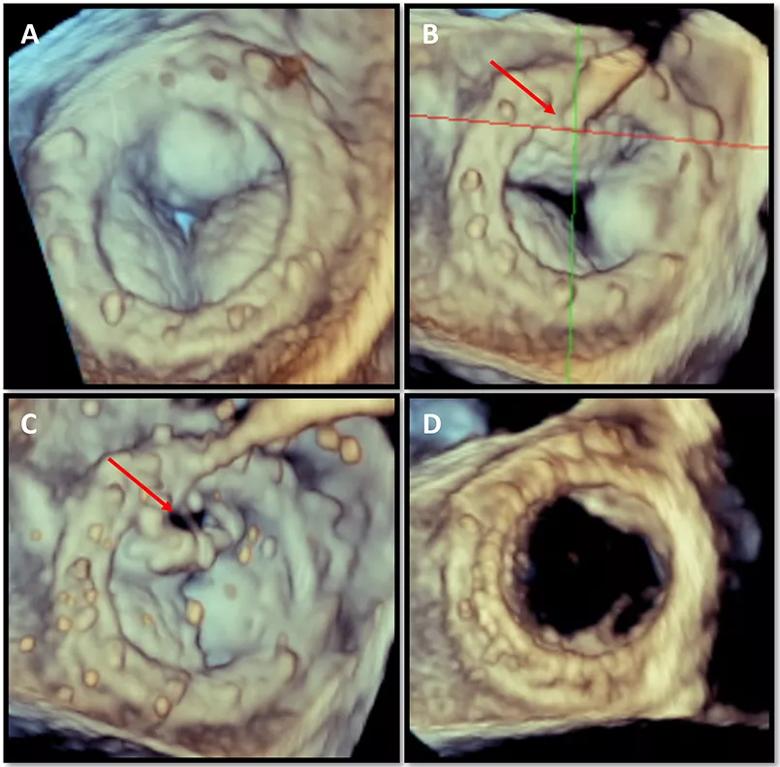
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/91b7ef86-6fa6-4b27-86a6-f41294c31014/24-HVI-4507865-CQD-Inset1_jpg)
Figure. 3D transesophageal echocardiographic images from a CLEVE procedure to facilitate mitral valve-in-valve replacement. (A) Calcified leaflets of a prosthetic valve after surgical mitral valve replacement. (B) Perforation catheter positioned at the base and center of the anterior prosthetic valve leaflet. (C) Separation of the prosthetic valve leaflet from the surgical frame. (D) New transcatheter valve in place.
“This technique is easier and more reproducible compared with alternative methods of lacerating the leaflet,” says Samir Kapadia, MD, Chair of Cardiovascular Medicine at Cleveland Clinic. “It also can be used for valve-in-valve procedures for aortic valve replacement.”
ViV TMVR is an important treatment option for patients with severe prosthetic valve degeneration who are considered at high risk for repeat surgical mitral valve replacement.
Additionally, redo surgical replacement carries a higher risk than the initial surgery, and recent registry data suggest that ViV TMVR may be as safe as or safer than reoperative treatment, Dr. Krishnaswamy notes.
A procedure known as LAMPOON (laceration of the anterior mitral leaflet to prevent outflow obstruction) is a safe and effective technique for reducing the risk of neo-LVOT obstruction in ViV TMVR. However, it can be difficult to perform, and its outcome is not assured.
Advertisement
“In LAMPOON, a leaflet of the prosthetic mitral valve is lacerated so that it splays like a V to create space for blood to flow out of the heart,” Dr. Krishnaswamy says. “However, when the leaflet is thickened and calcified, it is not always clear what path the lacerating wire will take. If the laceration does not occur where expected, the valve will not splay effectively. This sets up the patient for LVOT obstruction, which is a serious and life-threatening complication.”
He says that CLEVE is a simpler, more straightforward procedure that has been successfully used in a number of patients at Cleveland Clinic to date. In all cases the leaflet was cleared out of the way. “No patient was left with an obstruction,” Dr. Krishnaswamy notes. “All patients have fared well clinically without complications.”
While CLEVE is a technically straightforward procedure, it requires close collaboration between cardiac imaging specialists with expertise in procedural transesophageal echocardiography and interventional cardiologists with detailed knowledge of using transcatheter devices and electrosurgical techniques.
“Expert use of transesophageal echocardiography is imperative for guiding the procedure and confirming that the perforation has occurred at the correct location, ensuring that the leaflet is no longer at risk of obstructing the LVOT,” notes Serge Harb, MD, a Cleveland Clinic cardiovascular imaging specialist who has been involved in these procedures.
Dr. Krishnaswamy has spoken with colleagues about the procedure and made presentations on it at several international meetings. A case report detailing the procedure was recently published in Catheterization and Cardiovascular Interventions (2023;102:1149-1153). He hopes the procedure will be widely adopted.
Advertisement
“We are carefully using this procedure in patients with different types of surgical valves and also in different positions, including aortic valve-in-valve procedures,” Dr. Kapadia observes. “To make the procedure reproducible and safe, it’s necessary to employ proper imaging, to use embolic prevention devices to prevent procedural stroke, and to ensure relatively swift replacement of the valve after leaflet laceration to avoid hemodynamic instability.”
“CLEVE provides a potentially safe and effective percutaneous treatment option and an alternative to LAMPOON for patients who are anatomically unsuitable for valve-in-valve TMVR because the neo-LVOT would be prohibitively narrow,” Dr. Krishnaswamy concludes. “Until now, the choice for these patients was often open-heart surgery or no treatment at all.”
Advertisement
Advertisement
Scenarios where experience-based management nuance can matter most
Optimal management requires an experienced center
Multimodal evaluations reveal more anatomic details to inform treatment
While mortality was unaffected, later surgery was associated with more reoperations
Surgical tips on debridement of calcification to optimize valve replacement
Superiority continues even after significant crossovers from control group at 2 years
How Cleveland Clinic is using and testing TMVR systems and approaches
NIH-funded comparative trial will complete enrollment soon