Early results suggest positive outcomes from COVID-19 PrEP treatment
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/e89c4d0d-c49d-47be-9e3f-7952d33b0ecb/650x450-Covid-Virus-1305369724_jpg)
covid-19 virus
Editor’s Note: On January 26, 2023, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration revised the Emergency Use Authorization for Evusheld. While this pre-exposure prophylaxis is not effective for current vaccine variants, the positive results provide insights into future opportunities.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Patients receiving B-cell-depleting therapies (BCDT) for immune-mediated inflammatory diseases (IMIDs) and patients with inborn errors of humoral immunity (IEI) have high risk of poor COVID-19 outcomes. Risk mitigation strategies are of the utmost importance for this vulnerable group.
Pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) with tixagevimab/cilgavimab (Evusheld™) has been available in the United States under FDA Emergency Use Authorization since December 2021. This preventive treatment is administered to patients who have been vaccinated, and to those with contraindication to vaccination, who are unlikely to respond to COVID-19 vaccination.
Beginning Jan. 18, 2022, Cleveland Clinic made tixagevimab/cilgavimab available to patients receiving BCDT and other select high risk patients. By Oct. 31, 2022, we had administered at least one dose to 600 Cleveland Clinic rheumatology patients. We sought to describe the clinical outcomes of breakthrough COVID-19 in B-cell-depleted patients, either iatrogenic or from IEI. We retrospectively searched all pharmacy records for patients who met criteria to receive tixagevimab/cilgavimab (as defined by Cleveland Clinic’s COVID-19 Pharmacy & Therapeutics sub-committee) and who subsequently were diagnosed with COVID-19.
From this list, we manually reviewed electronic medical records to extract data on infection, vaccination status and outcomes as assessed by an eight-point NIH ordinal scale.
Between Jan. 18 and May 28, 2022, a total of 417 patients received tixagevimab/cilgavimab across the rheumatology (n=261), allergy/immunology (n=78) and neurology (n=78) departments. From this cohort, 13 patients (3%) experienced breakthrough COVID-19 after receiving PrEP. All patients had been vaccinated against COVID-19. Six of 13 patients developed infection a median of 19 days (range 13-84) after receiving 150/150 mg of tixagevimab/cilgavimab. Seven of 10 patients developed infection a median of 34 days (19-72) after either a single dose of 300/300 mg or after a second dose of 150/150 mg.
Advertisement
Overall, 12 patients had a mild course and recovered at home, and one patient was hospitalized and required high-flow oxygen. There were no deaths. Nine patients received appropriate outpatient treatment with oral antivirals, monoclonals or both.
Our early experience suggests that COVID-19 infection after tixagevimab/cilgavimab occurs infrequently, and with standard-of-care outpatient management, infection is mild in severity. Unknown at present is how effective this preventive strategy will be against newly circulating variants of concern.
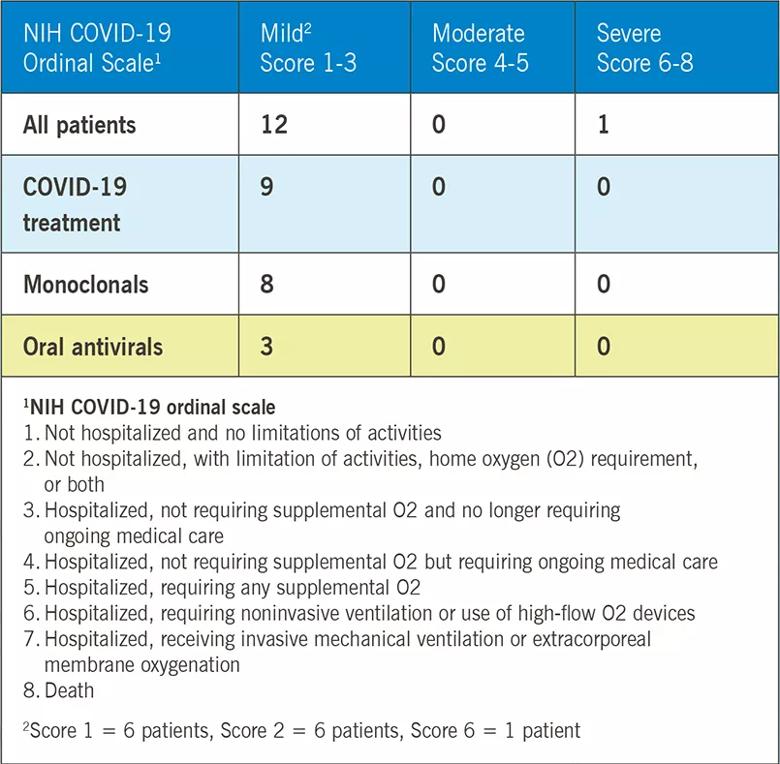
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/e9855228-f795-4361-b1b5-d710212586fa/22-RHE-3430658-CQD-Inset_jpg)
Advertisement
Advertisement
Dynamic modeling improves the accuracy of outcome predictions for ICU patients
A review of IDSA and NIH guidelines
Study sheds light on how clinicians addressed their patients’ pain and insomnia during the pandemic
Patients report improved sense of smell and taste
Clinicians who are accustomed to uncertainty can do well by patients
Unique skin changes can occur after infection or vaccine
Will enable patients with long COVID to enroll in national clinical trials
Cleveland Clinic analysis suggests that obtaining care for the virus might reveal a previously undiagnosed condition