After optimized medical and device therapy, is there a role for endocardial-epicardial VT ablation?
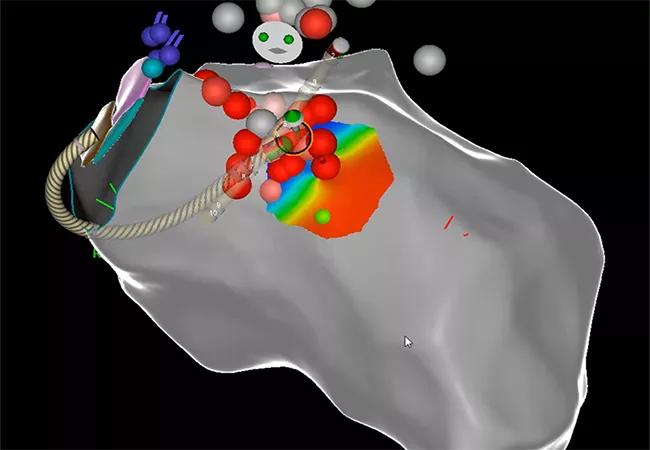
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/e2fdc83e-2954-41c6-b50e-9f8d66f87a20/22-HVI-3200903-CQD-650x450-1_jpg)
22-HVI-3200903 CQD 650×450
A 37-year-old man presented to Cleveland Clinic Fairview Hospital with a history of nonischemic cardiomyopathy. The prior year, he had received an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD) for secondary prevention due to syncope and monomorphic ventricular tachycardia (VT). Despite adequate trials of various combinations of antiarrhythmic medications and ICD adjustments, over the last several months he had repeated hospitalizations due to multiple ICD shocks. Most recently, he experienced syncope in front of his 6-year-old son while doing routine household activities. He reported that his mother had died suddenly at age 54 from a “large heart.”
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Previous coronary angiography revealed no stenosis, and a previous MRI was consistent with nonischemic cardiomyopathy but showed no additional specific findings; assessment of the MRI was limited by artifact from the patient’s ICD.
Electrical storm, defined as three or more episodes of VT or shocks from an ICD within a 24-hour period, is a life-threatening condition that is a criterion for hospitalization. The adrenaline surges associated with a storm can be self-perpetuating and exacerbate the condition.1
“Repeated electrical storm in a young man with optimized medical and device therapy and such a high-risk personal and family history requires a different strategy,” says Samuel Omotoye, MD, a cardiac electrophysiologist in Cleveland Clinic’s Section of Cardiac Electrophysiology and Pacing. “We wanted to offer him the best and optimal treatment, regardless of how complex it might be.”
Dr. Omotoye led a team that performed endocardial voltage mapping inside the patient’s left ventricle via a retro-aortic and trans-septal approach, which revealed a wide area of arrhythmogenicity originating at the basal anterior-lateral left ventricle and mitral annulus. They determined that ablation of only the endocardium would be insufficient to control the VT, given the substrate of his cardiomyopathy. Epicardial mapping was performed using a dry tap technique via subxiphoid epicardial access (see Figure). Coronary angiography was simultaneously performed during the case by interventional cardiologist Brian Li, MD, to ensure a safe distance was maintained between the area of interest and major epicardial coronary vessels.
Advertisement
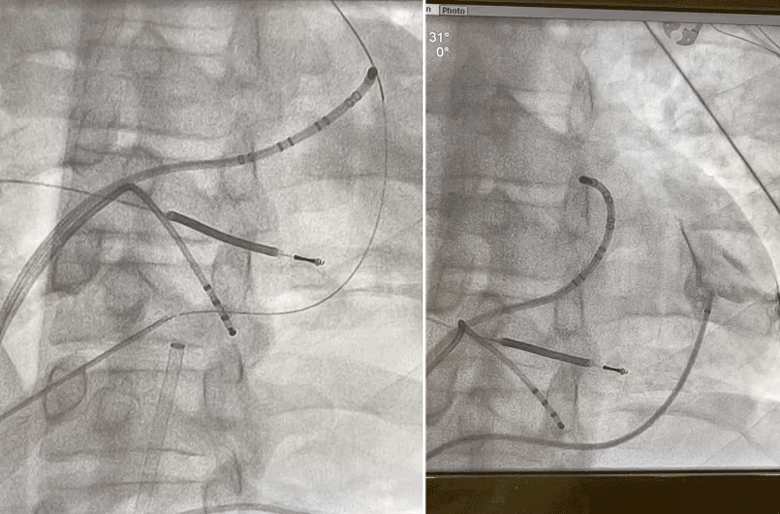
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/2ae833aa-030f-4439-8c31-23ed677d3224/22-HVI-3200903-CQD-Inset-1_gif)
Figure. Pericardiography showing epicardial access using a dry tap technique.
After precise identification of the VT sources, combined endocardial and epicardial ablation was performed with continued coronary angiography guidance and particular attention to avoiding the nearby left circumflex artery. The VTs were successfully terminated without complication. The following short videos illustrate a few key portions of the procedure. The first is a 3D voltage map showing VT ablation with real-time electrogram as it terminated.
Video content: This video is available to watch online.
View video online (https://cdnapisec.kaltura.com/p/2207941/sp/220794100/playManifest/entryId/1_2tmbnypn/flavorId/1_5f3sgelj/format/url/protocol/https/a.mp4)
The video below shows an epicardial substrate electrogram demonstrating late potentials.
Video content: This video is available to watch online.
View video online (https://cdnapisec.kaltura.com/p/2207941/sp/220794100/playManifest/entryId/1_0128ysk3/flavorId/1_5f3sgelj/format/url/protocol/https/a.mp4)
The video below features coronary angiography showing the epicardial ablation.
Video content: This video is available to watch online.
View video online (https://cdnapisec.kaltura.com/p/2207941/sp/220794100/playManifest/entryId/1_1xikzuwp/flavorId/1_5f3sgelj/format/url/protocol/https/a.mp4)
Three months postoperatively, the patient is off antiarrhythmic medications and has had no further hospitalizations or ICD shocks. He is currently only on beta-blocker therapy, and his ICD is continuously monitored at Cleveland Clinic’s dedicated Device Clinic.
This case illustrates the successful treatment of a young man at increased risk of morbidity and mortality from uncontrolled monomorphic VT/electrical storm in the setting of nonischemic cardiomyopathy, despite optimized medical and device therapy. His best chance of control was complete ablation of the arrhythmogenic source, which in this case was along the basal anterior-lateral left ventricle and mitral annulus, requiring both endocardial and epicardial approaches.
Epicardial mapping and ablation is associated with various risks, necessitating guidance with coronary angiography among other safety measures, and should be conducted by an experienced and trained cardiac electrophysiologist. Risks include puncture of surrounding thoracic and abdominal organs during access, in addition to ablation damage to nearby coronary arteries and other structures. Although these risks are greater than those with endocardial ablation alone, evidence indicates that combined endocardial-epicardial ablation is superior for lowering the risk of VT recurrence and mortality in certain cases of uncontrolled monomorphic VT.2
Advertisement
“Combined endocardial-epicardial ablation can be performed safely only in a center with experience in this procedure and with the capability to immediately address complications if they arise,” says Dr. Omotoye. “For this reason, we urge our colleagues in the community to refer complex patients with uncontrolled arrhythmias to a specialized facility. When conventional strategies aren’t adequate, the patient should be offered a chance to address the problem with a more complex solution where available.”
While this procedure is performed only in rare cases, it has been safely done by a handful of operators on Cleveland Clinic’s main campus; this case marks its first use at a Cleveland Clinic regional hospital.
“Dr. Omotoye has brought to bear considerable skill and vast experience to achieve a stellar outcome with this highly complex procedure,” says Christine Tanaka-Esposito, MD, Director of Cardiac Electrophysiology at Cleveland Clinic Fairview Hospital.
“I congratulate Dr. Omotoye and Fairview Hospital’s Heart, Vascular & Thoracic Institute leadership for providing cutting-edge cardiac electrophysiology services for patients at an additional care site in our health system,” adds Oussama Wazni, MD, MBA, Cleveland Clinic’s Section Head of Cardiac Electrophysiology and Pacing. “It is our institute’s vision to extend all such therapies in cardiology and cardiac surgery to the entire region.”
Advertisement
Advertisement
CD36 loss-of-function variant accounts for large portion of risk in this population
Cardiac imaging substudy is the latest paper originating from the VANISH trial
Vigilance for symptom emergence matters, a large 20-year analysis reveals
5% of flagged ECGs in real-world study were from patients with previously undiagnosed HCM
High composite score in myectomy specimens signals worse prognosis
Avoidance of septal reduction therapy continues while LVEF dysfunction remains infrequent
New risk score pools factors that may predict adverse outcomes in the uncommon phenotype
Technique may lay groundwork for personalized decision-making in procedural intervention